Navigating the Ideal: A Deep Dive into Utopia Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Ideal: A Deep Dive into Utopia Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Ideal: A Deep Dive into Utopia Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Ideal: A Deep Dive into Utopia Maps
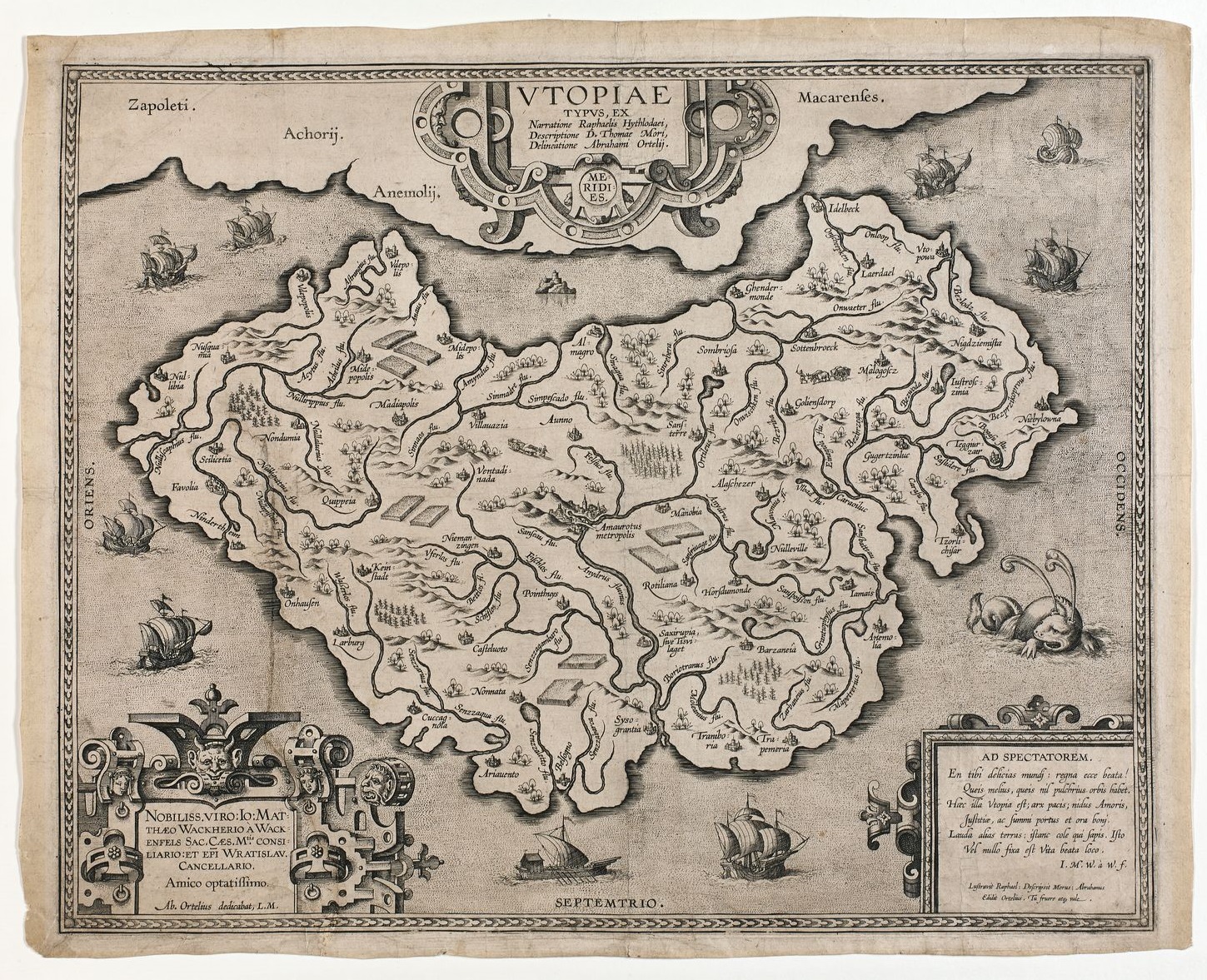
The concept of utopia, a perfect society free from hardship and strife, has captivated the human imagination for centuries. While the actual realization of such a society remains elusive, the pursuit of a better world continues to inspire thinkers, artists, and social reformers. Utopia maps, a fascinating and often overlooked aspect of this pursuit, offer a unique lens through which to understand the evolution of utopian thought and its potential impact on the real world.
