Navigating the Indian Subcontinent: A Comprehensive Guide to India’s Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Indian Subcontinent: A Comprehensive Guide to India’s Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Indian Subcontinent: A Comprehensive Guide to India’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Indian Subcontinent: A Comprehensive Guide to India’s Geography
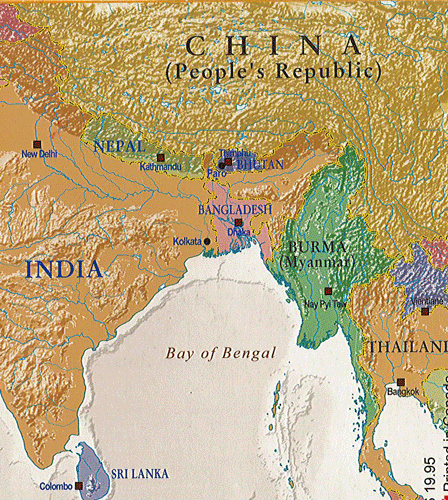
India, a land of diverse landscapes, rich culture, and vibrant history, occupies a strategically significant position on the world map. Understanding its geographical location is crucial for appreciating its unique characteristics and the profound impact it has on its people, environment, and global affairs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of India’s location, exploring its physical features, geopolitical significance, and the diverse ecosystems it encompasses.
A Land of Contrasts: India’s Geographical Boundaries
India’s geographical location is a testament to its multifaceted nature. Situated in South Asia, it occupies a vast peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. Its physical boundaries encompass:
- North: The majestic Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, act as a natural barrier, separating India from China, Nepal, Bhutan, and Pakistan.
- West: The Arabian Sea, along with the narrow land border with Pakistan, defines the western frontier.
