Eastern China: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse
Related Articles: Eastern China: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Eastern China: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Eastern China: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse

Eastern China, a region encompassing the eastern coastal provinces of the People’s Republic of China, holds immense significance in the country’s economic, cultural, and historical landscape. This region, blessed with fertile plains, extensive coastlines, and abundant resources, has been a focal point of Chinese civilization for centuries. Understanding its geographical characteristics and historical evolution is crucial to appreciating its multifaceted role in contemporary China.
Geographical Overview:
Eastern China’s geographical features are diverse and contribute significantly to its economic prosperity.
- Coastline and Islands: The region boasts a vast coastline stretching over 6,000 kilometers, encompassing numerous islands and inlets. This maritime advantage has historically facilitated trade and maritime activities, propelling economic growth and cultural exchange.
- River Systems: Major rivers like the Yangtze and the Yellow River flow through Eastern China, providing vital irrigation for agriculture, transportation routes for trade, and a rich source of freshwater. These rivers have also historically served as a lifeline for the region, fostering the development of ancient civilizations along their banks.
- Mountains and Plains: The region features a mix of mountainous terrain in the north and east, transitioning into vast, fertile plains in the central and southern regions. These plains, known for their agricultural productivity, have been instrumental in sustaining a large population and contributing to China’s food security.
- Climate: Eastern China experiences a diverse range of climates, from subtropical in the south to temperate in the north. This climatic variation allows for a wide variety of agricultural products, further contributing to the region’s economic strength.
Historical Significance:
Eastern China’s historical importance is deeply intertwined with its geography.
- Ancient Civilizations: The region served as the cradle of ancient Chinese civilization, with prominent dynasties like the Shang and the Zhou establishing their capitals along the Yellow River. This period witnessed the development of key aspects of Chinese culture, including writing, agriculture, and social structures.
