A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding American Indian Reservations
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding American Indian Reservations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding American Indian Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding American Indian Reservations
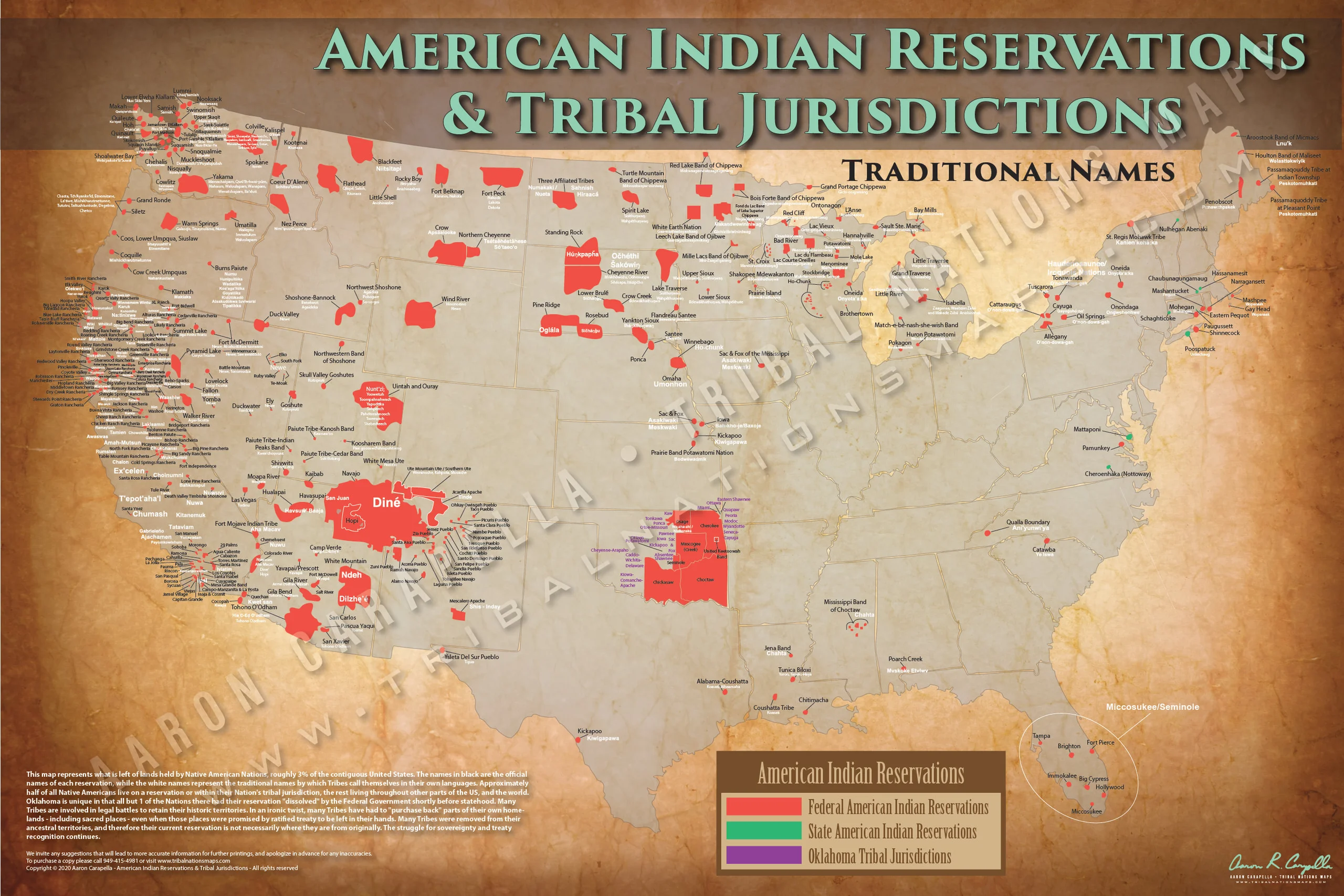
The United States is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, and within this fabric, American Indian reservations hold a unique and significant place. These designated lands, often referred to as "Indian Country," serve as more than just geographical locations; they represent the enduring legacy of Indigenous peoples, their sovereignty, and their cultural identity. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of American Indian reservations, encompassing their historical context, legal framework, and contemporary significance.
