Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Power of Grid Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Power of Grid Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Power of Grid Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Power of Grid Maps
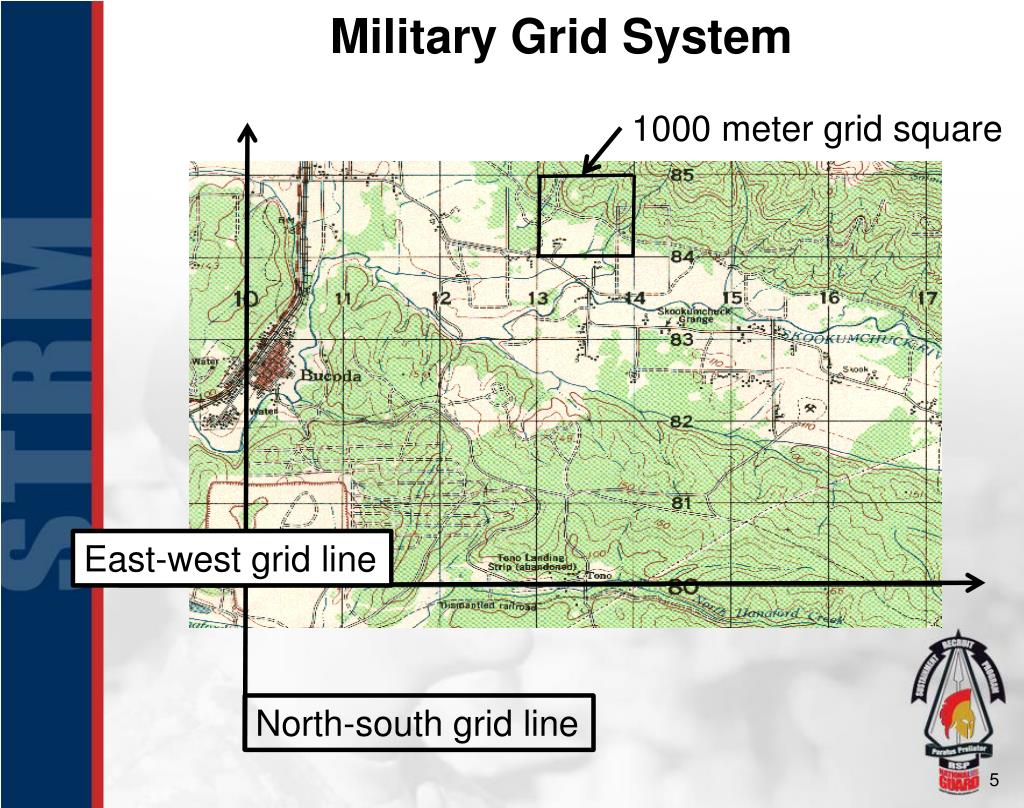
In a world driven by data and visualization, the ability to represent complex information in a clear and concise manner is paramount. Enter the grid map, a powerful tool that transforms data into actionable insights through a structured and visually compelling framework.
A Foundation of Structure and Clarity
At its core, a grid map is a visual representation of data organized into a rectangular grid, much like a spreadsheet. Each cell within the grid represents a specific data point, allowing for the analysis and comparison of information across different dimensions. This structured approach makes it easy to identify patterns, trends, and outliers, providing a comprehensive overview of the data.
