Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps
Related Articles: Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Foundation: What are X Y Coordinates?
- 3.2 Applications of X Y Coordinates: A Wide Spectrum of Use Cases
- 3.3 Benefits of Using X Y Coordinates: Precision, Standardization, and Accessibility
- 3.4 FAQs about X Y Coordinates: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing X Y Coordinates Effectively: Maximizing Their Potential
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Coordinates for a More Precise World
- 4 Closure
Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps

The world around us is a tapestry of locations, each with its own unique story. From bustling cities to serene landscapes, the ability to pinpoint and navigate these locations is crucial for various endeavors. Enter the realm of coordinates, a powerful tool that allows us to define and locate any point on a two-dimensional plane using a simple yet effective system.
Understanding the Foundation: What are X Y Coordinates?
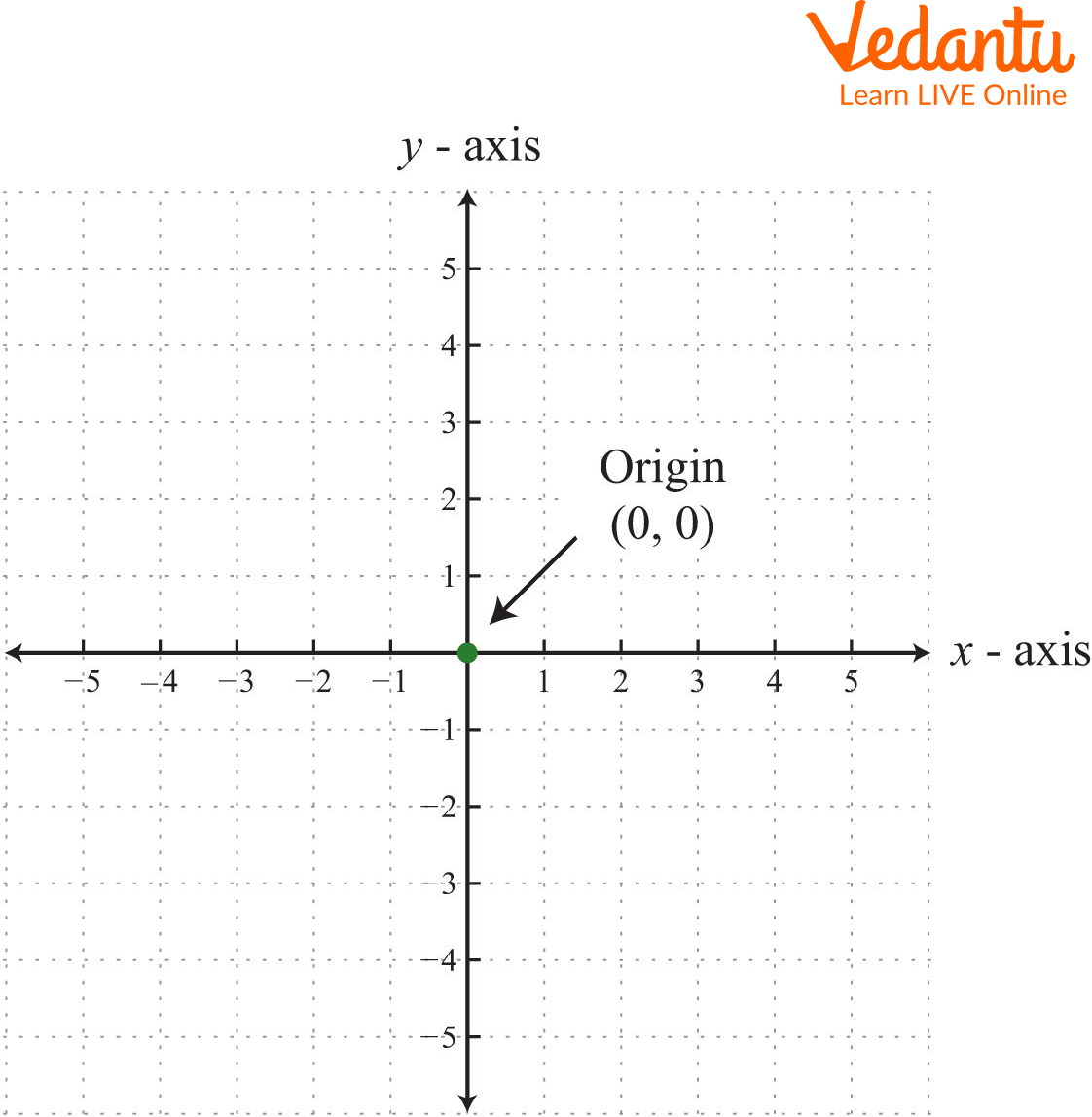
At its core, the X Y coordinate system is a mathematical framework that employs two perpendicular axes, labeled as X and Y, to define any point within a plane. The X-axis represents the horizontal direction, while the Y-axis represents the vertical direction. Each point on this plane is represented by a unique pair of numbers, known as coordinates, which indicate its position relative to the origin (the point where the two axes intersect).
