Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome
Related Articles: Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome
- 3.1 The Greek Landscape: A Cradle of Civilization
- 3.2 The Roman Empire: A Colossus of Power
- 3.3 The Importance of Maps in Understanding Antiquity
- 3.4 FAQs about Ancient Greece and Rome Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Maps to Study Ancient Greece and Rome
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome
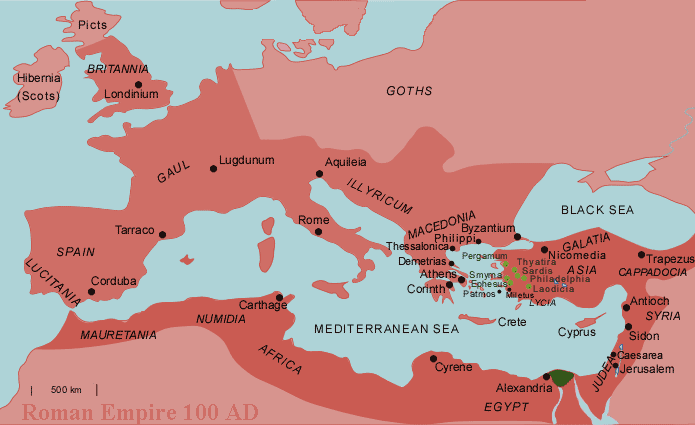
The ancient world, a tapestry woven with vibrant civilizations, empires, and cultures, unfolds before us with the aid of maps. These invaluable tools, more than mere representations of landmasses, provide a tangible framework for understanding the complexities of ancient Greece and Rome. They reveal the geographical influences that shaped these societies, their interactions with the wider world, and the legacies they left behind.
