Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps
- 3.1 The Power of Visual Representation: Deciphering Wind Gust Maps
- 3.2 Applications of Wind Gust Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.3 The Science Behind the Forecast: Unraveling the Complexity
- 3.4 Limitations and Considerations: Ensuring Accuracy
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Gust Maps
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps

Wind, a fundamental force of nature, plays a significant role in shaping our world. From influencing weather patterns to powering renewable energy sources, its impact is undeniable. However, wind is not a constant force; it exhibits variability in both speed and direction, often characterized by sudden bursts known as gusts. These gusts can pose significant risks, particularly for activities like aviation, sailing, and outdoor events. To better understand and predict these powerful wind fluctuations, specialized tools like wind gust maps have become invaluable resources.
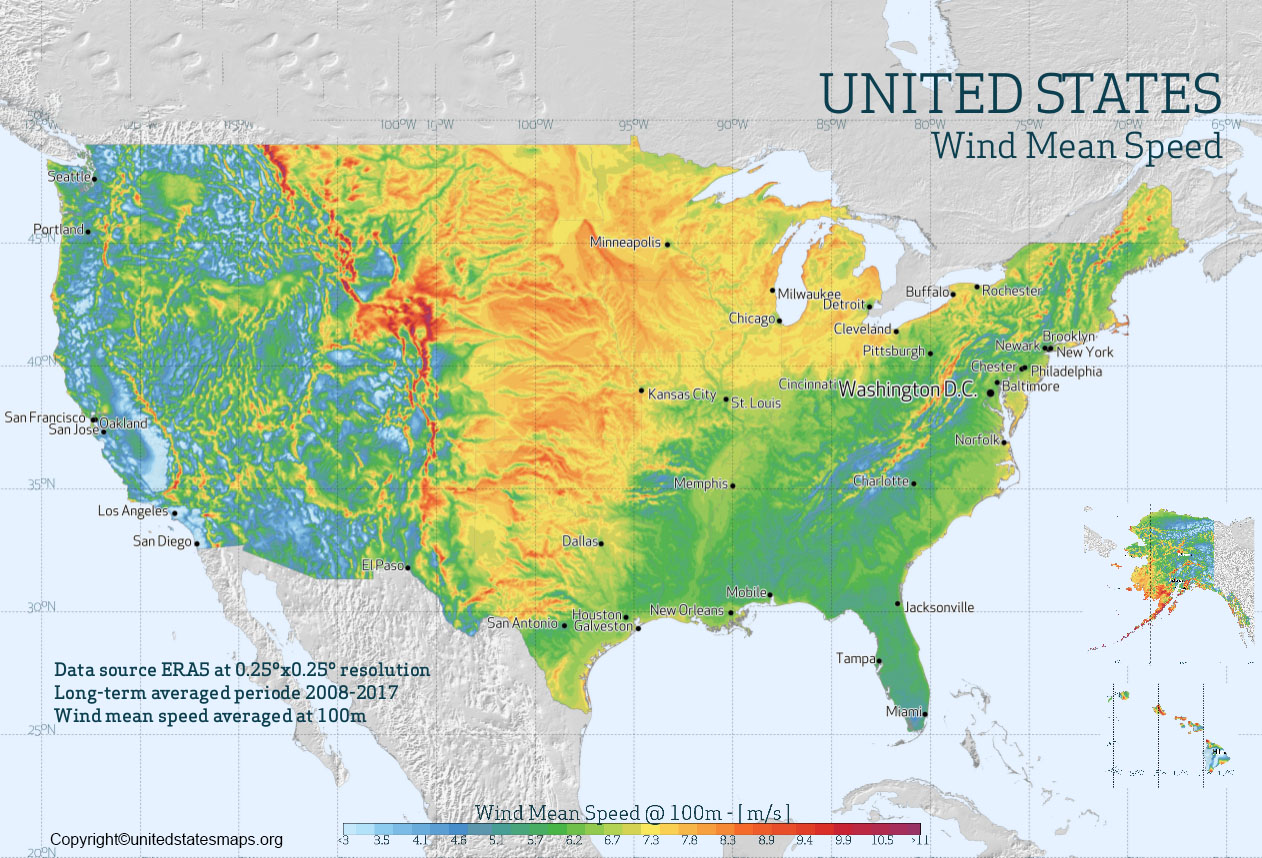
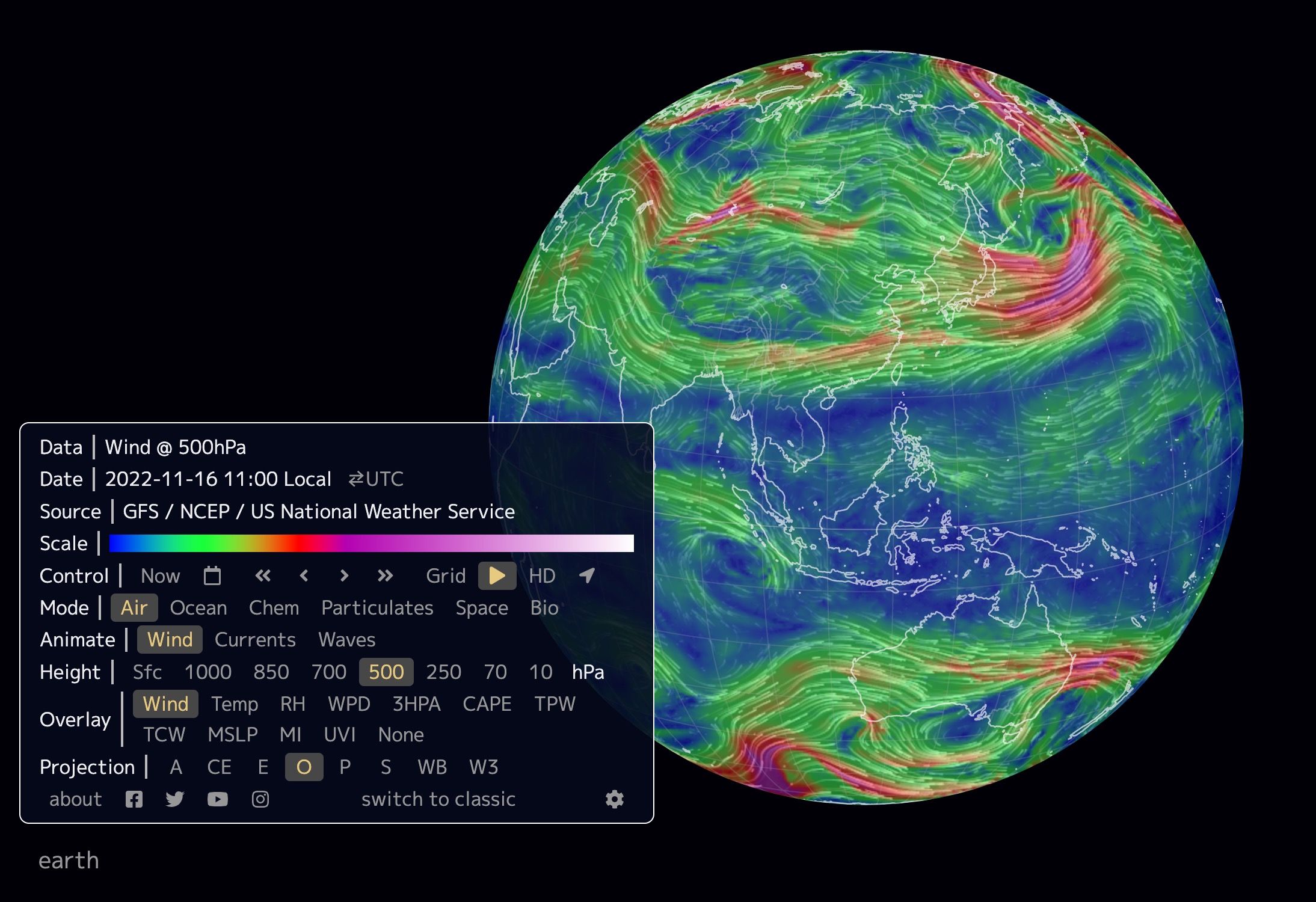
The Power of Visual Representation: Deciphering Wind Gust Maps
A wind gust map is a visual representation of predicted wind gusts across a specific geographical area. It typically displays wind speed and direction, highlighting areas where gusts are expected to be strongest. These maps rely on complex meteorological models that analyze various factors, including atmospheric pressure, temperature, and terrain, to forecast wind behavior.
Understanding the components of a wind gust map is crucial for interpreting its information:
- Color Coding: Wind gust maps often employ color gradients to represent wind speed. Typically, warmer colors indicate stronger gusts, while cooler colors represent weaker gusts.
- Arrows: Arrows on the map indicate the direction of the wind, providing insights into the movement of the wind flow.