- Trade and Maritime Activities: From ancient times, Eastern China’s coastal location facilitated trade with other countries, particularly through the Silk Road. This maritime activity fostered economic growth and cultural exchange, solidifying the region’s prominence in the East Asian sphere.
- Political and Economic Hub: Throughout Chinese history, Eastern China has been a center of political power and economic activity. The region has hosted numerous imperial capitals and has been a major contributor to the country’s economic development.
Economic Powerhouse:
Today, Eastern China is recognized as a major economic powerhouse, driving China’s rapid economic growth and global influence.
- Industrial Centers: The region is home to major industrial centers, including Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou, which are hubs for manufacturing, finance, and technology. These cities have attracted significant foreign investment, contributing to China’s rise as a global economic force.
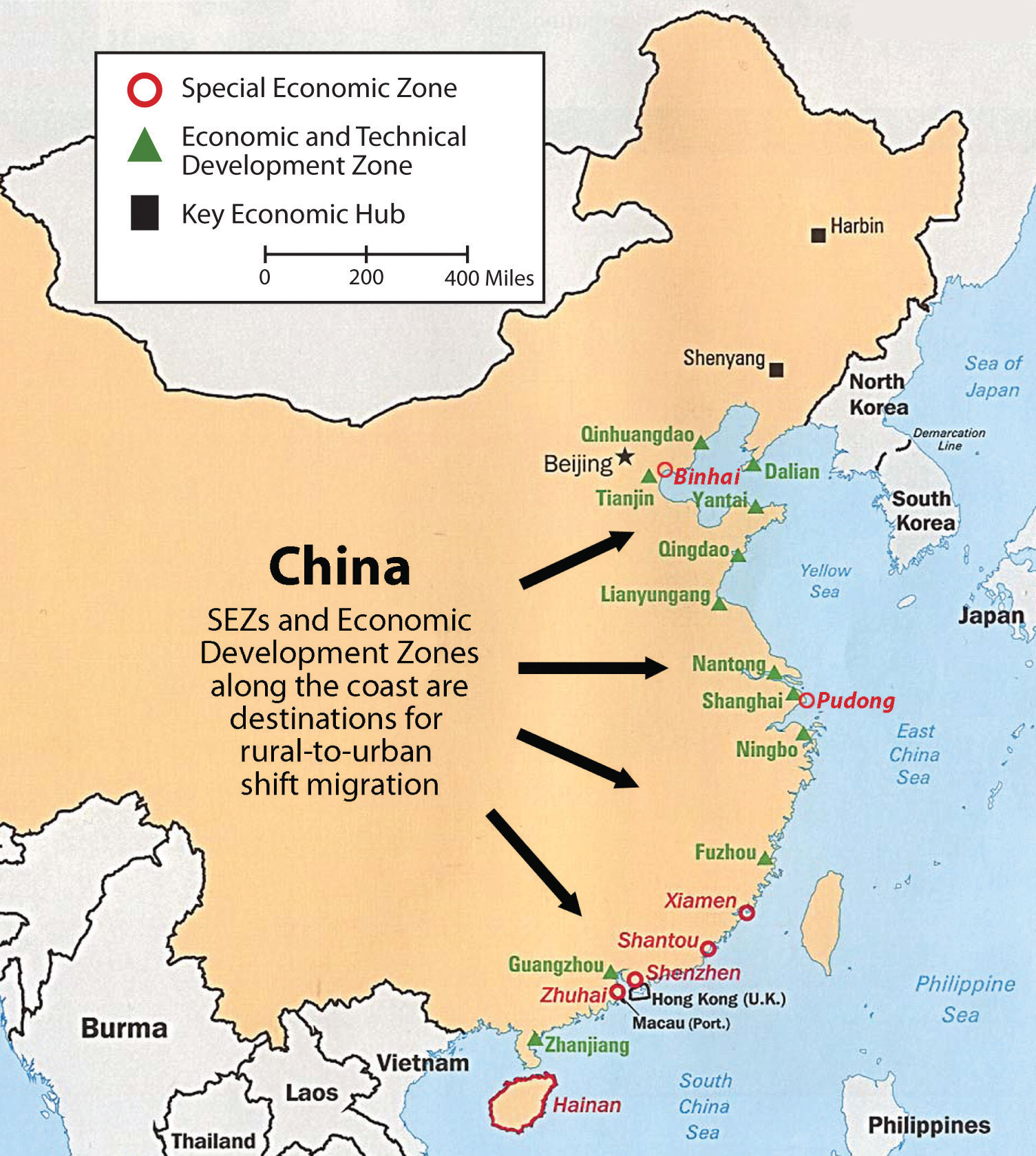
- Special Economic Zones: Eastern China boasts several Special Economic Zones (SEZs), such as Shenzhen and Xiamen, which have been instrumental in attracting foreign investment and promoting economic development. These zones have fostered innovation and entrepreneurship, contributing to China’s economic transformation.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Despite its industrialization, Eastern China remains a significant agricultural producer, supplying a large portion of China’s food needs. The region’s fertile plains and advanced agricultural techniques contribute to its food security and its role in feeding a vast population.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Eastern China enjoys significant advantages, it also faces challenges:
- Environmental Issues: Rapid industrialization has led to environmental issues such as air and water pollution, requiring significant efforts to address these challenges and ensure sustainable development.
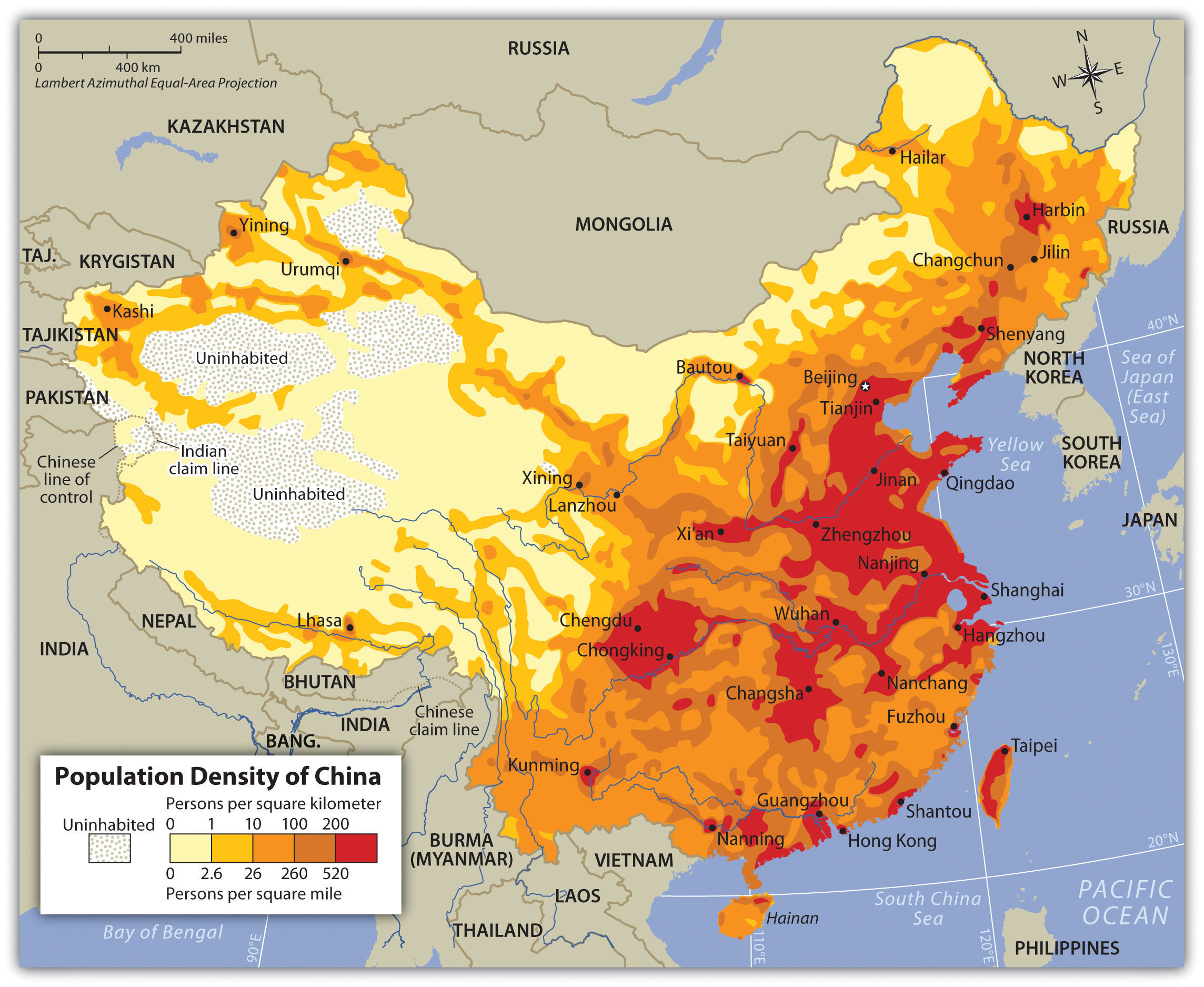
- Population Growth and Urbanization: The region’s high population density and rapid urbanization have created challenges in providing housing, infrastructure, and social services. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life for its residents.