The Greek Landscape: A Cradle of Civilization
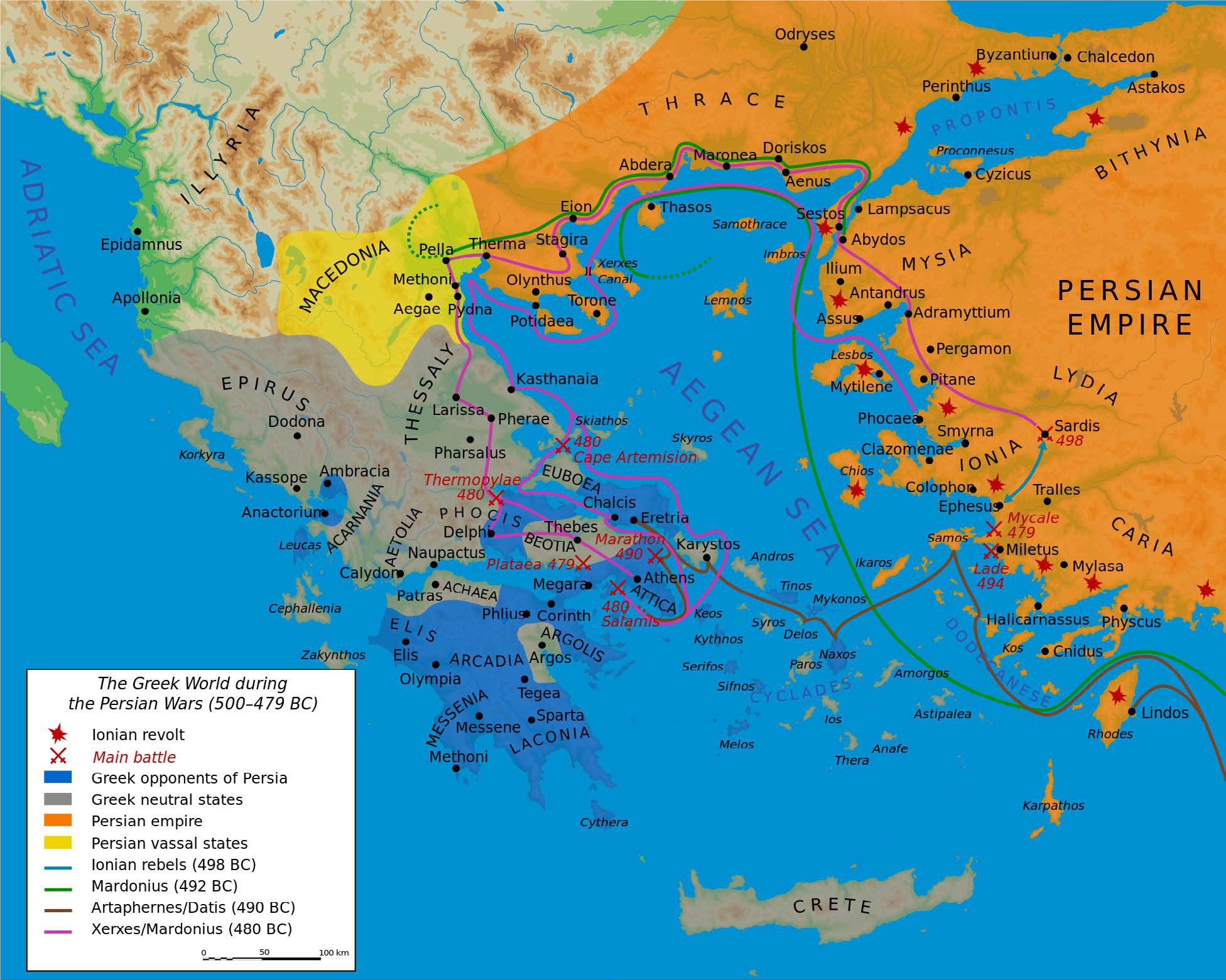
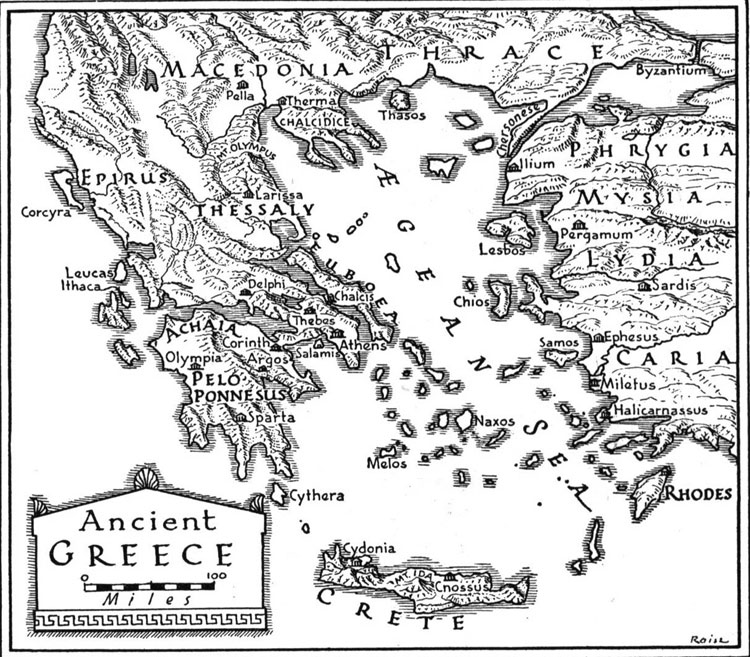
The map of ancient Greece, a fragmented archipelago punctuated by the mainland, tells a story of resilience and innovation. The Aegean Sea, a vital waterway, served as a conduit for trade and cultural exchange, connecting the scattered islands and mainland cities. This maritime landscape fostered a spirit of independence, with each city-state forging its own identity and governance.
A Tapestry of City-States: The map reveals a landscape dotted with powerful city-states, each vying for influence and dominance. Athens, renowned for its democracy and intellectual prowess, stands out as a beacon of cultural achievement. Sparta, a militaristic powerhouse, embodies the contrasting ethos of strength and discipline. The map illustrates the dynamic interplay between these city-states, their alliances and rivalries shaping the course of Greek history.
