Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Guide to the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore
Related Articles: Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Guide to the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Guide to the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Guide to the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore

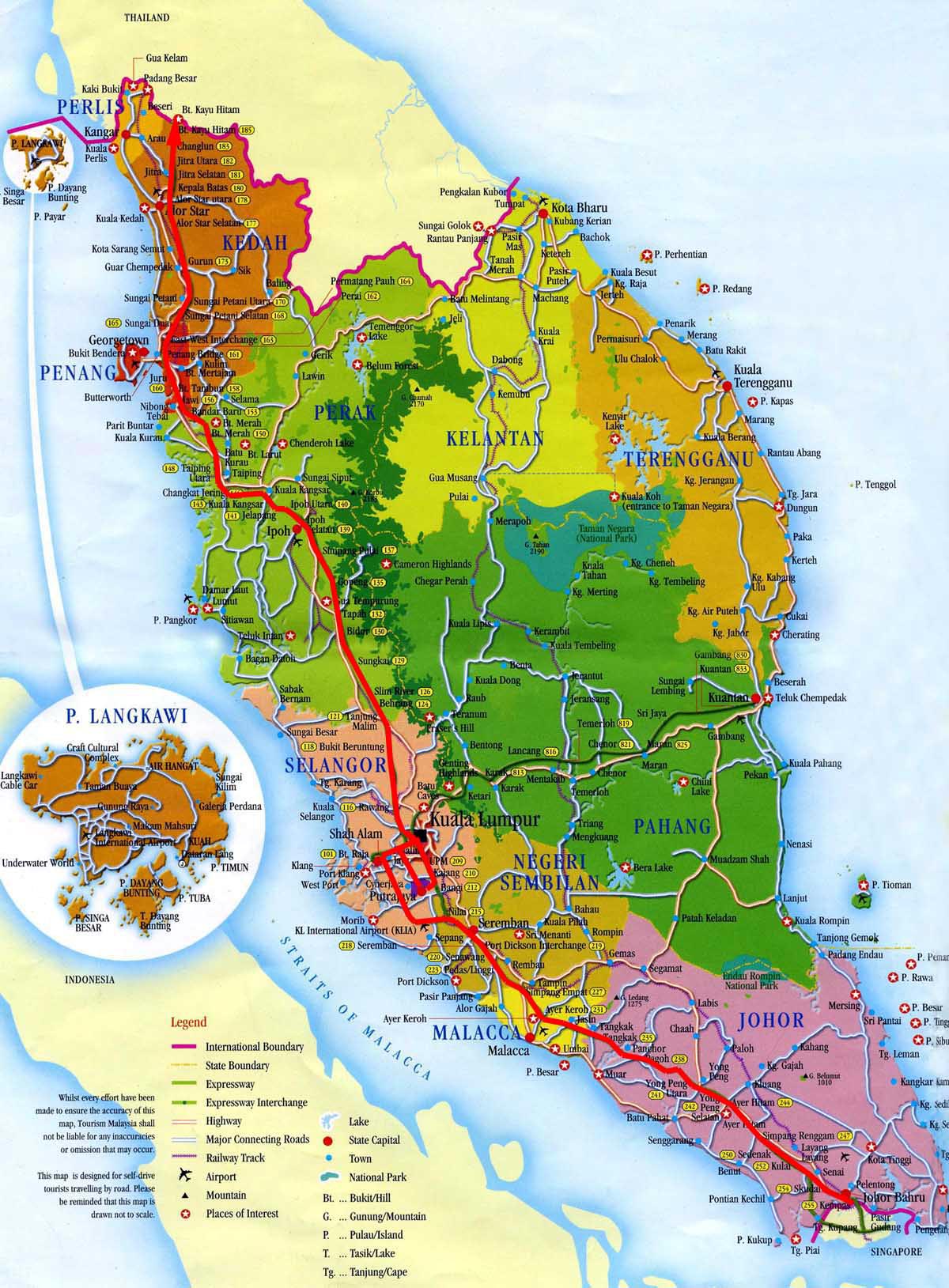
The maps of Malaysia and Singapore, two Southeast Asian nations sharing a rich history and vibrant present, offer a compelling glimpse into their diverse landscapes, bustling cities, and strategic geographic positions. Understanding these maps is crucial for appreciating the unique characteristics of each nation and the intricate web of connections that binds them.
