Deciphering the Visual Language of Heat Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Deciphering the Visual Language of Heat Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Visual Language of Heat Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Visual Language of Heat Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Heat maps, with their vibrant color gradients, offer a powerful visual representation of data, revealing patterns and insights often obscured in raw numbers. They are increasingly employed across various fields, from website design and marketing to product development and user experience analysis. Understanding how to read a heat map effectively is crucial for extracting valuable information and making data-driven decisions.
Understanding the Fundamentals
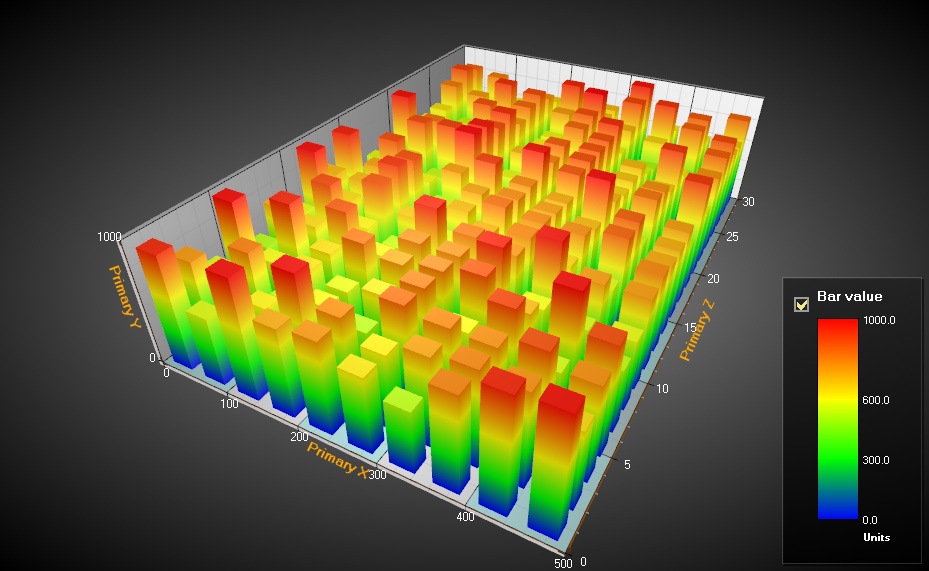
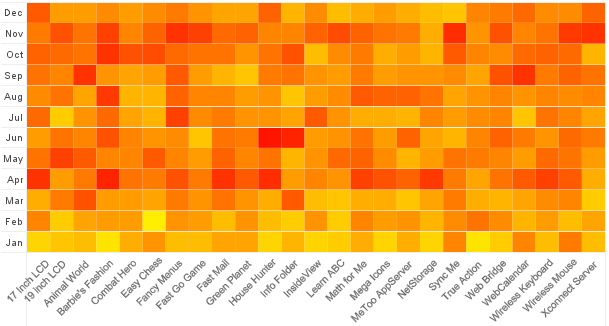
At its core, a heat map uses color intensity to depict the concentration of data points within a defined area. The most common color scheme employs a gradient from cool colors (e.g., blue) for low values to warm colors (e.g., red) for high values. This allows for a quick visual interpretation of areas with high activity or concentration, contrasting them with areas of low activity.