Understanding Utopia Maps: A Visual Representation of Ideal Societies
Utopia maps are visual representations of imagined perfect societies. They serve as blueprints for ideal social structures, often incorporating elements of geography, architecture, social organization, and even individual lives. These maps can take various forms, from detailed architectural plans to symbolic representations of social hierarchies and political systems.
Historical Context and Evolution of Utopia Maps
The history of utopia maps is intertwined with the evolution of utopian thought itself. Early examples can be traced back to ancient Greek philosophers like Plato, who envisioned a "Republic" based on social harmony and justice. Medieval and Renaissance thinkers, inspired by Plato and other classical sources, further developed the idea of utopia, often incorporating religious and spiritual elements into their imagined societies.
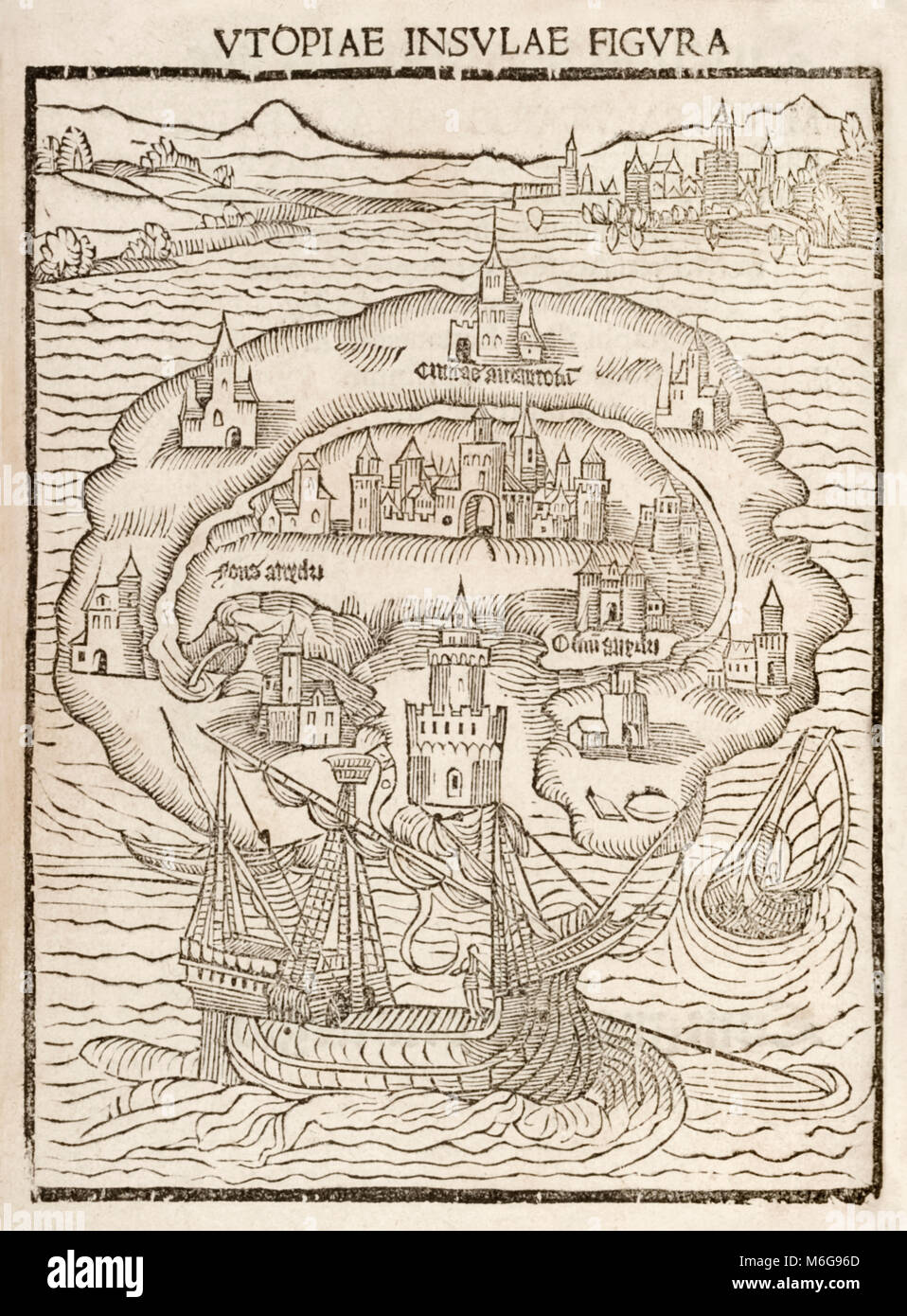
The 16th century witnessed the emergence of influential utopian texts like Thomas More’s "Utopia," which depicted a fictional island society with communal living, egalitarian principles, and a focus on education and public welfare. This period saw a surge in the creation of detailed utopia maps, often accompanying these literary works and providing visual interpretations of the imagined societies.