- East: The Bay of Bengal and the shared border with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands mark the eastern edge.
- South: The Indian Ocean, encompassing the Lakshadweep Islands, forms the southern boundary.
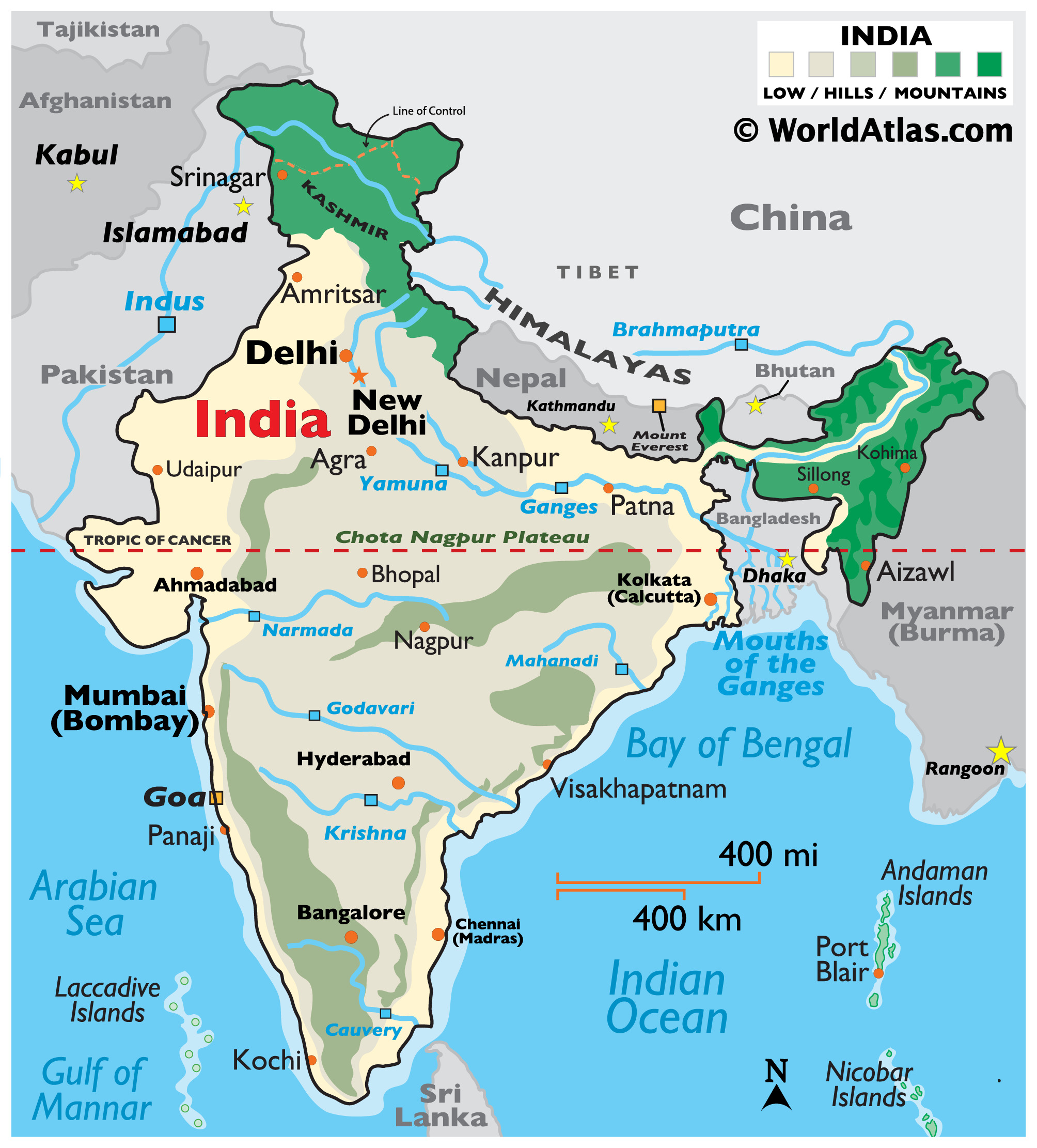
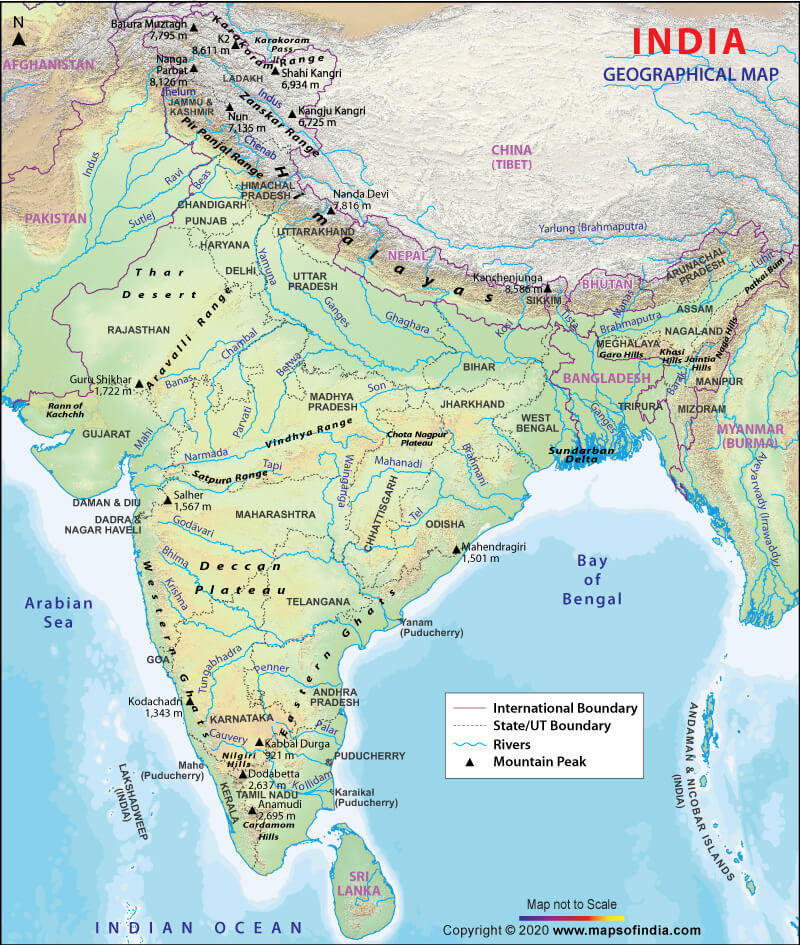
A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring India’s Diverse Landscapes
India’s geographical location is a catalyst for its extraordinary diversity. Its vast expanse encompasses a wide range of terrains, from the towering Himalayan peaks to the fertile plains of the Ganges River, and from the arid deserts of Rajasthan to the lush green landscapes of Kerala.
- The Himalayas: The mighty Himalayas, a defining feature of India’s northern landscape, play a crucial role in shaping the country’s climate and influencing its rivers. These snow-capped peaks are home to glaciers that feed vital river systems, and they act as a natural barrier, protecting India from cold winds from the north.
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain: The fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain, stretching across northern India, is a cradle of civilization, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting a dense population. The region is fed by major rivers like the Ganges, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra, which have nurtured civilizations for centuries.