Types of Heat Maps
The specific type of heat map dictates its application and interpretation. Here are some common types:
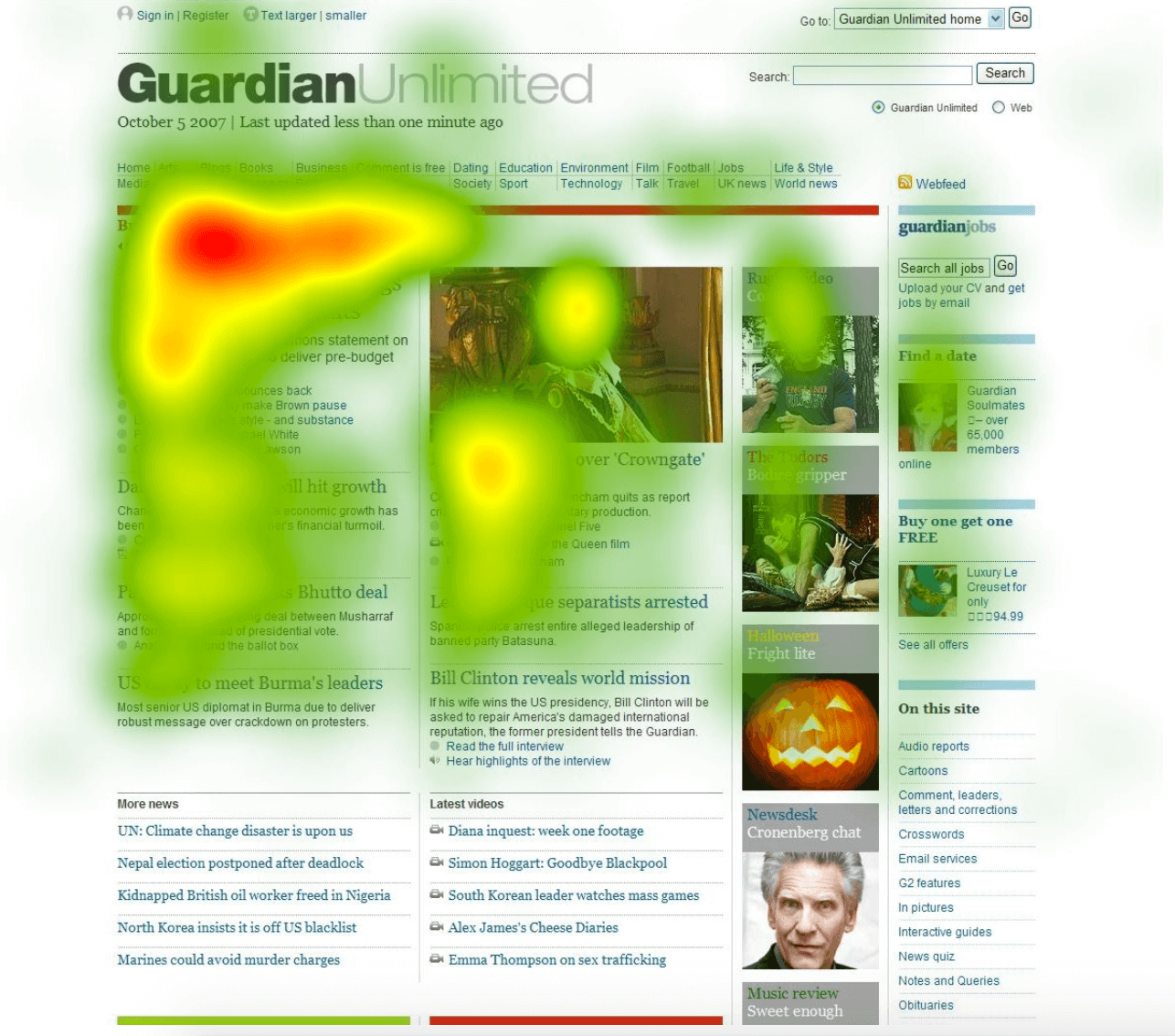
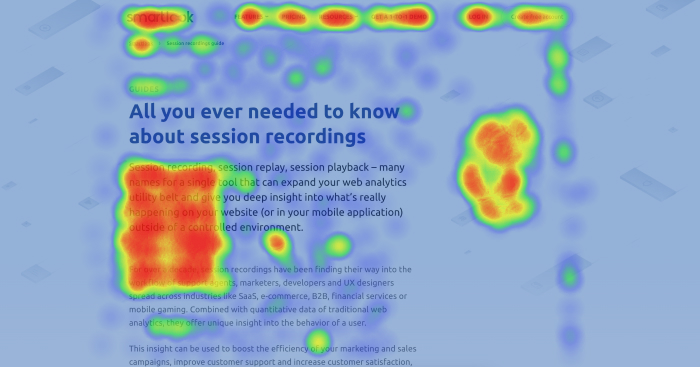
- Click Maps: These maps visualize user interactions on a website, highlighting areas where users click the most. They are valuable for understanding user behavior, identifying areas of interest, and optimizing website design.
- Scroll Maps: These maps track user scrolling behavior, revealing how far down a page users scroll. They are useful for understanding user engagement, identifying content that captures attention, and determining the effectiveness of page layouts.
- Mouse Movement Maps: These maps track the movement of a user’s mouse cursor, providing insights into how users navigate a website or interact with specific elements. They can help identify usability issues, understand user flow, and optimize user experience.