Key Elements of Utopia Maps
Utopia maps typically incorporate several key elements, reflecting the underlying principles and values of the imagined society:
- Geography and Landscape: The physical environment of the utopian society is often depicted as idyllic, with fertile lands, abundant resources, and a harmonious balance between nature and human civilization.
- Architecture and Urban Planning: Utopian cities are often designed with a focus on functionality, efficiency, and aesthetic harmony. They may incorporate innovative architectural designs, communal spaces, and sustainable living practices.
- Social Organization and Hierarchy: Utopia maps often illustrate the social structure of the imagined society, highlighting its principles of equality, cooperation, and shared governance.
- Economic Systems: Utopian societies often envision equitable economic systems, with shared resources, fair distribution of wealth, and an emphasis on collective prosperity.
- Education and Culture: Education and cultural development are frequently emphasized in utopia maps, reflecting a belief in the transformative power of knowledge and the arts.
The Significance of Utopia Maps
Utopia maps are not simply whimsical exercises in imagination. They serve several important purposes:
- Conceptualization of Ideal Societies: Utopia maps provide a tangible framework for visualizing and understanding the principles and values of a perfect society. They allow us to consider how different social, economic, and political structures might interact and influence the lives of individuals within a utopian context.
- Critique of Existing Societies: Utopia maps can act as critiques of existing social injustices and inequalities. By presenting a contrasting vision of a better world, they highlight the shortcomings of present-day societies and inspire efforts to address them.
- Inspiration for Social Change: Utopia maps can serve as sources of inspiration for social reformers and activists. By offering a vision of a more just and equitable world, they encourage individuals and communities to strive for positive change.
- Historical and Cultural Insight: Utopia maps offer valuable insights into the historical and cultural contexts in which they were created. They reflect the prevailing social, political, and philosophical ideas of their time and provide a window into the hopes and aspirations of past generations.
Examples of Notable Utopia Maps
Throughout history, numerous individuals and groups have created utopia maps, each reflecting their unique visions of a better world. Here are a few notable examples:
- The Republic by Plato: While not a map in the literal sense, Plato’s "Republic" outlines a philosophical framework for a just society, based on the division of labor, social harmony, and the pursuit of virtue.
- The City of the Sun by Tommaso Campanella: This 17th-century utopian text depicts a solar-powered city with communal living, a focus on education, and a system of governance based on reason and virtue.
- The New Atlantis by Francis Bacon: This 17th-century utopian novel describes a fictional island society known for its scientific advancements, technological innovations, and emphasis on knowledge and progress.
- The Garden City Movement: This early 20th-century movement advocated for the creation of self-sufficient, planned communities designed to promote social cohesion and environmental sustainability.
Utopia Maps in the 21st Century: Modern Interpretations and Applications
The concept of utopia continues to inspire and provoke in the 21st century. Modern interpretations of utopia maps often incorporate contemporary concerns, including:
- Sustainable Development: Utopia maps may focus on environmental sustainability, incorporating renewable energy sources, green infrastructure, and sustainable living practices.
- Technological Advancements: Modern utopia maps may explore the potential impact of emerging technologies on society, such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology.
- Social Justice and Equality: Utopia maps continue to address issues of social justice and equality, advocating for greater inclusivity, diversity, and equitable access to resources.