- The Deccan Plateau: The Deccan Plateau, a massive triangular plateau located in the south, is characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and ancient rock formations. The plateau’s unique geological structure influences the region’s climate and contributes to its diverse flora and fauna.
- The Coastal Plains: India’s extensive coastline, stretching along the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, features diverse coastal plains, including the Konkan Coast, Coromandel Coast, and Malabar Coast. These coastal regions are home to a rich marine ecosystem, bustling port cities, and vibrant coastal communities.
- The Islands: India’s geographical location extends beyond the mainland, encompassing the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea. These islands are home to unique ecosystems, diverse flora and fauna, and rich cultural traditions.
Geopolitical Significance: India’s Strategic Location
India’s geographical location has played a pivotal role in its history and continues to shape its geopolitical landscape. Its strategic position at the crossroads of Asia and the Indian Ocean makes it a key player in global affairs.
- The Indian Ocean Rim: India’s location on the Indian Ocean rim gives it a strategic advantage in maritime trade and naval power. The Indian Ocean is a vital waterway for global commerce, and India’s position allows it to influence trade routes, secure its maritime interests, and contribute to regional stability.
- The Silk Road: Historically, India’s location facilitated trade along the Silk Road, connecting it to the East and the West. This ancient trade route played a crucial role in cultural exchange and economic development, contributing to the growth of civilizations in the region.
- The Land Bridge: India’s land borders with neighboring countries, including Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, make it a crucial land bridge connecting South Asia to Central Asia and beyond. This strategic location has both advantages and challenges, as it requires India to manage complex relationships with its neighbors.
A Diverse Ecosystem: India’s Unique Flora and Fauna
India’s geographical location and diverse terrain have resulted in a rich and varied ecosystem, home to a wide range of flora and fauna. The country’s unique biodiversity is a testament to its geographical diversity and its role as a global biodiversity hotspot.
- The Himalayas: The Himalayas are home to a unique alpine ecosystem, featuring high-altitude forests, glaciers, and snow-capped peaks. The region is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including rare and endangered species like the snow leopard, the Himalayan musk deer, and the red panda.
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain: The fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain supports a rich agricultural ecosystem, with diverse crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane. The region is also home to a wide variety of birds, mammals, and reptiles, including the Indian rhinoceros, the Bengal tiger, and the Indian peacock.
- The Deccan Plateau: The Deccan Plateau is characterized by dry deciduous forests, scrublands, and grasslands. The region is home to a unique array of flora and fauna, including the Indian wild dog, the sloth bear, and the Indian pangolin.
- The Coastal Plains: India’s coastal plains are home to a rich marine ecosystem, with diverse coral reefs, mangrove forests, and seagrass beds. The region is also home to a variety of marine species, including whales, dolphins, turtles, and sharks.
- The Islands: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands are home to unique ecosystems, with diverse flora and fauna adapted to their island environments. These islands are particularly important for their marine biodiversity, with a variety of coral reefs, sea turtles, and marine mammals.
FAQs on India’s Geographical Location
Q: What are the major geographical features of India?
A: India’s major geographical features include the Himalayas, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Deccan Plateau, the coastal plains, and the islands.
Q: What is the significance of the Himalayas for India?
A: The Himalayas act as a natural barrier, protecting India from cold winds from the north and influencing the country’s climate and river systems.
Q: What is the significance of the Indo-Gangetic Plain for India?
A: The Indo-Gangetic Plain is a cradle of civilization, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting a dense population.
Q: What is the significance of the Deccan Plateau for India?
A: The Deccan Plateau is a massive triangular plateau that influences the region’s climate and contributes to its diverse flora and fauna.
Q: What is the significance of the coastal plains for India?
A: India’s coastal plains are home to a rich marine ecosystem, bustling port cities, and vibrant coastal communities.
Q: What is the significance of the islands for India?
A: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands are home to unique ecosystems, diverse flora and fauna, and rich cultural traditions.
Tips for Understanding India’s Geographical Location
- Use a map: A detailed map of India is an invaluable tool for understanding its geographical location.
- Explore online resources: Websites and online resources provide comprehensive information on India’s geography, including detailed maps, satellite images, and interactive features.
- Read books and articles: Books and articles on Indian geography offer insightful perspectives on the country’s diverse landscapes, ecosystems, and cultural heritage.
- Travel to India: Experiencing India firsthand provides a unique perspective on its geographical location and its diverse cultural landscape.