Imagine a grid, like a chessboard, with the X-axis running horizontally and the Y-axis vertically. Each square on this grid can be identified by its unique combination of X and Y values. For instance, the point (3, 2) represents a location that is three units to the right of the origin along the X-axis and two units upward along the Y-axis. This simple system provides a standardized and unambiguous way to pinpoint any location within the plane.
Applications of X Y Coordinates: A Wide Spectrum of Use Cases
The power of X Y coordinates extends far beyond the realm of theoretical mathematics. Their applications are diverse, permeating various fields and impacting our daily lives in numerous ways.
1. Mapping and Navigation:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): X Y coordinates form the backbone of GIS, enabling the creation of detailed maps that depict various spatial features, such as roads, buildings, and natural landscapes. These maps are instrumental in urban planning, disaster management, and resource management.
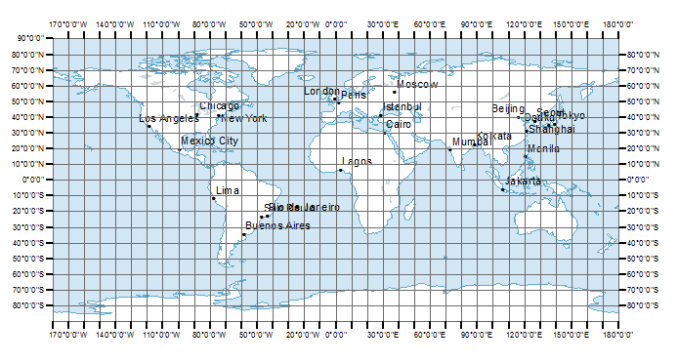
- Navigation Apps: Our smartphones rely on GPS technology, which uses latitude and longitude coordinates (a variation of the X Y system) to determine our location and guide us through unfamiliar streets.
- Cartography: Cartographers, who create maps, utilize X Y coordinates to precisely represent geographical features on a map, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
2. Engineering and Design:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Architects, engineers, and designers use CAD software that relies heavily on X Y coordinates to create blueprints and models of buildings, machines, and other structures.
- Robotics: Robots use X Y coordinates to navigate their environment, perform tasks, and interact with objects.
- Manufacturing: X Y coordinates are essential in CNC machining, where machines are programmed to cut and shape materials with precision based on defined coordinates.
3. Data Visualization and Analysis:
- Data Plotting: X Y coordinates are fundamental to creating graphs and charts, enabling the visualization of data patterns and relationships.
- Statistical Analysis: Data analysis techniques rely on X Y coordinates to represent data points and perform calculations, revealing insights and trends.
- Image Processing: Image processing techniques often utilize X Y coordinates to analyze and manipulate pixels within an image, enabling tasks such as object detection and image enhancement.
4. Other Applications:
- Gaming: X Y coordinates are used to define the position of objects, characters, and players within a virtual world.
- Computer Graphics: X Y coordinates are essential for creating visual effects and animations, defining the position and movement of objects on a screen.
- Scientific Research: X Y coordinates are used in various scientific fields, such as astronomy, physics, and biology, to analyze data and model complex phenomena.