FAQs about Utopia Maps
1. Are utopia maps purely fictional?
While utopia maps often depict fictional societies, they are not merely flights of fancy. They are rooted in real-world concerns and reflect the aspirations and ideals of their creators.
2. What is the purpose of creating utopia maps?
Utopia maps serve as a tool for imagining, visualizing, and critiquing existing social structures. They offer a vision of a better world, inspiring efforts towards positive change.
3. Can utopia maps be used to guide real-world planning?
While utopia maps are not blueprints for immediate implementation, they can provide inspiration for urban planning, social policy, and sustainable development. They can help us envision more equitable and sustainable societies.
4. What are the limitations of utopia maps?
Utopia maps are inherently idealistic and may fail to account for the complexities and challenges of real-world societies. They can also be susceptible to bias and reflect the values and perspectives of their creators.
5. Are utopia maps relevant in the 21st century?
Utopia maps remain relevant in the 21st century as they provide a framework for envisioning a more just and sustainable future. They help us grapple with contemporary challenges and inspire efforts towards positive change.
Tips for Understanding and Creating Utopia Maps
- Consider the Context: When analyzing utopia maps, it is crucial to understand the historical and cultural context in which they were created. This will provide insights into the motivations, values, and concerns of their creators.
- Identify Key Elements: Pay attention to the key elements of the utopia map, such as geography, architecture, social organization, and economic systems. These elements reveal the underlying principles and values of the imagined society.
- Analyze the Critique: Utopia maps often offer a critique of existing social structures and inequalities. Consider how the map highlights these issues and what it suggests as potential solutions.
- Explore the Potential Impact: Think about the potential impact of the utopia map on real-world societies. What aspects of the imagined society could be adapted or implemented in the present day?
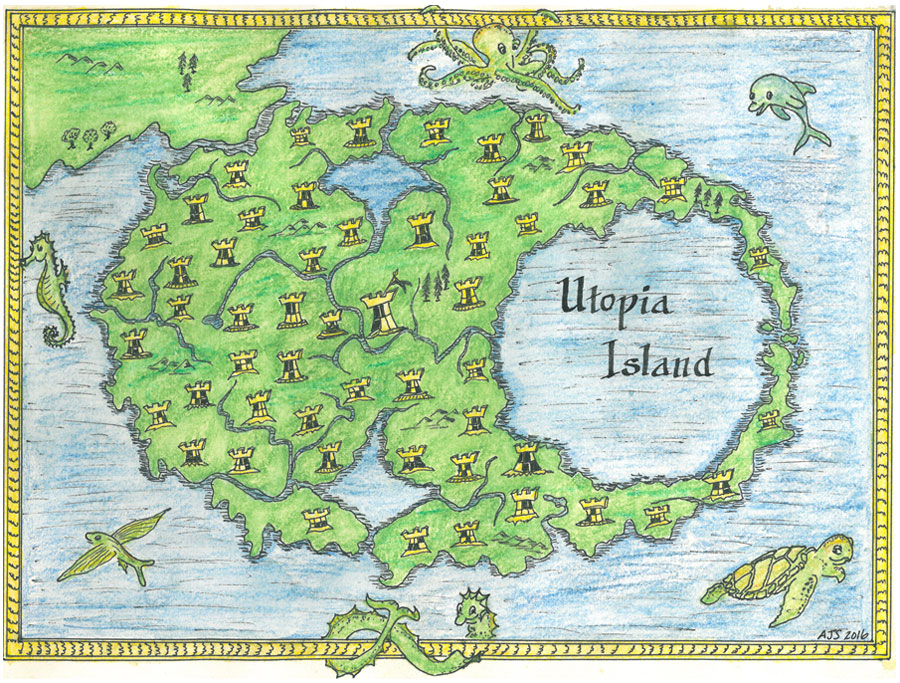
- Create Your Own Vision: Engage in the process of creating your own utopia map. This exercise can be a powerful tool for reflection, critical thinking, and envisioning a better world.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Utopia Maps
Utopia maps are more than just whimsical drawings. They are powerful tools for envisioning, critiquing, and inspiring change. By exploring the history, elements, and significance of these maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of the enduring pursuit of a better world and the potential impact of utopian thought on our present and future. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, utopia maps offer a valuable lens through which to consider the possibilities for a more just, equitable, and sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Ideal: A Deep Dive into Utopia Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!