Beyond Simple Tables: The Versatility of Grid Maps
While grid maps may appear similar to simple tables, their versatility extends far beyond basic data presentation. They can be employed in a multitude of contexts, including:
-
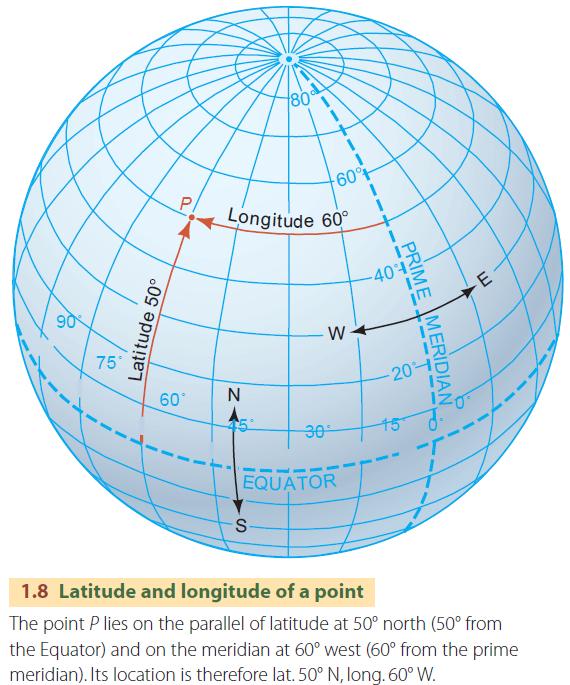
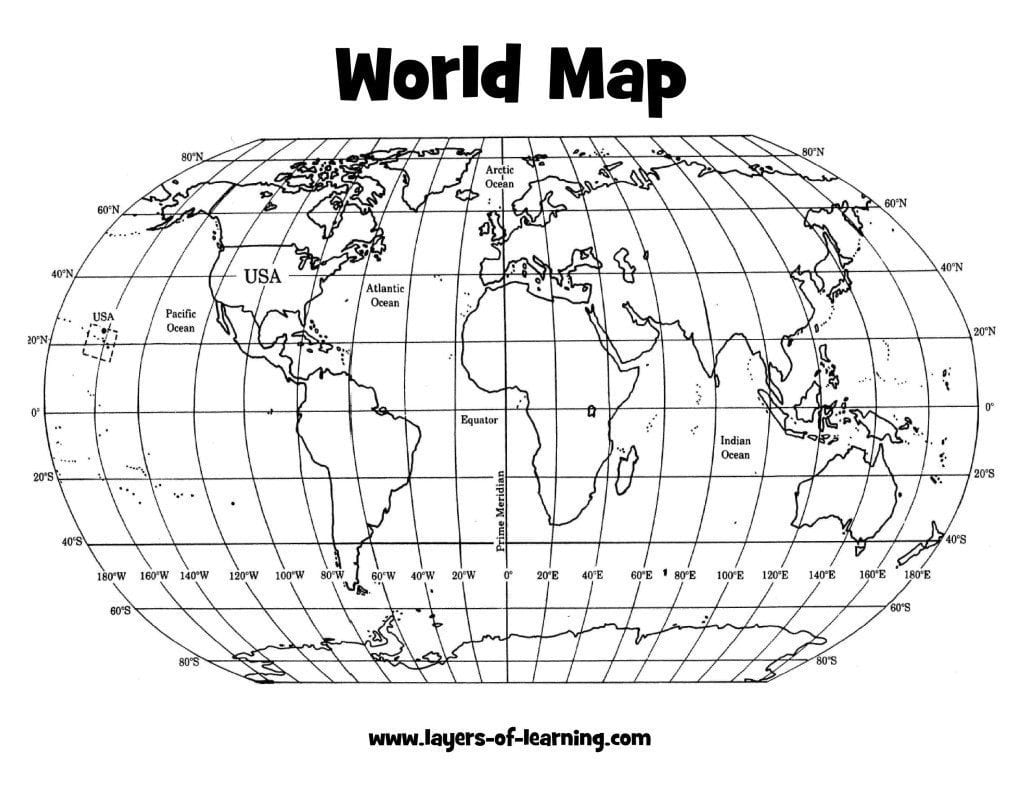
Geographic Mapping: Grid maps serve as the foundation for various geographical mapping techniques, enabling the visualization of spatial data. They allow for the representation of geographical features, population density, resource distribution, and other spatial phenomena.
-
Data Analysis: Grid maps facilitate data analysis by providing a clear visual representation of relationships between variables. They can be used to identify correlations, cluster data points, and reveal hidden patterns within datasets.
-
Project Management: Grid maps are invaluable tools for project management, allowing teams to track progress, allocate resources, and monitor task dependencies. They offer a visual roadmap for project execution, ensuring clarity and transparency throughout the process.