Benefits of Using X Y Coordinates: Precision, Standardization, and Accessibility
The widespread adoption of X Y coordinates stems from their inherent benefits:
- Precision: X Y coordinates offer a precise and unambiguous way to define any location within a plane. This precision is crucial for applications requiring accuracy, such as engineering, manufacturing, and navigation.
- Standardization: The X Y coordinate system provides a universal language for representing locations, enabling seamless communication and data sharing across various disciplines.
- Accessibility: The simplicity of the X Y system makes it easy to understand and apply, making it accessible to individuals from various backgrounds and skill levels.
FAQs about X Y Coordinates: Addressing Common Queries
1. What are the different types of coordinate systems?
While the X Y coordinate system is a fundamental framework, various types of coordinate systems exist, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Some notable examples include:
- Cartesian Coordinates: The standard X Y coordinate system, often used in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- Polar Coordinates: This system uses a distance from the origin and an angle from a reference axis to define a point. It is often used in navigation and astronomy.
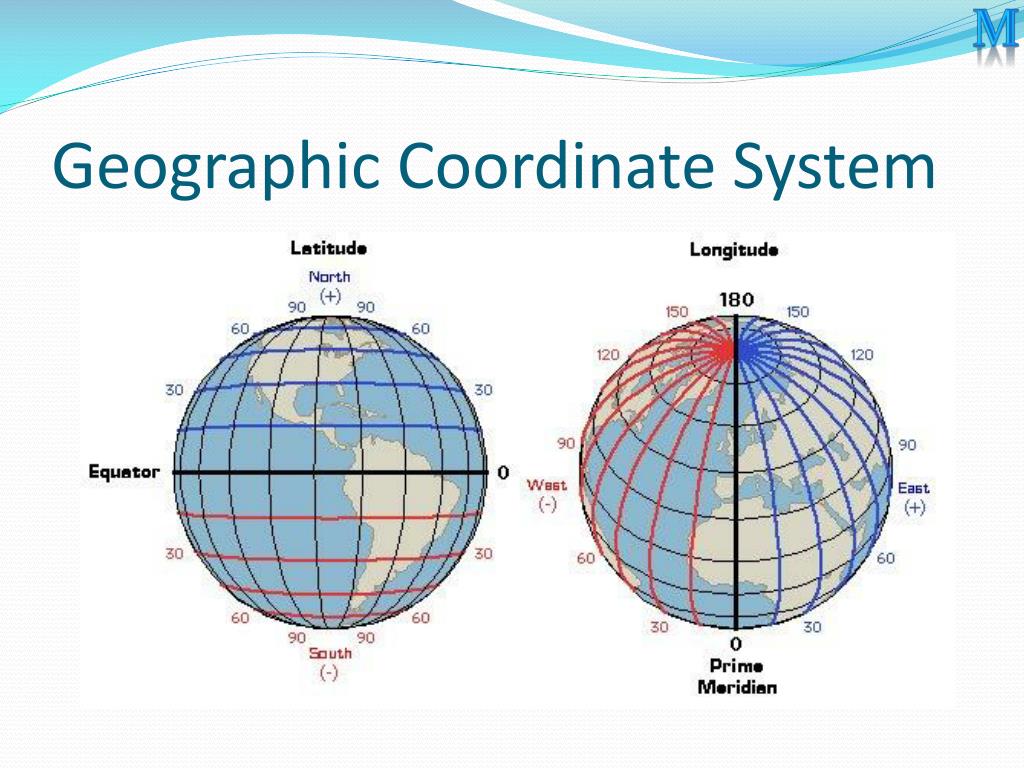
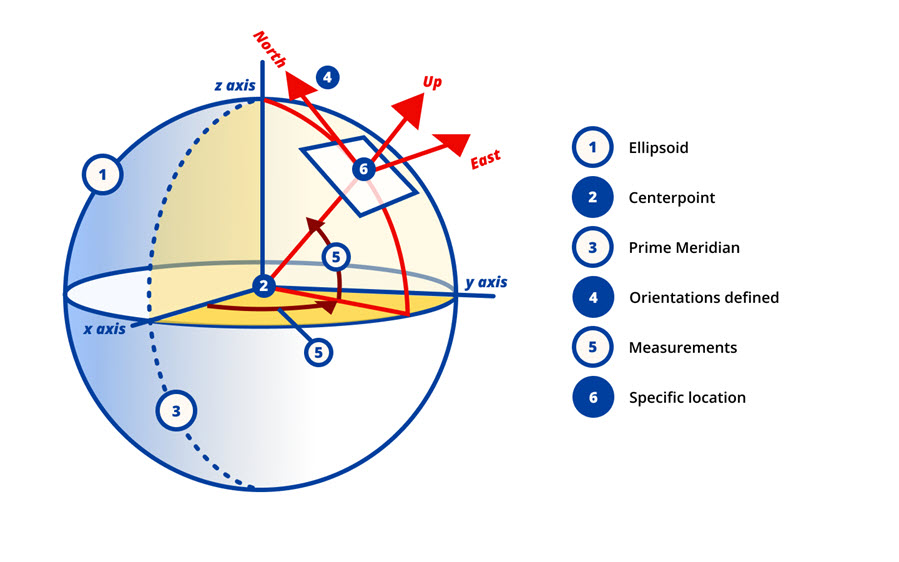
- Geographic Coordinates: This system uses latitude and longitude to define a location on the Earth’s surface. It is widely used in mapping and navigation.
- Spherical Coordinates: This system uses a distance from the origin, an angle from the z-axis, and an angle from the x-axis to define a point in three-dimensional space. It is often used in physics and astronomy.
2. How are X Y coordinates used in real-world applications?
X Y coordinates are ubiquitous in real-world applications, driving advancements in various fields:
- GPS Navigation: Smartphones use GPS technology to determine our location based on latitude and longitude coordinates, guiding us through unfamiliar territories.
- CAD Software: Architects and engineers rely on CAD software that utilizes X Y coordinates to create detailed blueprints and models of buildings, machines, and other structures.
- Robotics: Robots use X Y coordinates to navigate their environment, perform tasks, and interact with objects.
- Mapping and GIS: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) heavily rely on X Y coordinates to create detailed maps that depict various spatial features, aiding in urban planning, disaster management, and resource management.
