Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Mapping
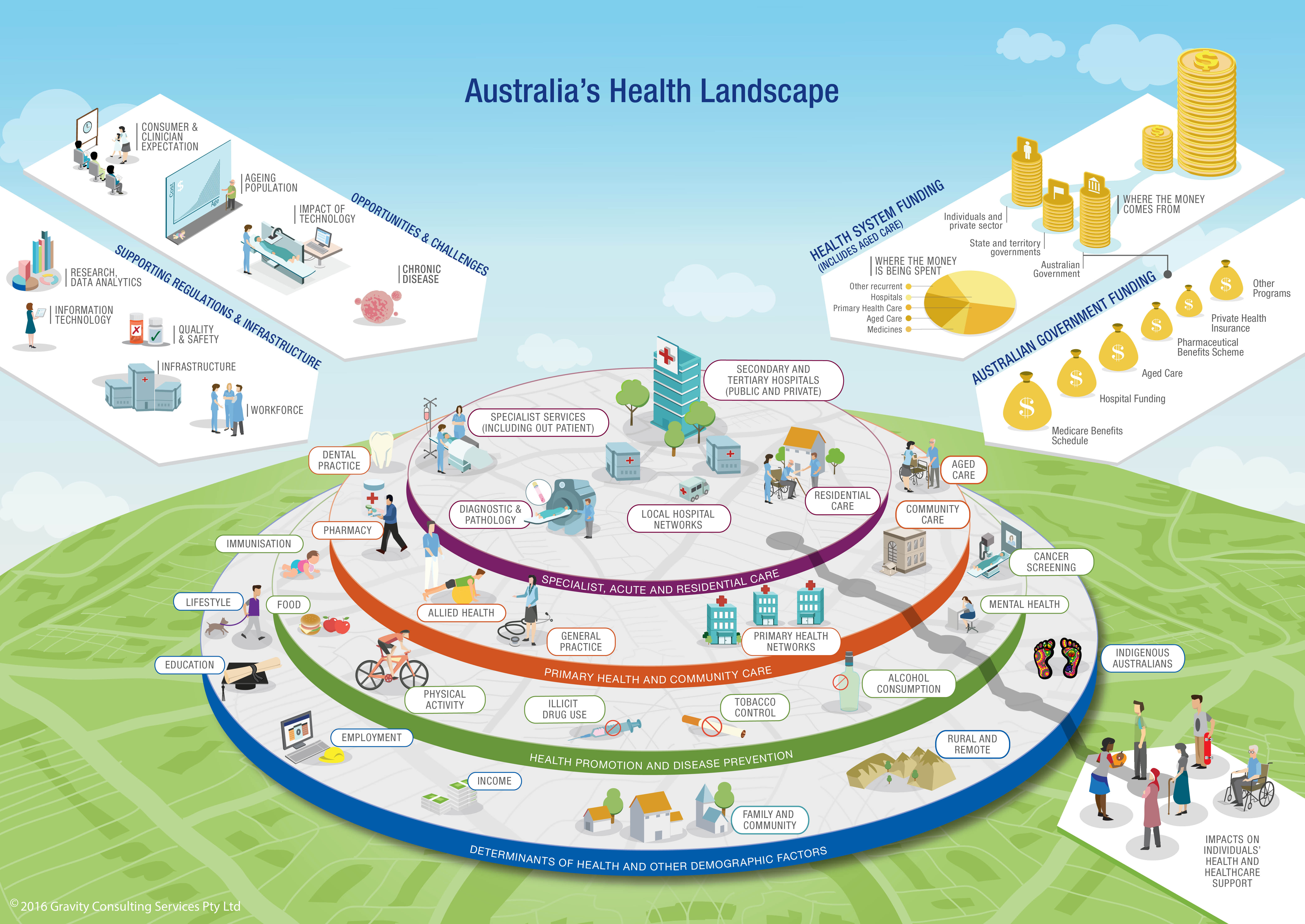
The healthcare industry is a complex ecosystem, characterized by intricate networks of providers, facilities, and services. This complexity can pose significant challenges for patients, healthcare professionals, and organizations alike. Navigating this landscape effectively requires a clear understanding of its various components and their interrelationships. This is where medical mapping comes into play, offering a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing healthcare data, ultimately leading to improved decision-making and enhanced patient care.
Understanding the Essence of Medical Mapping
Medical mapping, also known as healthcare mapping, is a data visualization technique that employs geographical information systems (GIS) to represent and analyze healthcare data spatially. This approach goes beyond simple data aggregation, providing a visual representation of the distribution, accessibility, and utilization of healthcare resources across a defined geographic area.
Key Components of Medical Mapping:
-
Data Collection: The foundation of any medical mapping project lies in the collection of relevant healthcare data. This data can encompass a wide range of information, including:
- Provider Locations: Mapping the distribution of hospitals, clinics, physicians, and other healthcare providers.
- Patient Demographics: Visualizing the distribution of patient populations based on age, gender, socioeconomic status, and other factors.
- Healthcare Utilization: Analyzing patterns of healthcare service utilization, such as hospital admissions, emergency room visits, and outpatient appointments.
- Health Outcomes: Tracking and mapping health outcomes, such as mortality rates, disease prevalence, and vaccination coverage.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Mapping the availability of healthcare facilities, equipment, and resources.
- GIS Technology: Medical mapping relies heavily on GIS software, which allows for the spatial representation and analysis of collected data. This software enables the creation of interactive maps, incorporating various layers of information and facilitating data exploration.