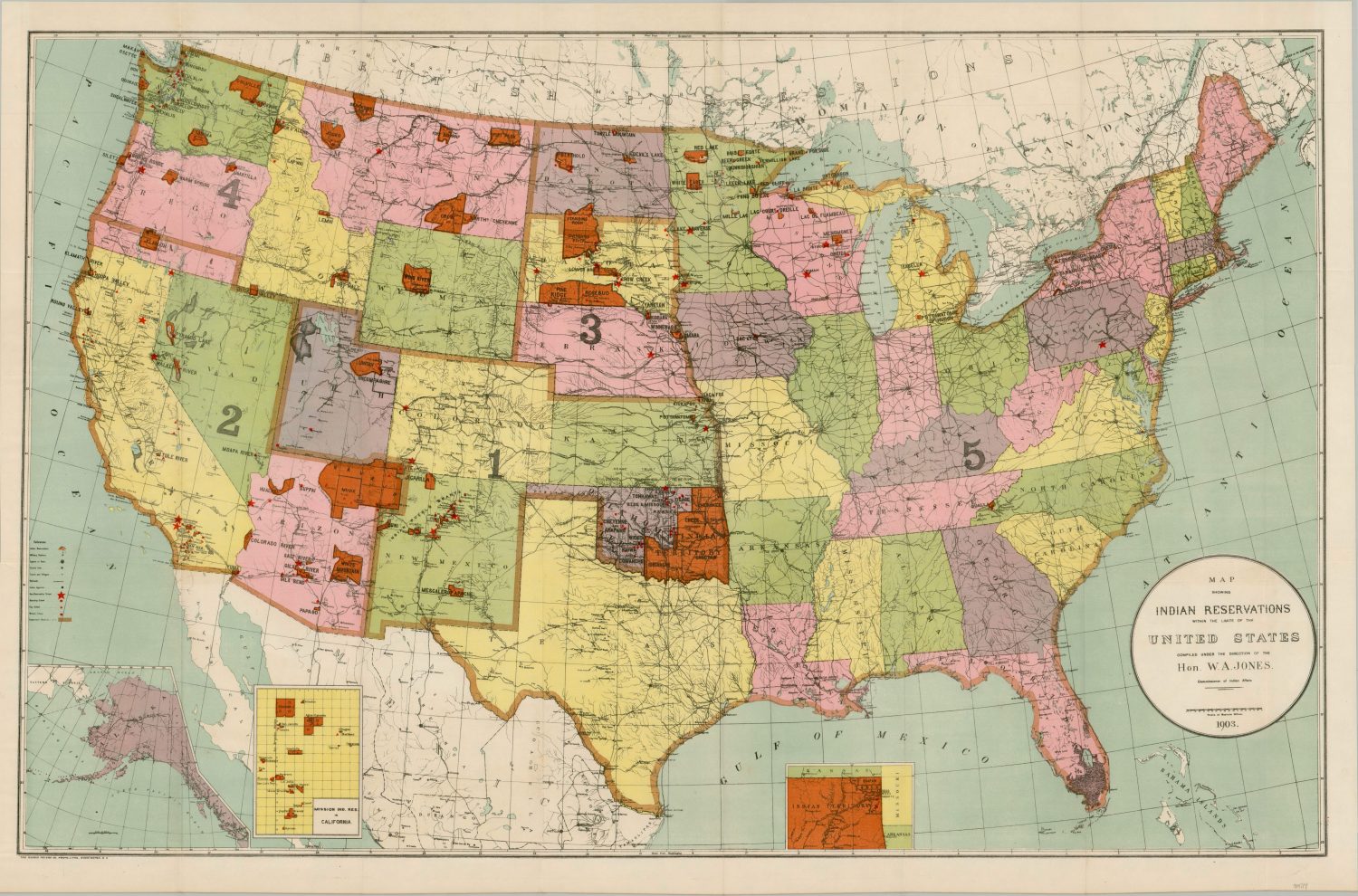
Historical Context: A Legacy of Treaties and Forced Relocation
The establishment of American Indian reservations is intrinsically tied to the complex and often tragic history of the United States’ relationship with Indigenous peoples. From the 17th century onwards, European colonization and westward expansion led to a series of treaties and agreements, many of which were broken or disregarded by the U.S. government. These treaties often designated specific lands for Indigenous tribes, acknowledging their sovereign rights and establishing the foundation for reservations.
However, the history of reservations is also marked by forced displacement and assimilation policies. The Indian Removal Act of 1830, for instance, led to the brutal relocation of numerous tribes from their ancestral lands to designated reservations, often in harsh and unfamiliar environments. This policy aimed to diminish tribal sovereignty and force Indigenous peoples to adopt European-American culture.
The Legal Framework: Defining Indian Country
American Indian reservations are defined by federal law, specifically through the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 and subsequent legislation. These laws establish the legal framework for the recognition of tribal sovereignty, granting tribes the authority to govern themselves within their designated territories.