- Contour Lines: Some maps might utilize contour lines to represent areas with similar wind gust intensity.
- Time Stamps: Wind gust maps are dynamic, meaning they reflect wind conditions at a specific point in time. Therefore, they usually include time stamps to indicate the validity period of the forecast.
Applications of Wind Gust Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Wind gust maps find applications across a wide range of disciplines, serving as vital tools for:
- Aviation: Pilots rely heavily on wind gust maps for safe flight planning and execution. Gusts can significantly impact aircraft performance, particularly during takeoff and landing. By understanding predicted wind gusts, pilots can adjust their flight paths and speeds to mitigate risks.
- Sailing: Sailors utilize wind gust maps to optimize their sailing routes and strategies. Wind gusts can provide bursts of speed but also pose challenges in terms of boat control. Maps help sailors anticipate these fluctuations and navigate accordingly.
- Outdoor Events: Organizers of outdoor events, especially those involving large structures or open-air activities, rely on wind gust maps to ensure safety. Strong gusts can damage structures, disrupt events, and pose risks to participants.
- Renewable Energy: Wind gust maps are crucial for wind energy generation. Wind turbines are designed to harness wind energy, but excessive gusts can damage the turbines. Wind gust maps help optimize turbine operation and minimize potential damage.
- Emergency Management: Meteorologists and emergency response teams use wind gust maps to assess potential hazards associated with strong winds. These maps help in predicting and mitigating risks from wind-related events like dust storms, wildfires, and tornadoes.
The Science Behind the Forecast: Unraveling the Complexity
The generation of wind gust maps involves a complex interplay of data collection, analysis, and modeling:
- Data Collection: Meteorological agencies collect data from various sources, including weather stations, satellites, and radar systems. This data encompasses factors like wind speed, direction, temperature, and atmospheric pressure.
- Model Integration: This data is then fed into numerical weather prediction models, which simulate atmospheric conditions and predict future wind behavior. These models incorporate complex equations and algorithms to account for various factors influencing wind patterns.
- Visualization: The model output is then visualized through wind gust maps, offering a user-friendly representation of predicted wind conditions.
Limitations and Considerations: Ensuring Accuracy
While wind gust maps offer invaluable insights, it’s crucial to recognize their limitations:
- Accuracy: Wind gust forecasts are not perfect, and their accuracy can vary depending on the complexity of the model and the availability of data. Factors like terrain, local weather patterns, and unpredictable atmospheric events can influence the accuracy of predictions.
- Resolution: Maps typically display wind conditions over a specific geographical area, and the resolution might not be sufficient for detailed local analysis.
- Dynamic Nature: Wind conditions are constantly changing, and maps reflect a snapshot in time. It’s crucial to consult updated forecasts regularly to stay informed about evolving wind patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions about Wind Gust Maps
Q: What is the difference between a wind speed map and a wind gust map?
A: A wind speed map displays the average wind speed over a period, while a wind gust map focuses on the maximum expected wind speed, highlighting sudden bursts of wind.
Q: How often are wind gust maps updated?
A: Wind gust maps are typically updated at regular intervals, ranging from hourly to several times a day, depending on the source and the complexity of the model.
Q: How reliable are wind gust maps?
A: The reliability of wind gust maps depends on various factors, including the quality of data, model complexity, and the specific location. Generally, maps generated by reputable meteorological agencies and based on advanced models tend to be more reliable.
Q: Can I access wind gust maps for a specific location?
A: Yes, many online resources provide access to wind gust maps, allowing you to view forecasts for specific locations. Some websites allow users to customize map parameters, including location, time frame, and resolution.
Q: What are some tips for using wind gust maps effectively?
A:
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare wind gust maps from different sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of predicted wind conditions.
- Consider Local Factors: Remember that wind gusts can be influenced by local terrain and weather patterns.
- Stay Informed: Check for updated forecasts regularly, especially if you are planning outdoor activities or operations that are sensitive to wind conditions.
- Interpret Maps Carefully: Pay attention to the color coding, arrows, and time stamps on the map to understand the predicted wind gusts.
Conclusion:
Wind gust maps have emerged as indispensable tools for understanding and predicting wind behavior, offering valuable insights across various domains. By visualizing wind gusts, these maps empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, mitigating risks and optimizing operations. While acknowledging their limitations, wind gust maps continue to play a crucial role in navigating the unpredictable nature of wind, enhancing safety and efficiency in our interaction with this powerful force of nature.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Winds: Understanding Wind Gust Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!