Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation
Related Articles: Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation
- 3.1 Understanding the Importance of Antarctic Research Bases
- 3.2 A Glimpse into the Life at Antarctic Research Bases
- 3.3 Exploring the Network of Antarctic Research Bases
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Antarctic Research Bases
- 3.5 Tips for Visiting an Antarctic Research Base
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation

Antarctica, the Earth’s southernmost continent, is a land of ice, wind, and extremes. Yet, beneath its frozen surface lies a treasure trove of scientific knowledge, attracting researchers from around the globe. This frigid landscape is dotted with research stations, serving as hubs for scientific exploration and international collaboration. These research stations, often referred to as "bases," play a crucial role in understanding the Earth’s past, present, and future.
Understanding the Importance of Antarctic Research Bases
Antarctic research bases are not merely isolated outposts but serve as vital components of a global scientific network. Their strategic locations allow scientists to study a diverse range of phenomena, from climate change and glaciology to atmospheric science and marine biology. The research conducted at these bases contributes to our understanding of:
- Climate Change: Antarctica holds a vast store of ice, which acts as a sensitive indicator of global warming. Studying the ice sheets, glaciers, and sea ice provides valuable insights into the rate and extent of climate change.
- Atmospheric Science: Antarctica’s unique location and relatively pristine atmosphere make it an ideal laboratory for studying atmospheric processes, including ozone depletion, greenhouse gas concentrations, and air pollution.
- Biodiversity and Ecology: Despite the harsh conditions, Antarctica supports a diverse array of life, from microscopic organisms to penguins and seals. Research at these bases helps understand the adaptations and resilience of these unique ecosystems.
- Geology and Geophysics: The continent’s ancient rocks and tectonic plates provide insights into the Earth’s history and formation. Studies of the ice sheet and its underlying bedrock reveal clues about past climate and tectonic events.
- Astronomy: Antarctica’s clear skies and long periods of darkness make it an ideal location for astronomical observations, particularly for studying the cosmic microwave background radiation.
A Glimpse into the Life at Antarctic Research Bases
Life at an Antarctic research base is far from ordinary. Researchers live and work in close proximity, often enduring long periods of isolation and extreme weather conditions.
- Logistical Challenges: Operating research stations in Antarctica presents significant logistical challenges. Supplies and equipment must be transported by sea or air, and the harsh climate can disrupt operations.
- International Collaboration: Most Antarctic research bases are operated by international collaborations, fostering scientific exchange and cooperation among nations.
- Scientific Focus: The research conducted at these bases spans a wide range of disciplines, from physics and chemistry to biology and geology.