Key Legal Definitions:
- Indian Country: This term encompasses reservations, dependent Indian communities, and off-reservation trust lands. It is defined by federal law and establishes the legal jurisdiction of tribal governments within these areas.
- Tribal Sovereignty: This principle recognizes the inherent right of American Indian tribes to govern themselves, manage their resources, and make decisions concerning their communities.
- Trust Responsibility: The U.S. government has a legal and moral obligation to uphold the treaties and agreements made with American Indian tribes, including the protection of their lands and resources.
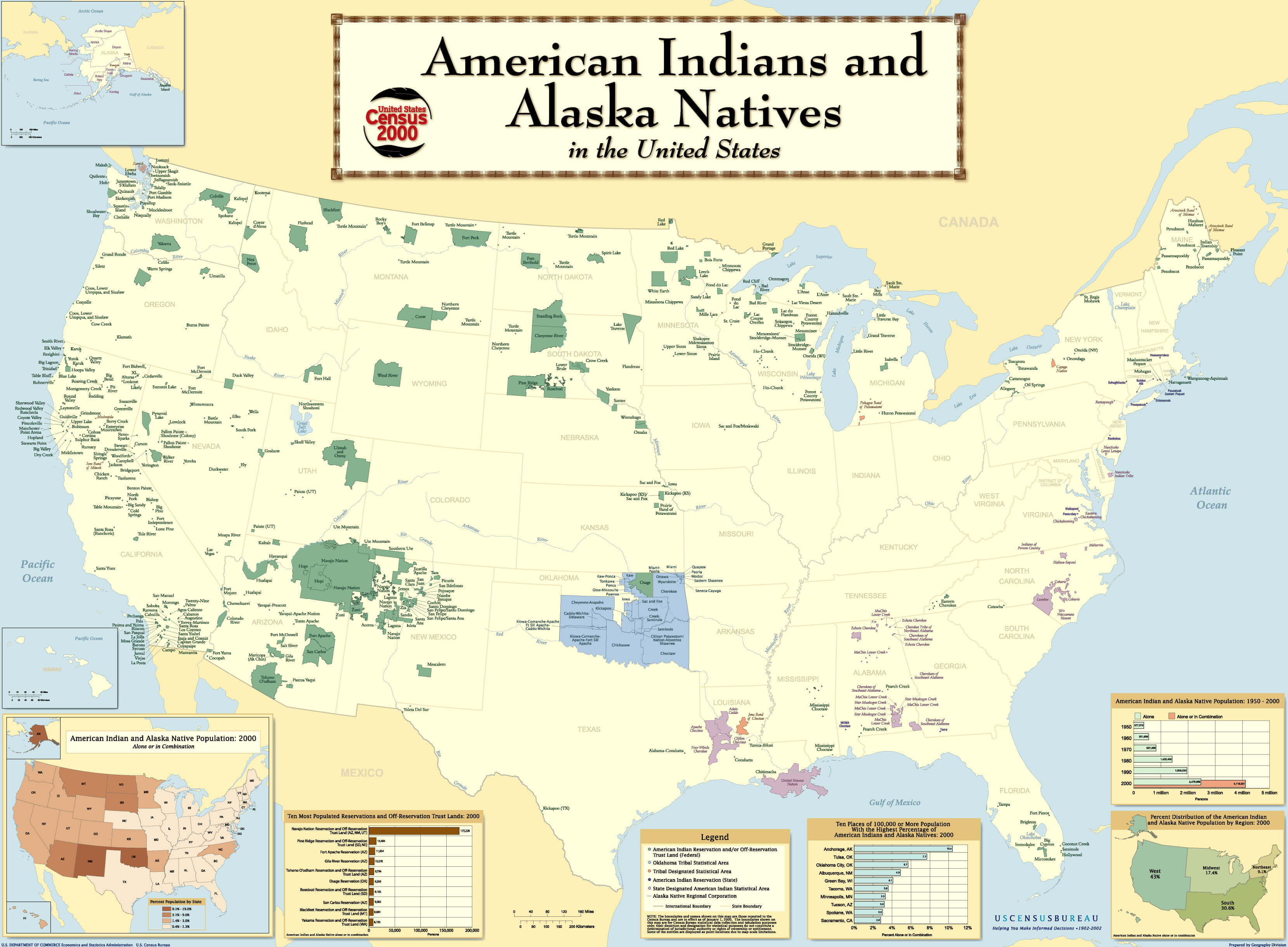
Navigating the Map: Understanding Reservation Locations and Demographics
American Indian reservations are scattered across the United States, with varying sizes and populations. Understanding their geographic distribution and demographics is crucial for comprehending the diversity of Indigenous communities and their unique challenges.