3. What are the limitations of X Y coordinates?
While X Y coordinates are powerful, they have limitations:
- Two-Dimensional Representation: X Y coordinates only represent locations on a two-dimensional plane. They cannot fully represent the three-dimensional nature of the real world.
- Limited to Flat Surfaces: X Y coordinates are most effective for representing locations on flat surfaces. Applying them to curved surfaces, such as the Earth’s surface, requires complex transformations.
- Scale Dependence: The accuracy of X Y coordinates is dependent on the scale of the coordinate system. A large-scale map might not be accurate for representing locations at a smaller scale.
Tips for Utilizing X Y Coordinates Effectively: Maximizing Their Potential
- Understanding the Coordinate System: Thoroughly understand the specific coordinate system used for your application, including its origin, units, and any specific transformations required.
- Data Accuracy: Ensure the accuracy of the X Y coordinate data used in your application. Errors in coordinates can lead to inaccurate results and misinterpretations.
- Scale Considerations: Consider the appropriate scale for your application and choose a coordinate system that provides sufficient accuracy for your needs.
- Visualization Tools: Utilize visualization tools, such as graphs and charts, to effectively represent and analyze data based on X Y coordinates.
- Coordinate Transformations: If necessary, learn and apply appropriate coordinate transformations to convert data between different coordinate systems.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Coordinates for a More Precise World
The X Y coordinate system, with its simple yet powerful framework, serves as a fundamental tool for representing and navigating the world around us. Its applications span various fields, enabling us to understand, analyze, and interact with our surroundings in unprecedented ways. By understanding and effectively utilizing X Y coordinates, we can unlock a world of possibilities, driving advancements in mapping, navigation, engineering, design, data visualization, and beyond. As we continue to explore and innovate, the X Y coordinate system will remain a cornerstone for a more precise, efficient, and interconnected world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Power of Coordinates: A Comprehensive Guide to X Y Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!