- Economic Inequality: Despite its economic success, Eastern China faces issues of economic inequality, with significant disparities between urban and rural areas. Addressing these disparities is essential for ensuring social stability and inclusive growth.
Opportunities:
Despite the challenges, Eastern China holds immense potential for continued growth and development:
- Innovation and Technology: The region is a hub for innovation and technology, with major investments in research and development. This focus on technological advancement positions Eastern China to lead in emerging industries and contribute to global technological progress.
- Sustainable Development: With a focus on addressing environmental challenges, Eastern China has the potential to become a model for sustainable development. This can involve promoting renewable energy, improving waste management, and implementing green technologies.
- Regional Integration: Eastern China can leverage its geographical advantages to strengthen regional integration within China and beyond. This can involve enhancing infrastructure, promoting cross-border trade, and fostering cultural exchange.
FAQs:
1. What are the major cities in Eastern China?
Eastern China is home to several major cities, including:
- Shanghai: The largest city in China and a global financial hub.
- Beijing: The capital of China and a major political and cultural center.
- Guangzhou: A major commercial and industrial center in southern China.
- Shenzhen: A Special Economic Zone known for its technological innovation.
- Hangzhou: A historic city known for its beautiful scenery and tea production.
- Nanjing: A former imperial capital and a major cultural and educational center.
- Suzhou: A historic city known for its classical gardens and silk production.
- Wuhan: A major transportation hub and industrial center in central China.
2. What are the main industries in Eastern China?
Eastern China is a diverse economic region, with major industries including:
- Manufacturing: The region is a major manufacturing hub, producing a wide range of goods from electronics to textiles.
- Finance: Shanghai is a global financial center, attracting significant foreign investment and playing a key role in China’s financial market.
- Technology: Eastern China is a hub for technological innovation, with major investments in research and development.
- Tourism: The region’s rich history, diverse landscapes, and vibrant culture attract millions of tourists each year.
- Agriculture: Despite its industrialization, Eastern China remains a significant agricultural producer, contributing to China’s food security.
3. What are the major environmental challenges facing Eastern China?
Eastern China faces several environmental challenges, including:
- Air Pollution: Rapid industrialization has led to severe air pollution in many cities, affecting public health and the environment.
- Water Pollution: Industrial waste and agricultural runoff have polluted rivers and lakes, affecting water quality and biodiversity.
- Deforestation: Deforestation for agriculture and urbanization has led to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Climate Change: The region is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
4. What are the opportunities for future development in Eastern China?
Eastern China holds immense potential for future development, including:
- Innovation and Technology: The region can continue to invest in research and development, becoming a global leader in emerging technologies.
- Sustainable Development: By addressing environmental challenges, Eastern China can become a model for sustainable development, promoting renewable energy and green technologies.
- Regional Integration: The region can strengthen regional integration within China and beyond, enhancing infrastructure, promoting trade, and fostering cultural exchange.
Tips for Visiting Eastern China:
- Plan your trip in advance: Eastern China is a vast region with numerous attractions. Planning your itinerary in advance will help you make the most of your time.
- Consider the best time to visit: The best time to visit Eastern China depends on your interests and preferences. Spring and autumn offer mild weather and beautiful scenery, while summer is hot and humid.
- Learn some basic Mandarin: While English is spoken in major cities, knowing some basic Mandarin will enhance your travel experience.
- Respect local customs: China has a rich culture and unique customs. Be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Try local cuisine: Eastern China offers a diverse and delicious cuisine. Be sure to try local specialties like dumplings, noodles, and seafood.
- Explore beyond the major cities: While major cities offer plenty of attractions, consider exploring smaller towns and villages to experience the true essence of Eastern China.
Conclusion:
Eastern China stands as a testament to the dynamism and resilience of the Chinese people. Its rich history, diverse geography, and thriving economy make it a crucial region in shaping China’s future. The challenges and opportunities facing Eastern China are intertwined with the country’s overall development trajectory. Understanding the region’s complexities is essential for appreciating its significance in the global context and for navigating the complex dynamics of the 21st century.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Eastern China: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!