Conclusion: India’s Geographical Significance
India’s geographical location is a defining factor in its identity, shaping its climate, environment, culture, and geopolitical significance. From the majestic Himalayas to the fertile plains of the Ganges, from the arid deserts of Rajasthan to the lush green landscapes of Kerala, India’s diverse landscapes and ecosystems offer a glimpse into the country’s extraordinary beauty and cultural richness. Understanding India’s geographical location is essential for appreciating its unique characteristics and its profound impact on the world.
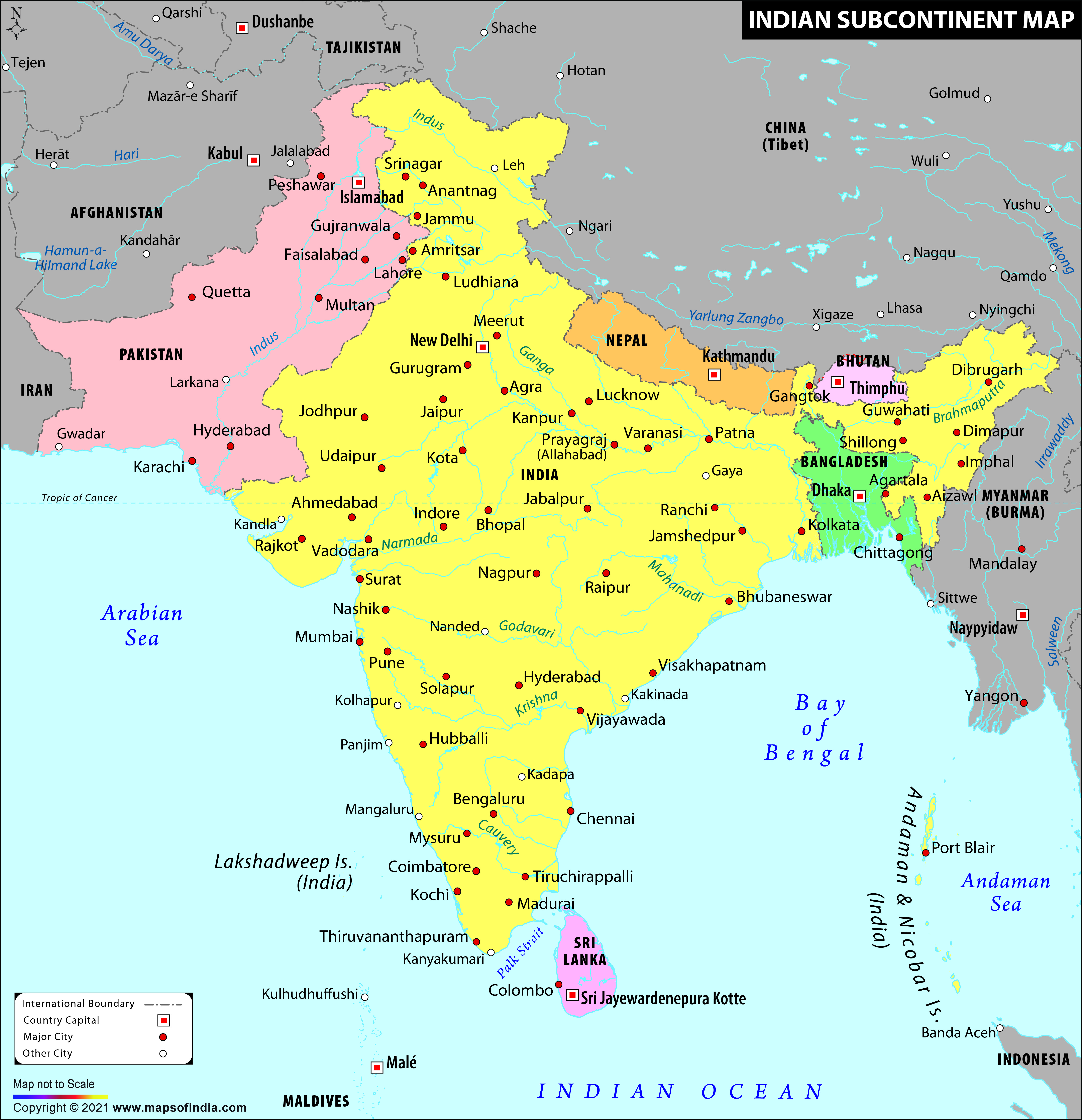
.svg/500px-Indian_Subcontinent_(orthographic_projection).svg.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Indian Subcontinent: A Comprehensive Guide to India’s Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!