-
Data Visualization: Medical mapping utilizes various visualization techniques to present the collected data in a clear and concise manner. This includes:
- Point Maps: Representing healthcare facilities, providers, or patient locations as points on a map.
- Choropleth Maps: Using color gradients to depict variations in healthcare data across geographic regions.
- Thematic Maps: Highlighting specific features of interest, such as areas with high disease prevalence or limited access to healthcare services.
- Network Maps: Visualizing the interconnectedness of healthcare providers and facilities, demonstrating referral patterns and service pathways.
Benefits of Medical Mapping for Healthcare Stakeholders:
Medical mapping offers a wealth of benefits for various stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem:
1. Improved Patient Care:
- Enhanced Access to Care: Medical mapping helps identify areas with limited access to healthcare services, facilitating the development of strategies to improve service availability and reach underserved populations.
- Targeted Interventions: By visualizing health outcomes and disease prevalence, medical mapping enables healthcare providers to tailor interventions and resources to specific geographic areas with the greatest need.
- Personalized Care: Medical mapping can support the development of personalized care plans by providing insights into patient demographics, disease patterns, and access to healthcare services within their specific geographic context.
2. Optimized Healthcare Operations:
- Strategic Planning: Medical mapping aids in planning for future healthcare needs, identifying areas with potential resource shortages or service gaps, and guiding the allocation of resources effectively.
- Resource Allocation: By visualizing the distribution of healthcare resources, medical mapping facilitates informed decisions regarding the allocation of personnel, equipment, and funding to areas with the greatest need.
- Quality Improvement: Medical mapping can be used to track and monitor healthcare quality indicators, identifying areas requiring improvement and implementing targeted interventions.
3. Enhanced Research and Policy Development:
- Disease Surveillance: Medical mapping facilitates the tracking and analysis of disease outbreaks, enabling public health officials to monitor disease trends, identify potential hotspots, and implement timely interventions.
- Health Equity Analysis: By visualizing health disparities across different geographic regions, medical mapping contributes to the development of policies and programs aimed at promoting health equity and reducing disparities in access to healthcare.
- Health Impact Assessment: Medical mapping allows for the assessment of the potential health impacts of various policy decisions, such as infrastructure development, environmental regulations, or economic policies.
Applications of Medical Mapping in Healthcare:
Medical mapping has a wide range of applications in various healthcare settings, including:
- Public Health: Disease surveillance, health equity analysis, health impact assessment, and the planning and implementation of public health programs.
- Hospital Administration: Resource allocation, capacity planning, patient flow optimization, and quality improvement initiatives.
- Primary Care: Identifying underserved communities, optimizing clinic locations, and tailoring care plans to specific patient populations.
- Emergency Medical Services: Optimizing ambulance response times, identifying areas with limited access to emergency care, and planning for disaster response.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Targeting drug development and marketing efforts to specific geographic areas with high disease prevalence.
FAQs About Medical Mapping:
1. What data is used in medical mapping?
Medical mapping utilizes a wide range of healthcare data, including patient demographics, provider locations, healthcare utilization patterns, health outcomes, and infrastructure data. The specific data sources vary depending on the intended use of the mapping project.
2. What software is used for medical mapping?
Medical mapping relies on GIS software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Pro. These software packages provide tools for data visualization, analysis, and map creation.
3. How is medical mapping used to improve patient care?
Medical mapping helps identify areas with limited access to healthcare services, enabling the development of strategies to improve service availability and reach underserved populations. It also facilitates the tailoring of interventions and resources to specific geographic areas with the greatest need.
4. What are the limitations of medical mapping?
While medical mapping offers significant benefits, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations. Data quality and availability can be a challenge, and the interpretation of results requires careful consideration of potential biases.
5. What are the future trends in medical mapping?
Medical mapping is evolving rapidly, incorporating advancements in data analytics, artificial intelligence, and mobile technology. Future trends include the integration of real-time data, predictive modeling, and personalized health insights.
Tips for Effective Medical Mapping:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the purpose and goals of the mapping project to ensure relevant data collection and analysis.
- Ensure Data Quality: Utilize reliable and accurate data sources to maintain the validity of the mapping results.
- Choose Appropriate Visualization Techniques: Select visualization methods that effectively communicate the intended message and cater to the target audience.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engage with healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community members to ensure the mapping project aligns with local needs and priorities.
- Disseminate Findings Effectively: Communicate the results of the mapping project in a clear and concise manner, utilizing interactive maps, reports, and presentations.
Conclusion:
Medical mapping is a powerful tool that empowers healthcare stakeholders to visualize and analyze healthcare data spatially, leading to improved decision-making and enhanced patient care. By leveraging the capabilities of GIS technology, medical mapping facilitates the identification of healthcare needs, the allocation of resources, and the development of targeted interventions. As technology continues to advance, medical mapping is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery.




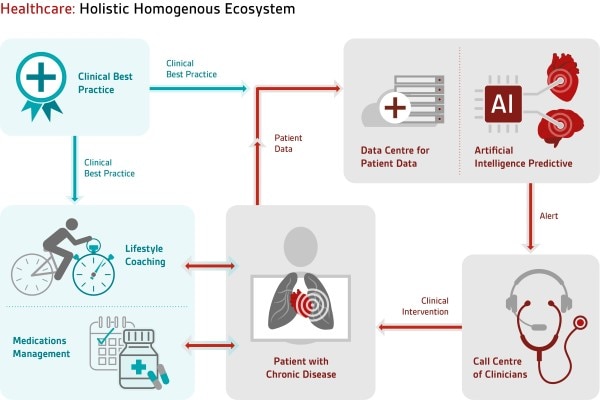


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!