Unveiling Malaysia’s Geographic Tapestry
Malaysia, a nation of diverse landscapes and vibrant cultures, sprawls across the Malay Peninsula and the northern portion of the island of Borneo. Its map reveals a fascinating tapestry of geographical features:
- Peninsular Malaysia: This region, connected to mainland Southeast Asia, is dominated by the mountainous spine of the Titiwangsa Range, which runs parallel to the west coast. Rolling hills, fertile plains, and extensive coastal areas characterize this region. The west coast is home to major cities like Kuala Lumpur, the capital, and Malacca, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The east coast boasts pristine beaches and verdant rainforests.
- East Malaysia (Sabah and Sarawak): Situated on the island of Borneo, these states are renowned for their vast rainforests, towering mountains, and diverse wildlife. The island’s interior is dominated by the rugged Crocker Range, while the coastal areas offer stunning beaches and coral reefs.
Singapore: A City-State Defined by its Location
Singapore, a city-state nestled at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, boasts a unique geographical identity. Its map reveals a compact island nation, strategically located at the crossroads of major shipping routes.
- Island Geography: Singapore’s landscape is defined by its small size and diverse terrain. The island’s central region is characterized by gentle hills, while its coastal areas are dominated by reclaimed land and harbors. The island’s proximity to Malaysia and Indonesia makes it a vital hub for trade and transportation.
Understanding the Shared History and Connections
The maps of Malaysia and Singapore are not merely geographical representations; they are also powerful narratives of shared history and interconnectedness.
- Colonial Legacy: Both nations were once under British rule, leaving a lasting impact on their political systems, legal frameworks, and infrastructure. The maps reflect this shared colonial past, with many cities and towns bearing names reflecting their British origins.
- Economic Interdependence: Singapore’s strategic location and robust infrastructure have made it a vital trading partner for Malaysia. The maps highlight the flow of goods, services, and people between these two nations, underscoring their economic interdependence.
Navigating the Maps: Key Points of Interest
Malaysia:
- Kuala Lumpur: The capital city, a bustling metropolis with iconic landmarks like the Petronas Twin Towers and the Batu Caves.
- Malacca: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, renowned for its historic architecture, colonial buildings, and vibrant cultural scene.
- Penang: A popular tourist destination, known for its diverse cuisine, street art, and UNESCO-listed George Town.
- Sabah: A state in East Malaysia, famous for its Mount Kinabalu, the highest peak in Southeast Asia, and its diverse wildlife.
- Sarawak: Another state in East Malaysia, renowned for its vast rainforests, diverse indigenous cultures, and the iconic Mulu Caves.
Singapore:
- Singapore City: A global financial hub, home to iconic landmarks like the Marina Bay Sands and the Gardens by the Bay.
- Sentosa Island: A popular tourist destination, renowned for its beaches, theme parks, and entertainment venues.
- Changi Airport: A world-class airport, serving as a major hub for air travel in Southeast Asia.
- Jurong Bird Park: A world-renowned bird park, home to a vast collection of avian species.
- Singapore Botanic Gardens: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, renowned for its diverse flora and serene environment.
Understanding the Maps: Key Benefits
- Navigational Tool: The maps provide essential information for navigating these nations, aiding in planning travel routes, exploring key destinations, and understanding the layout of cities and towns.
- Historical Perspective: The maps offer a visual representation of the historical development of these nations, showcasing the evolution of their boundaries, cities, and infrastructure.
- Cultural Insight: The maps highlight the diverse cultural landscapes of Malaysia and Singapore, revealing the distribution of ethnic groups, languages, and religious communities.
- Economic Understanding: The maps provide insights into the economic activities and infrastructure of these nations, revealing major trade routes, industrial hubs, and transportation networks.