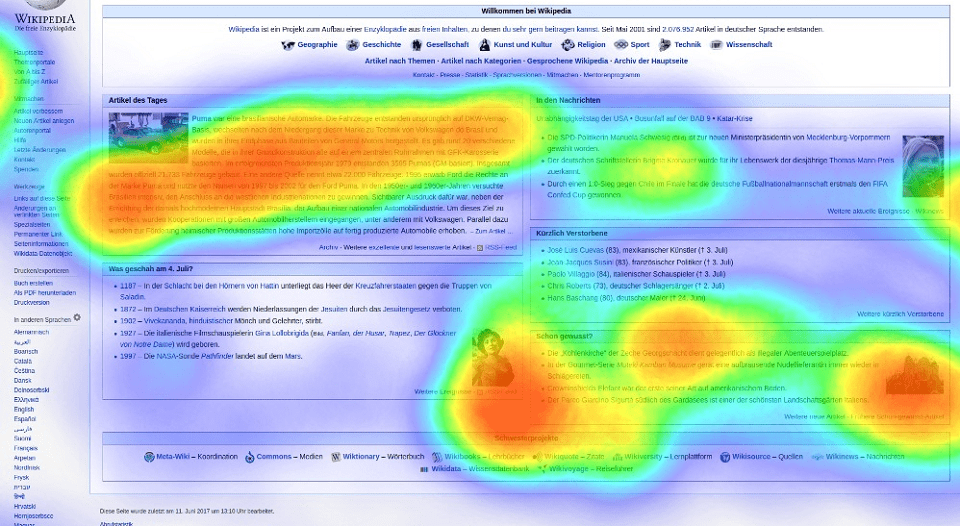
- Eye-Tracking Heat Maps: These maps visualize eye movements, revealing areas of visual focus during user interactions. They are highly valuable for understanding user attention, identifying areas of interest, and optimizing content presentation.
Decoding the Visual Language
To effectively interpret a heat map, consider the following:
- Color Intensity: Pay close attention to the color gradient. The areas with the most intense color (e.g., red) represent the highest activity or concentration, while areas with the least intense color (e.g., blue) represent the lowest activity.
- Color Scale: The color scale provides a visual representation of the data range. Understanding the scale allows for a more precise interpretation of the data values represented by different colors.
- Legend: The legend explains the color scheme and provides context for interpreting the data. It typically defines the data range represented by each color, allowing for a more accurate understanding of the heat map’s findings.
- Context: Always consider the context of the data. The meaning of the heat map depends on the specific data being visualized. For example, a heat map of website clicks will be interpreted differently than a heat map of product sales.
Applications and Benefits
Heat maps have a wide range of applications across various disciplines. Here are some key benefits:
- User Experience Optimization: Heat maps provide valuable insights into user behavior, allowing designers and developers to identify usability issues, improve website navigation, and optimize user experience.
- Marketing Insights: By understanding user behavior on landing pages and marketing materials, businesses can optimize content, target specific audiences, and improve conversion rates.
- Product Development: Heat maps can reveal user preferences and identify areas of interest in product design. This information can be used to enhance product features and improve user satisfaction.
- Sales and Marketing Strategy: Heat maps can help identify high-performing products or services, optimize pricing strategies, and improve customer engagement.
- Research and Analysis: Heat maps are powerful tools for visualizing data, identifying patterns, and supporting research findings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a heat map and a scatter plot?
A: While both heat maps and scatter plots visualize data points, they differ in their representation. A heat map uses color intensity to depict the concentration of data points within a defined area, while a scatter plot uses individual points to represent each data point.
Q: How can I create a heat map?
A: There are numerous tools available for creating heat maps. Some popular options include:
- Google Analytics: Provides built-in heat map functionality for analyzing website user behavior.
- Hotjar: Offers a comprehensive suite of heat map tools for website analysis, including click maps, scroll maps, and mouse movement maps.
- Crazy Egg: Provides detailed heat map analysis, including click maps, scroll maps, and A/B testing.
Q: What are the limitations of heat maps?
A: While heat maps are powerful visualization tools, they have some limitations:
- Sample Size: The accuracy of a heat map depends on the sample size. A small sample size may not accurately represent the overall user behavior.
- Bias: Heat maps can be influenced by user bias. For example, users may be more likely to click on specific areas of a website due to external factors.
- Context: It is important to consider the context of the data when interpreting a heat map. The meaning of the data can vary depending on the specific situation.
Tips for Effective Heat Map Interpretation
- Focus on the overall patterns: Don’t get bogged down in individual data points. Look for overall trends and patterns in the data.
- Consider the context: Always consider the context of the data when interpreting a heat map. The meaning of the data can vary depending on the specific situation.
- Use multiple heat maps: Use multiple heat maps to get a more comprehensive understanding of the data. For example, use a click map to understand user interactions and a scroll map to understand user engagement.
- Test your assumptions: Don’t assume that the heat map is telling the whole story. Test your assumptions by conducting additional research or user testing.
Conclusion
Heat maps offer a powerful visual representation of data, revealing patterns and insights often hidden in raw numbers. By understanding the fundamentals of heat map interpretation, you can effectively extract valuable information and make data-driven decisions. Whether you’re optimizing a website, analyzing user behavior, or developing new products, heat maps provide a valuable tool for understanding user needs and driving successful outcomes.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Visual Language of Heat Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!