The Rise and Fall of Empires: Beyond the city-states, the map reveals the expansion of Greek influence through colonization. Greek settlements sprang up along the Mediterranean coastline, establishing trade routes and spreading Hellenistic culture far and wide. The rise and fall of empires, from the Macedonian conquest to the Roman domination, are etched onto the map, marking the ebb and flow of power in the ancient world.
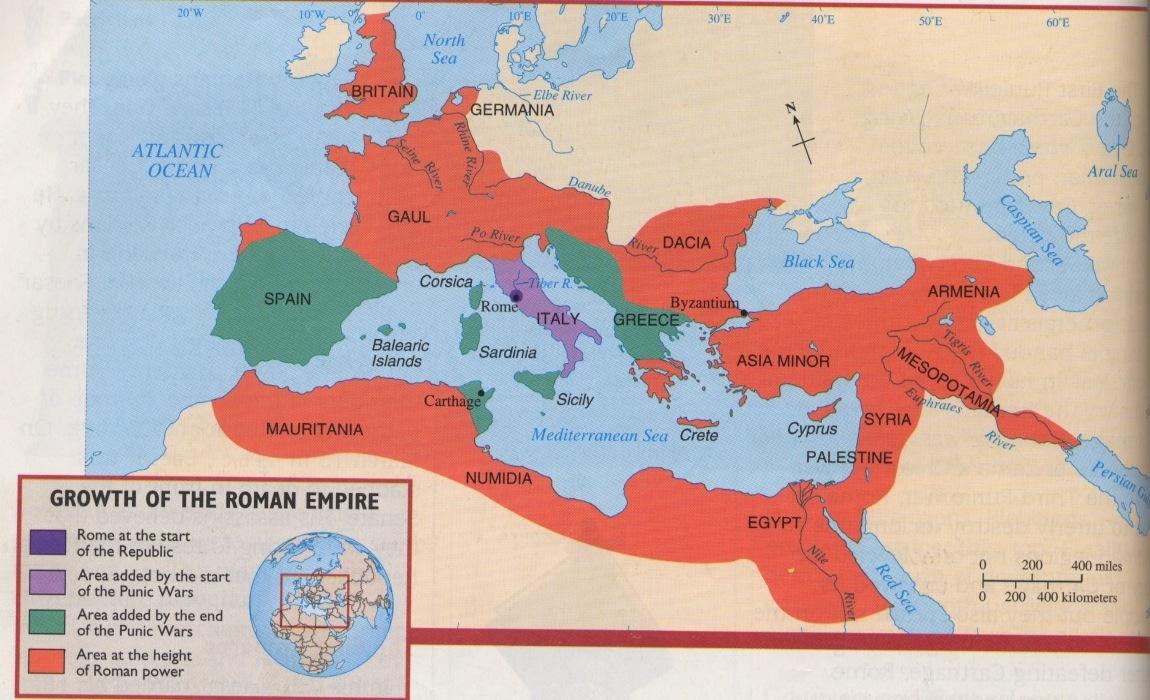
The Roman Empire: A Colossus of Power
The map of the Roman Empire, a vast expanse encompassing the Mediterranean basin, is a testament to the enduring legacy of Roman power. From the Italian peninsula, the empire stretched its reach across Europe, North Africa, and the Near East, establishing a network of roads, aqueducts, and fortifications that facilitated communication, trade, and military control.
A Network of Roads and Cities: The map showcases the intricate web of Roman roads, arteries of communication and trade that connected the far reaches of the empire. Major cities like Rome, Alexandria, and Antioch, bustling centers of commerce, culture, and administration, are prominent features on the map, highlighting the empire’s urban fabric.
The Legacy of Roman Engineering: The Roman Empire’s engineering prowess is evident in the map’s depiction of aqueducts, bridges, and fortifications. These remarkable feats of construction, vital for supplying water, facilitating travel, and defending the empire, serve as a testament to Roman ingenuity and organizational skills.