- Environmental Awareness: The maps illustrate the diverse ecosystems of Malaysia and Singapore, highlighting their natural resources, protected areas, and environmental challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
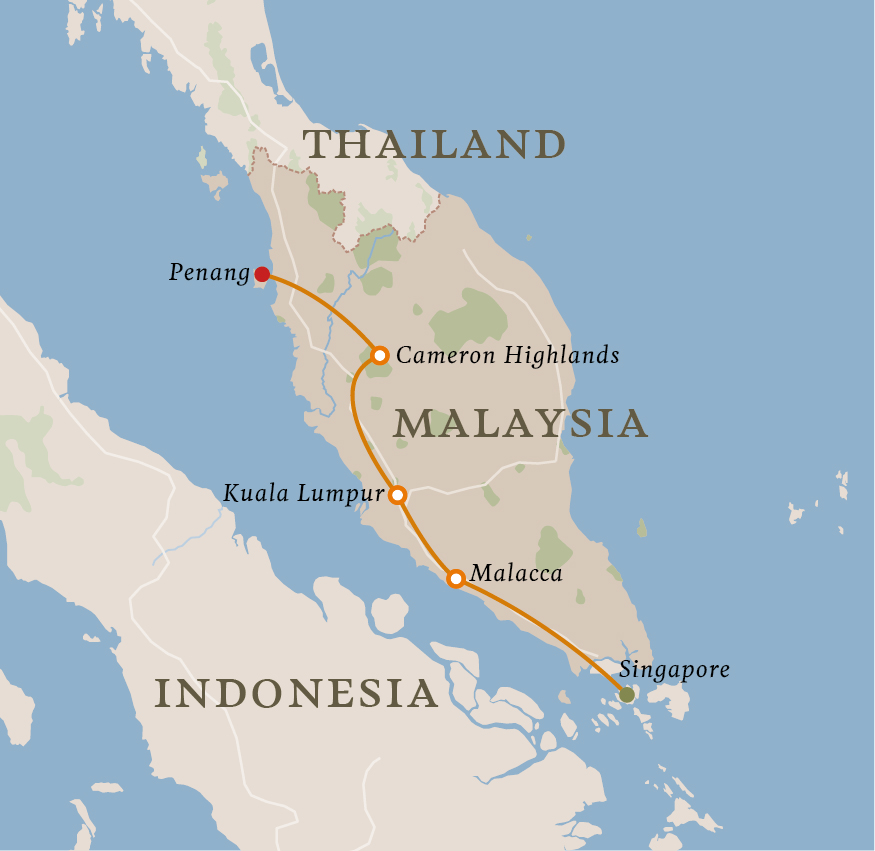
1. What is the distance between Kuala Lumpur and Singapore?
The distance between Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and Singapore is approximately 350 kilometers (217 miles).
2. What are the major languages spoken in Malaysia and Singapore?
The official language of Malaysia is Bahasa Melayu, while English is widely spoken. In Singapore, the official languages are English, Mandarin, Malay, and Tamil.
3. What are the major religions practiced in Malaysia and Singapore?
Islam is the dominant religion in Malaysia, while Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, and Sikhism are also practiced. In Singapore, the major religions include Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Taoism, and Sikhism.
4. What are the major industries in Malaysia and Singapore?
Malaysia’s economy is based on agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and mining. Singapore is a global financial hub, with strong sectors in manufacturing, tourism, and services.
5. What are the major environmental concerns in Malaysia and Singapore?
Deforestation, pollution, and climate change are major environmental concerns in both countries.
Tips for Navigating the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore
- Utilize online mapping tools: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap provide detailed maps, including street views, satellite imagery, and real-time traffic updates.
- Consult travel guides: Travel guides offer valuable information about key destinations, transportation options, and cultural insights.
- Engage with locals: Asking for directions and seeking advice from locals can enhance your understanding of the maps and provide valuable insights.
- Learn basic phrases: Knowing a few basic phrases in the local language can be helpful when navigating and interacting with locals.
- Respect local customs: Familiarize yourself with local customs and etiquette to ensure a respectful and enjoyable experience.
Conclusion
The maps of Malaysia and Singapore are more than just geographical representations; they are windows into the vibrant cultures, diverse landscapes, and shared history of these two nations. By understanding these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique characteristics of each nation and the intricate web of connections that binds them. As we continue to explore the dynamic landscapes of Malaysia and Singapore, these maps will serve as invaluable guides, offering a glimpse into the past, present, and future of these captivating nations.




/map-singapore-56a040775f9b58eba4af8962.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Guide to the Maps of Malaysia and Singapore. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!