- Environmental Stewardship: Research at these bases emphasizes environmental protection and sustainable practices, ensuring the preservation of this fragile ecosystem.
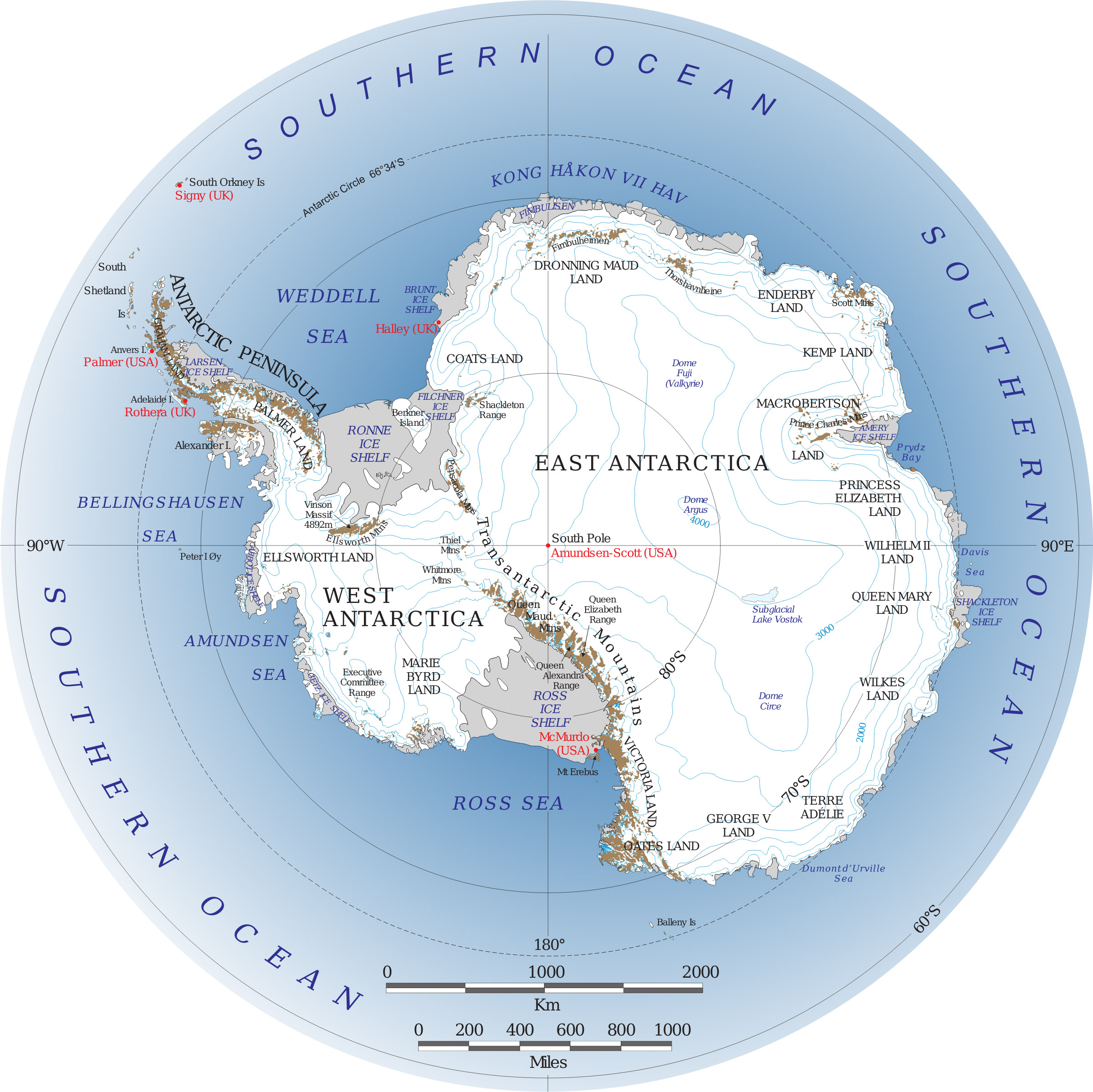
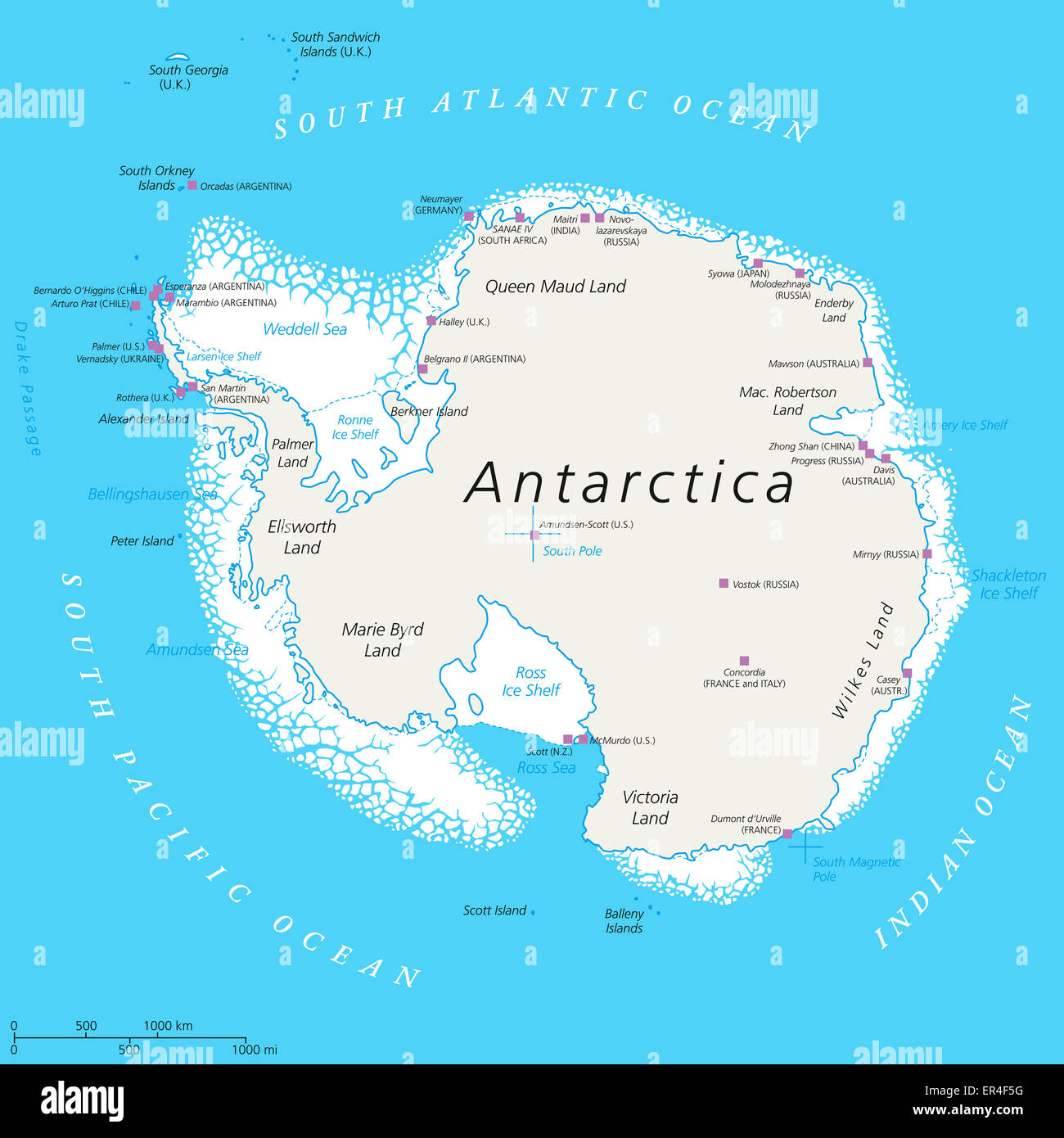
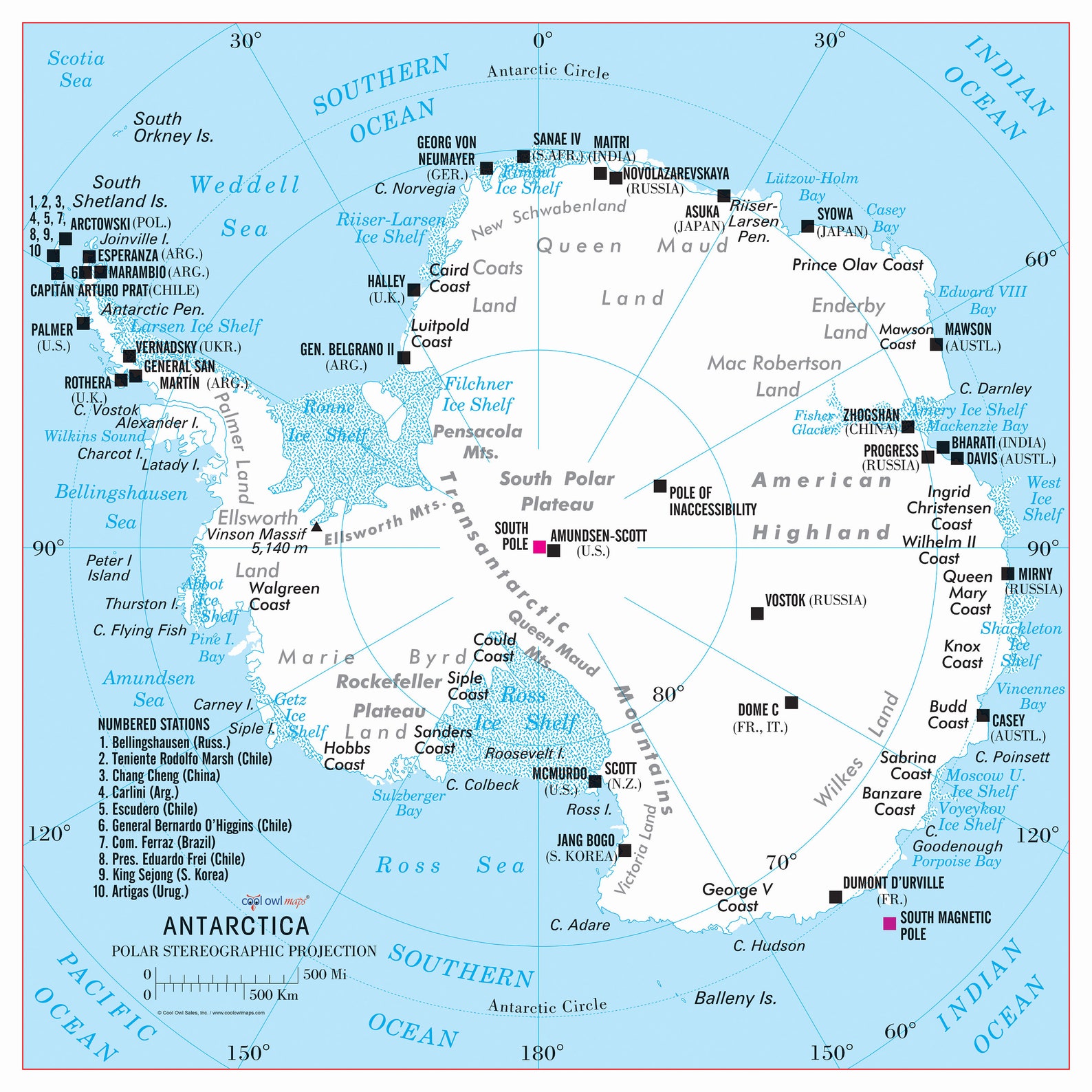
Exploring the Network of Antarctic Research Bases
Over 60 research stations dot the Antarctic continent and surrounding islands. These stations, operated by various countries and international collaborations, offer a diverse range of research facilities and capabilities. Some prominent examples include:
- McMurdo Station (United States): Located on Ross Island, McMurdo Station is the largest research base in Antarctica, supporting a wide range of scientific projects.
- Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station (United States): Situated at the geographic South Pole, this station serves as a hub for astronomical observations, atmospheric research, and glaciological studies.
- Palmer Station (United States): Situated on Anvers Island, Palmer Station focuses on research in marine biology, ecology, and oceanography.
- Rothera Research Station (United Kingdom): Located on Adelaide Island, Rothera Station supports a variety of research activities, including glaciology, atmospheric science, and marine biology.
- Mawson Station (Australia): Situated on the coast of Mac. Robertson Land, Mawson Station is known for its research in glaciology, atmospheric science, and geology.
- Vostok Station (Russia): Located in East Antarctica, Vostok Station is renowned for its subglacial lake, which holds potential for discovering ancient life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Antarctic Research Bases
1. What are the challenges of conducting research in Antarctica?
Research in Antarctica faces numerous challenges, including:
- Extreme weather conditions: Low temperatures, high winds, and limited daylight hours can pose significant logistical challenges.
- Remote location: The continent’s remoteness makes transportation and communication difficult and expensive.
- Environmental sensitivity: The fragile ecosystem of Antarctica requires careful consideration of environmental impacts.
- Limited infrastructure: Research stations often have limited resources and infrastructure, requiring adaptation and ingenuity.
2. What are the benefits of conducting research in Antarctica?
Antarctica offers unique opportunities for scientific research, including:
- Global significance: Research in Antarctica has implications for understanding global climate change, atmospheric processes, and biodiversity.
- Unique environment: The continent’s extreme conditions and unique ecosystems provide valuable insights into life on Earth.
- International collaboration: Research stations foster international collaboration and scientific exchange.
- Technological advancements: Research in Antarctica often drives the development of new technologies and methodologies.
3. How are Antarctic research bases funded?
Antarctic research bases are typically funded by national governments, international organizations, and private foundations. Funding sources vary depending on the station’s location, research focus, and operating costs.