The Spread of Roman Culture: The map reveals the dissemination of Roman culture, language, and law across the empire. Latin, the language of administration and law, became the lingua franca of the empire, leaving an enduring mark on the languages and cultures of Europe. Roman legal principles, emphasizing fairness and order, laid the foundation for legal systems across the Western world.
The Importance of Maps in Understanding Antiquity
Maps are not mere static representations of landmasses; they are powerful tools that illuminate the dynamics of history. They reveal the interplay between geography, politics, and culture, providing a framework for understanding the rise and fall of civilizations.
Visualizing the Past: Maps bring the past to life, offering a visual representation of the physical world in which ancient societies flourished. They allow us to trace the paths of armies, trade routes, and cultural diffusion, providing a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations.
Understanding Geographical Influences: Maps highlight the impact of geography on ancient societies. The mountainous terrain of Greece, for example, fostered a fragmented political landscape, while the fertile plains of Italy provided the foundation for Roman agriculture and prosperity. The map reveals the ways in which geography shaped the development of ancient civilizations.
Connecting the Pieces of History: Maps provide a visual context for understanding historical events. They help us connect the dots, revealing the relationships between different regions, cultures, and empires. By tracing the movements of armies, the spread of trade networks, and the flow of ideas, maps offer a richer understanding of the interconnectedness of history.
FAQs about Ancient Greece and Rome Maps
1. What are the most important features to look for on a map of ancient Greece?
The most important features to look for on a map of ancient Greece include the Aegean Sea, the mainland peninsula, the major city-states (Athens, Sparta, Corinth), and the locations of significant colonies like Syracuse and Alexandria.
2. What are the key features to identify on a map of the Roman Empire?
Key features on a map of the Roman Empire include the Italian peninsula, the Mediterranean Sea, the major cities (Rome, Alexandria, Antioch), the network of Roman roads, and the boundaries of the empire at its peak.
3. How do maps help us understand the interactions between ancient Greece and Rome?
Maps reveal the geographical proximity of Greece and Rome, highlighting their interactions through trade, conquest, and cultural exchange. They illustrate how Roman expansion ultimately encompassed Greece, bringing the two civilizations into closer contact.
4. Are there different types of maps that are useful for studying ancient Greece and Rome?
Yes, there are various types of maps that can be helpful for studying ancient Greece and Rome. These include:
- Political Maps: These maps depict the boundaries of states, empires, and regions, providing a visual understanding of political structures.
- Physical Maps: These maps show the terrain, rivers, mountains, and other geographical features, revealing the physical environment that shaped ancient societies.
- Historical Maps: These maps illustrate specific events, movements, or periods in history, providing a context for understanding historical developments.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific themes, such as trade routes, population density, or the spread of culture, offering insights into particular aspects of ancient life.
Tips for Using Maps to Study Ancient Greece and Rome
- Focus on Key Geographical Features: Identify the major geographical features, such as seas, mountains, rivers, and plains, as these played a crucial role in shaping ancient societies.
- Locate Major Cities and Settlements: Pay attention to the location of important cities and settlements, as these were centers of power, trade, and culture.
- Trace Trade Routes and Military Campaigns: Study the routes used for trade and military campaigns, as these reveal the flow of goods, ideas, and armies.
- Consider the Time Period: Remember that maps are snapshots in time, so it’s essential to consider the specific historical period being studied.
- Use Maps in Conjunction with Other Sources: Combine maps with other sources, such as historical texts, archaeological evidence, and artwork, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of ancient Greece and Rome.
Conclusion
Maps provide a valuable tool for understanding the ancient world. They reveal the geographical influences that shaped societies, the dynamics of political power, and the interconnectedness of civilizations. By studying maps of ancient Greece and Rome, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of the past, the legacies these civilizations left behind, and the enduring influence they continue to exert on the world today. These maps, more than just representations of landmasses, are windows into the vibrant tapestry of ancient history, offering a glimpse into the lives, achievements, and challenges of those who came before us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course of Antiquity: Exploring the Maps of Ancient Greece and Rome. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!