-
Decision-Making: Grid maps empower decision-making by providing a structured framework for evaluating options and assessing potential outcomes. By visualizing data and relationships, they facilitate informed choices and mitigate risks.
Benefits of Using Grid Maps
The widespread adoption of grid maps across diverse fields stems from their inherent benefits:
-
Enhanced Clarity: The structured grid format ensures clarity in data presentation, making complex information easily digestible and interpretable.
-
Data Visualization: Grid maps offer a visual representation of data, facilitating a deeper understanding of relationships, trends, and patterns.
-
Data Comparison: The grid structure enables the comparison of data points across different dimensions, highlighting similarities, differences, and outliers.
-
Data Exploration: Grid maps provide a framework for data exploration, allowing users to identify areas of interest and delve deeper into specific data points.
-
Communication: Grid maps serve as a powerful communication tool, effectively conveying complex information to a wider audience.
Types of Grid Maps
The versatility of grid maps extends to their numerous types, each tailored to specific applications and data characteristics:
-
Choropleth Maps: These maps use different shades or colors to represent varying data values within geographical regions, providing a visual representation of spatial data distribution.
-
Dot Density Maps: These maps utilize dots to represent data points, with the density of dots reflecting the magnitude of the data in a specific location.
-
Isopleth Maps: These maps use lines to connect points of equal value, creating contours that highlight the distribution of data across a geographical area.
-
Heat Maps: These maps use color gradients to represent data values, with hotter colors indicating higher values and cooler colors representing lower values.
-
Flow Maps: These maps use arrows to represent movement or flow of data, providing insights into direction, magnitude, and patterns of movement.
Applications of Grid Maps
The applications of grid maps are as diverse as the fields they serve:
-
Business Intelligence: Grid maps assist businesses in analyzing market trends, customer behavior, and sales performance, providing insights for strategic decision-making.
-
Healthcare: Grid maps are used in healthcare to track patient data, monitor disease outbreaks, and analyze medical records, supporting clinical decision-making and public health initiatives.
-
Urban Planning: Grid maps are essential for urban planning, enabling the visualization of population density, transportation networks, and infrastructure development, guiding urban development strategies.
-
Environmental Science: Grid maps are used to monitor environmental conditions, track pollution levels, and analyze climate change impacts, providing valuable data for environmental management and conservation efforts.
-
Social Sciences: Grid maps are employed in social sciences to analyze demographic data, study social trends, and map social inequalities, contributing to social research and policy development.
FAQs on Grid Maps
Q: What are the key advantages of using grid maps?
A: Grid maps offer several advantages, including enhanced clarity, data visualization, data comparison, data exploration, and improved communication.
Q: How can I create a grid map?
A: There are various software tools available for creating grid maps, including GIS software, spreadsheet programs, and data visualization tools.
Q: What are some common applications of grid maps?
A: Grid maps are widely used in business intelligence, healthcare, urban planning, environmental science, and social sciences.
Q: What are some different types of grid maps?
A: Common types of grid maps include choropleth maps, dot density maps, isopleth maps, heat maps, and flow maps.
Tips for Effective Grid Map Creation
- Choose the right type of grid map: Select the type of grid map that best suits the data and the intended message.
- Use clear and concise labels: Label axes, data points, and regions clearly to ensure easy interpretation.
- Employ appropriate colors and symbols: Use color schemes and symbols that are visually appealing and convey the data effectively.
- Maintain a consistent scale: Ensure that the scale of the grid map is consistent throughout, avoiding distortions and misinterpretations.
- Include a legend: Provide a legend to explain the meaning of colors, symbols, and other visual elements used in the grid map.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information; prioritize clarity and focus.
Conclusion
Grid maps are a powerful tool for data visualization and analysis, providing a structured and visually compelling framework for understanding complex information. Their versatility, clarity, and ease of interpretation make them indispensable across diverse fields, from business intelligence to healthcare and environmental science. By harnessing the power of grid maps, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and drive progress in their respective domains.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Understanding the Power of Grid Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!