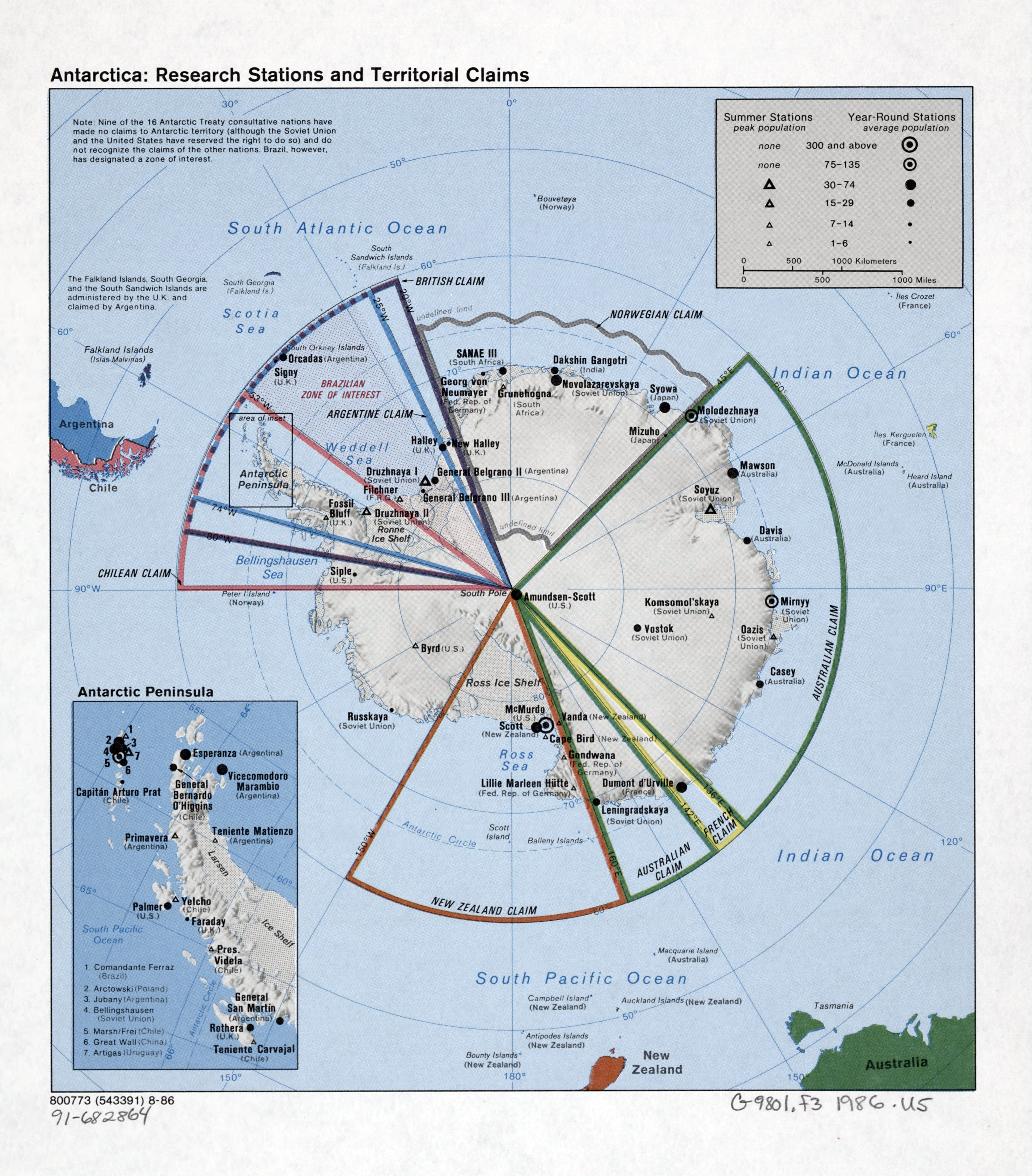
4. What is the role of international cooperation in Antarctic research?
International cooperation is essential for conducting research in Antarctica. The Antarctic Treaty System, signed in 1959, establishes a framework for scientific collaboration and environmental protection.
5. What are the ethical considerations of conducting research in Antarctica?
Ethical considerations in Antarctic research include:
- Environmental protection: Minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring sustainable practices.
- Cultural sensitivity: Respecting the cultural and historical significance of the continent.
- Scientific integrity: Maintaining high ethical standards in research conduct.
Tips for Visiting an Antarctic Research Base
While visiting an Antarctic research base is not accessible to everyone, it is a unique and rewarding experience for those who have the opportunity. Here are some tips for planning a visit:
- Research your options: Different research bases offer varying levels of accessibility and visitor programs.
- Plan well in advance: Visiting Antarctica requires extensive planning and preparation.
- Be prepared for the environment: Expect extreme weather conditions and limited amenities.
- Respect the environment: Adhere to strict environmental protocols and minimize your impact on the fragile ecosystem.
- Learn about the research: Take the opportunity to learn about the scientific work being conducted at the base.
Conclusion
Antarctic research bases serve as vital hubs for scientific exploration, international collaboration, and environmental stewardship. These remote outposts provide unique insights into the Earth’s history, climate, and biodiversity. The research conducted at these bases contributes to our understanding of global change and the interconnectedness of life on our planet. By fostering international cooperation and promoting responsible research practices, these bases play a crucial role in safeguarding this pristine and valuable ecosystem for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Antarctica: A Continent of Research and International Cooperation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!