Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Zones: A Geographic Guide to Plant Hardiness
- 3.2 The Importance of Plant Growing Zones Maps: A Foundation for Successful Gardening
- 3.3 Navigating the Zones: A Deeper Look into the Map’s Information
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Plant Growing Zones Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Plant Growing Zones Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Guide to Success in the Garden
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps
The world of gardening is a fascinating tapestry woven with the threads of sunlight, water, and temperature. Understanding the specific needs of plants and how they interact with their environment is crucial for successful cultivation. This is where plant growing zones maps come into play, providing a valuable tool for gardeners, farmers, and horticulturalists alike.
Unveiling the Zones: A Geographic Guide to Plant Hardiness
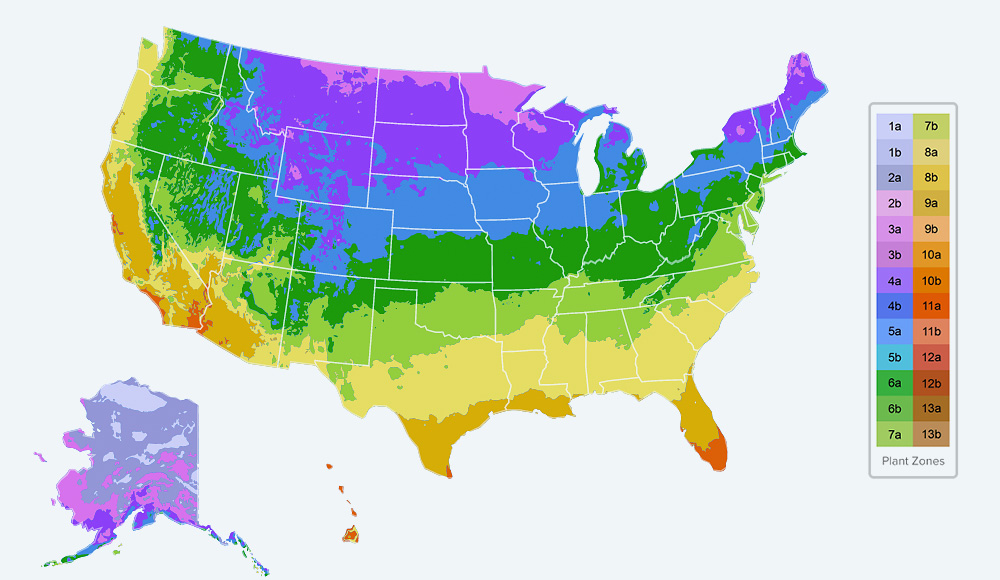
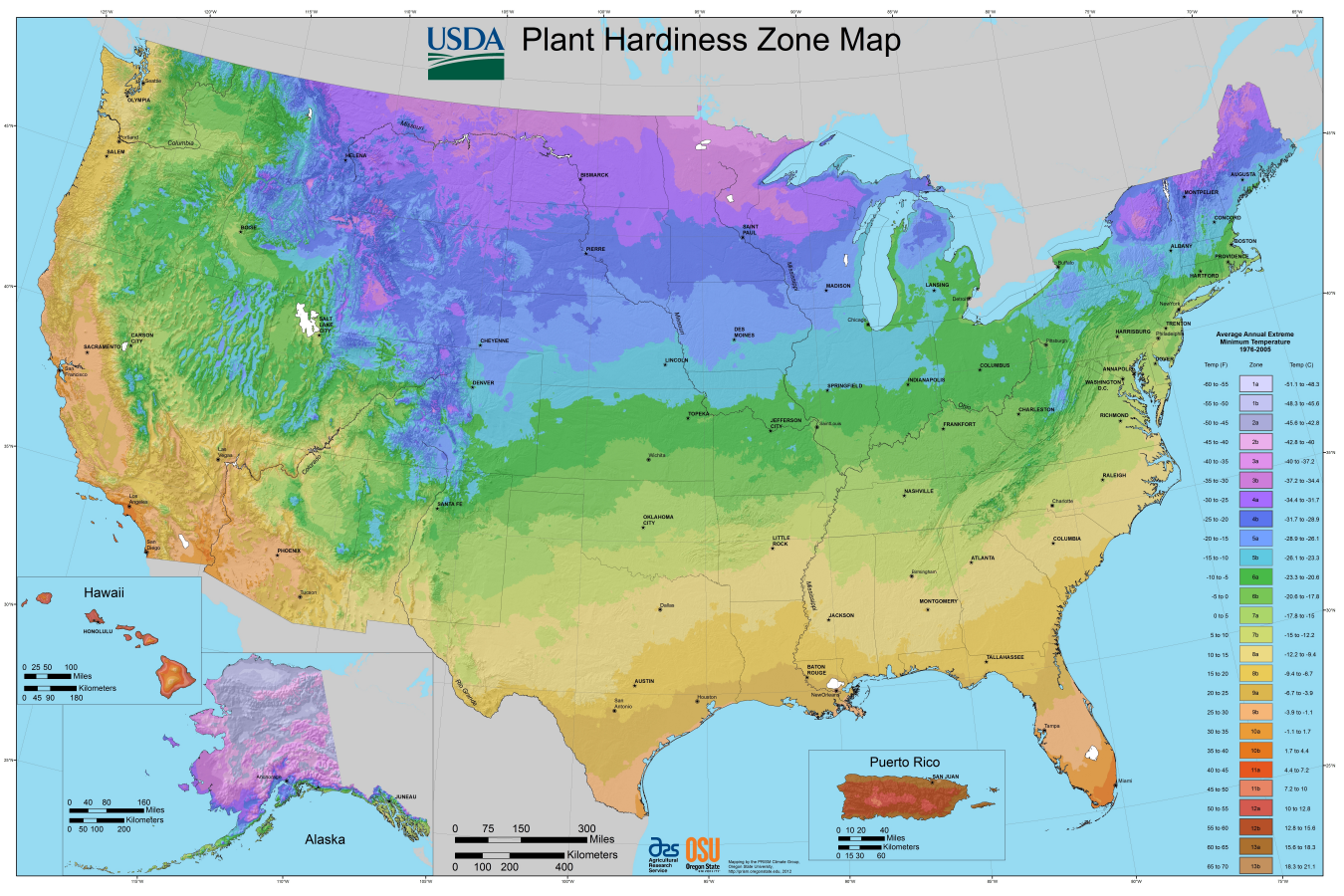
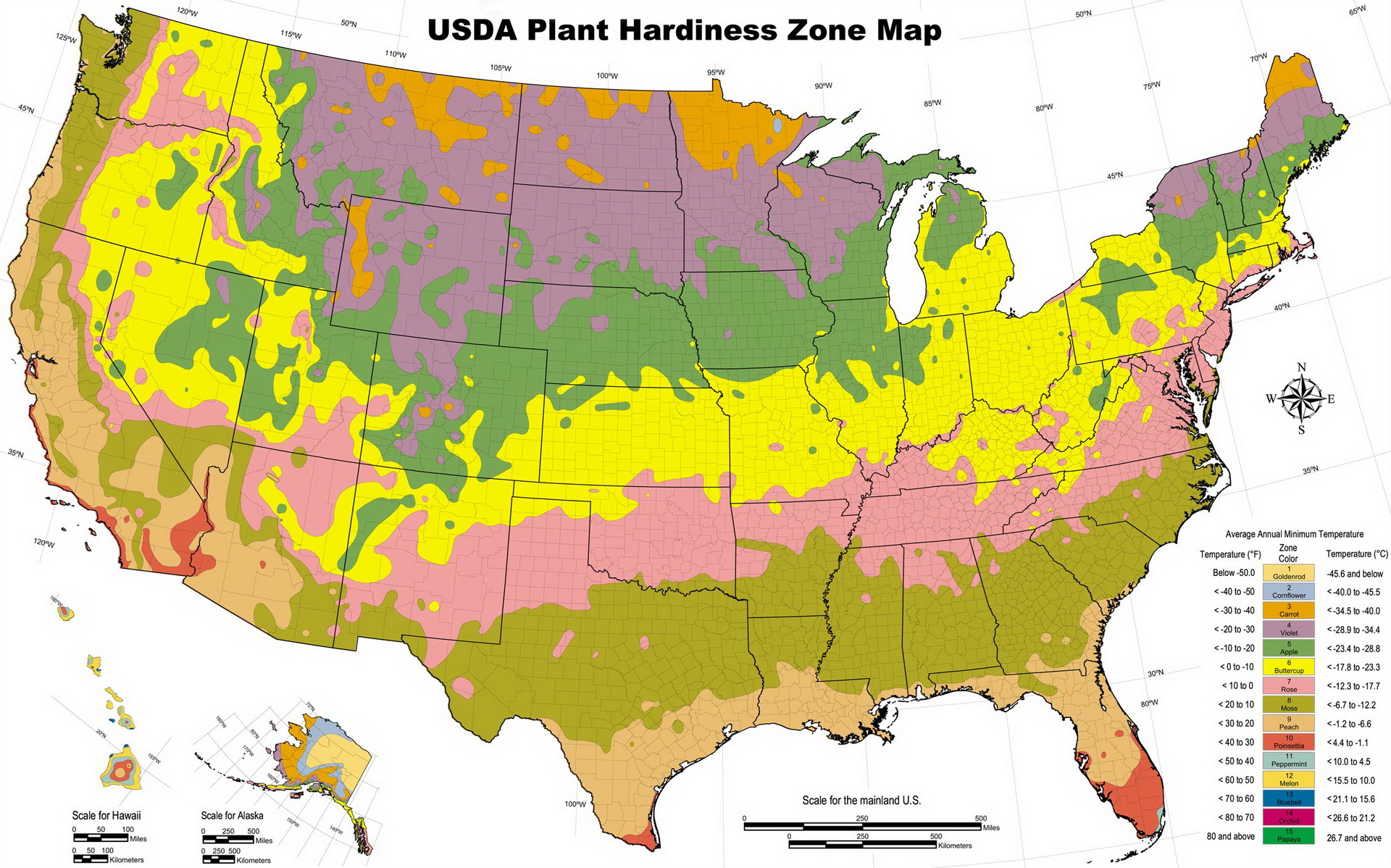
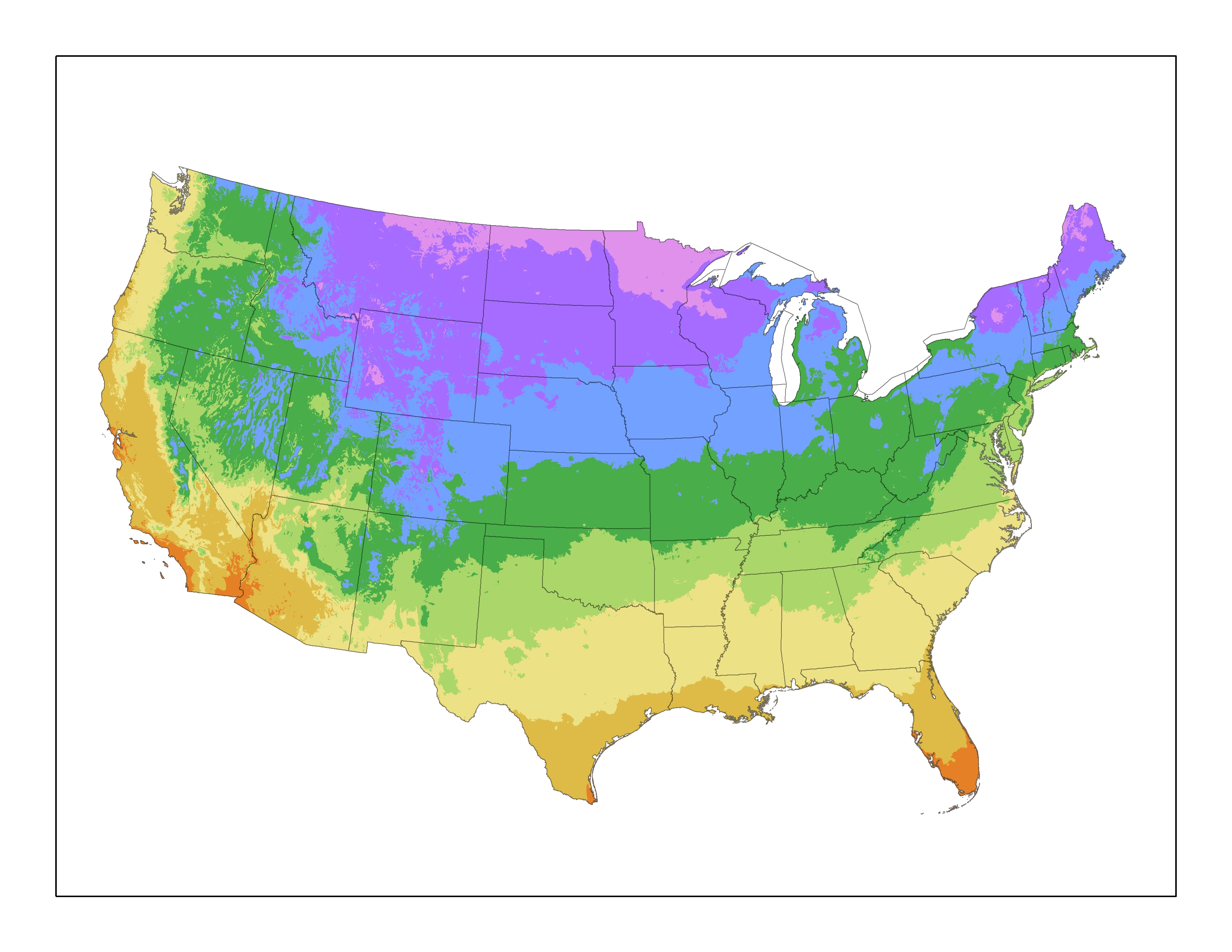
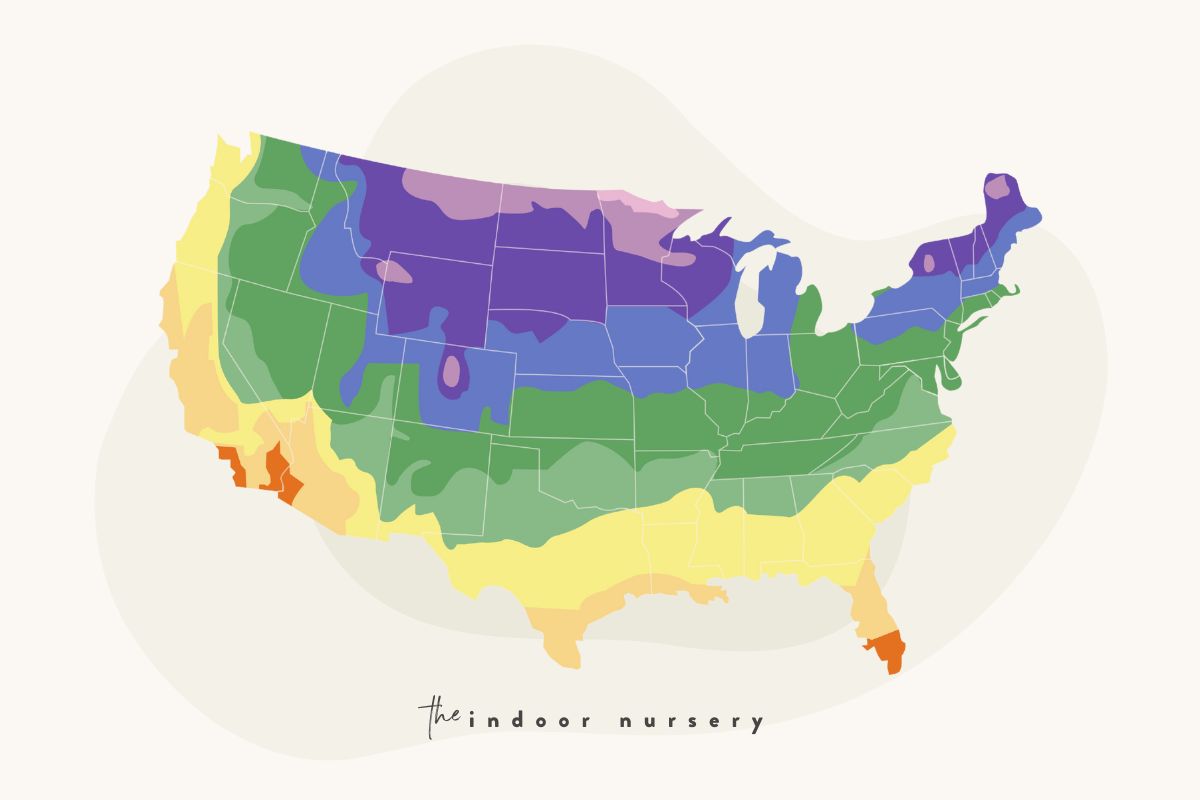
Plant growing zones maps, also known as hardiness zone maps, are visual representations of geographic areas with similar climatic conditions. These maps are typically based on the average minimum winter temperatures, a crucial factor determining which plants can survive and thrive in a particular region. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map, one of the most widely used maps globally, divides the country into 13 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in average minimum winter temperatures.