Key Features of a Reservation Map:
- Location: Reservations are geographically diverse, ranging from vast arid lands in the southwest to forested areas in the northeast.
- Tribal Affiliation: Each reservation is associated with a specific tribe or band, reflecting the diverse cultural heritage of Indigenous peoples.
- Population: Reservations vary significantly in population, from small communities to large urban centers.
- Economic Development: The economic landscape of reservations can vary greatly, with some experiencing economic prosperity and others facing significant challenges.
The Importance of Reservations: Preserving Culture and Identity
American Indian reservations play a vital role in preserving the cultural heritage and identity of Indigenous peoples. They serve as centers for language revitalization, traditional arts and crafts, and spiritual practices. Reservations also provide spaces for tribal governance, community building, and economic development.
Benefits of Reservations:
- Cultural Preservation: Reservations provide a safe haven for the transmission of cultural traditions, languages, and values.
- Self-Governance: Tribal sovereignty allows for the development of laws and policies that reflect the needs and priorities of Indigenous communities.
- Economic Development: Reservations offer opportunities for economic diversification, including tourism, agriculture, and resource management.
- Social Services: Reservations often provide essential social services, such as healthcare, education, and housing, to their residents.
Challenges Facing Reservations: Poverty, Health Disparities, and Economic Inequality
Despite the legal protections and benefits associated with reservations, they continue to face significant challenges, including poverty, health disparities, and economic inequality. These issues are often rooted in the historical injustices and systemic discrimination experienced by Indigenous peoples.
Key Challenges:
- Poverty: High rates of poverty persist on many reservations, linked to limited employment opportunities, inadequate infrastructure, and historical dispossession.
- Health Disparities: Indigenous peoples experience higher rates of chronic diseases, substance abuse, and mental health issues, often stemming from historical trauma and limited access to quality healthcare.
- Economic Inequality: Reservations often lack access to capital, technology, and infrastructure, hindering their economic development and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
Addressing Challenges: Empowering Indigenous Communities
Addressing the challenges facing reservations requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes Indigenous self-determination, economic development, and social justice.
Key Strategies:
- Tribal Sovereignty: Upholding and strengthening tribal sovereignty is crucial for allowing Indigenous communities to govern themselves and address their unique needs.
- Economic Development: Investing in infrastructure, education, and job creation programs can create economic opportunities and improve quality of life on reservations.
- Healthcare Access: Expanding access to quality healthcare services, including mental health care and substance abuse treatment, is essential for addressing health disparities.
- Education: Supporting Indigenous education, including language revitalization and culturally relevant curricula, is crucial for empowering future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the legal distinctions between reservations and other types of Indian lands?
Reservations are the most common form of Indian land, established through treaties or executive orders. Other types of Indian lands include dependent Indian communities, which are similar to reservations but often have less autonomy, and off-reservation trust lands, which are lands held in trust by the U.S. government for the benefit of tribes.
2. How are tribal governments structured?
Tribal governments vary in structure, but they typically have elected leaders and a system of checks and balances. Some tribes have constitutions that outline their governance structures, while others rely on traditional customs and practices.
3. What are the rights and responsibilities of tribal citizens?
Tribal citizens have a range of rights and responsibilities, including the right to vote in tribal elections, access to tribal services, and the obligation to abide by tribal laws.
4. How do reservations contribute to the U.S. economy?
Reservations contribute to the U.S. economy through various activities, including tourism, agriculture, gaming, and resource extraction. However, economic development on reservations is often hampered by limited access to capital, infrastructure, and markets.
5. What are the historical and cultural significance of reservations?
Reservations represent the enduring legacy of Indigenous peoples, their resilience in the face of colonization, and their commitment to preserving their cultures and traditions. They serve as centers for cultural revitalization, language transmission, and spiritual practices.
Tips for Learning More About American Indian Reservations
- Visit a reservation: Many reservations welcome visitors and offer tours and cultural experiences.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous resources available on the history, culture, and contemporary issues facing American Indian reservations.
- Support Indigenous businesses and organizations: Patronizing Indigenous-owned businesses and supporting organizations that advocate for Indigenous rights can help empower Indigenous communities.
- Attend cultural events: Many reservations host powwows, festivals, and other events that showcase Indigenous culture and traditions.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity and Recognizing Indigenous Rights
American Indian reservations are not simply geographic locations; they are living testaments to the resilience and cultural richness of Indigenous peoples. Understanding the history, legal framework, and contemporary challenges facing reservations is essential for fostering a more equitable and inclusive society. By recognizing tribal sovereignty, supporting economic development, and addressing historical injustices, we can work towards a future where Indigenous communities thrive and their unique contributions to American culture are celebrated.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding American Indian Reservations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!