For instance, Zone 1 experiences the coldest average minimum winter temperatures, while Zone 13 experiences the warmest. Each zone is further subdivided into "a" and "b" subzones, reflecting a 5-degree Fahrenheit variation in average minimum winter temperatures. This granular approach offers a more precise understanding of the plant’s hardiness requirements.
The Importance of Plant Growing Zones Maps: A Foundation for Successful Gardening
Plant growing zones maps are not merely academic exercises. They serve as practical guides, offering invaluable information for several aspects of gardening:
- Plant Selection: The map is a cornerstone for choosing plants that will thrive in a specific location. Understanding the plant’s hardiness zone allows gardeners to select species that can withstand the local climate, minimizing the risk of winter damage or mortality.
- Gardening Calendar: By knowing the prevailing climate, gardeners can plan their planting and harvesting schedules effectively. The map provides insights into the optimal time for sowing seeds, transplanting seedlings, and harvesting mature plants.
- Pest and Disease Management: Climate plays a crucial role in the prevalence and spread of pests and diseases. The map helps identify potential threats and enables gardeners to adopt appropriate preventative measures.
- Water Conservation: Understanding the climate allows gardeners to adopt efficient watering practices, minimizing water usage and promoting sustainable gardening.
- Landscape Design: Plant growing zones maps are essential for landscape architects and designers. They help select plants that will flourish in specific microclimates, contributing to the overall aesthetic and ecological harmony of the landscape.
Navigating the Zones: A Deeper Look into the Map’s Information
Beyond the basic zone designations, plant growing zones maps often provide additional information, enhancing their usefulness:
- Average Annual Precipitation: This information helps assess the water availability and understand the specific watering needs of plants.
- Average Annual Temperature: This data provides insights into the overall climate and helps identify suitable plants for specific temperature ranges.
- Soil Type: The map may indicate prevalent soil types, which can influence plant selection and soil amendment strategies.
- Growing Season Length: This information is crucial for planning planting dates and ensuring sufficient time for plants to mature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Plant Growing Zones Maps
1. Can a plant survive in a zone lower than its hardiness zone?
While a plant can survive in a zone lower than its hardiness zone, it may experience winter damage or struggle to thrive. The plant may require extra protection, such as mulching, winter coverings, or sheltered locations.
2. Can a plant survive in a zone higher than its hardiness zone?
Yes, a plant can generally survive in a zone higher than its hardiness zone. However, it may not reach its full potential growth or flowering, as it may lack the cold stimulus necessary for dormancy and subsequent spring growth.
3. How do I find my plant growing zone?
Numerous online resources, including the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website, allow you to enter your zip code or address to determine your plant growing zone.
4. Are plant growing zones maps accurate for all regions?
Plant growing zones maps are generally accurate for large geographic areas, but local microclimates can influence the actual hardiness of plants. Factors such as elevation, proximity to water bodies, and urban heat islands can create variations in temperature and moisture levels.
5. What are the limitations of plant growing zones maps?
Plant growing zones maps are based on average minimum winter temperatures, which may not reflect the full spectrum of climatic conditions. Other factors, such as soil type, sunlight exposure, and air circulation, also play a significant role in plant growth and survival.
Tips for Utilizing Plant Growing Zones Maps Effectively
- Consult Multiple Resources: While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable tool, it’s beneficial to consult other maps and resources for a more comprehensive understanding of the local climate.
- Consider Microclimates: Recognize that microclimates within a larger zone can significantly influence plant hardiness. Assess factors like elevation, slope, and proximity to structures or water bodies.
- Focus on Specific Needs: Beyond the general hardiness zone, consider the specific needs of each plant, such as sunlight requirements, water tolerance, and soil preferences.
- Embrace Experimentation: Don’t be afraid to experiment with plants outside your zone. Observe their growth and make adjustments as needed.
- Stay Informed: Climate change is altering plant growing zones, so it’s crucial to stay updated on the latest information and potential shifts in hardiness zones.
Conclusion: A Guide to Success in the Garden
Plant growing zones maps serve as invaluable tools for gardeners, providing a foundation for successful cultivation. By understanding the language of plants and the nuances of climate, gardeners can make informed decisions about plant selection, cultivation practices, and overall garden management. As the world continues to evolve, understanding plant growing zones and adapting to changing climates will become increasingly crucial for nurturing healthy and vibrant gardens.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Plants: Understanding Plant Growing Zones Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!