Palestine: A Complex History and Uncertain Future in the Middle East
Related Articles: Palestine: A Complex History and Uncertain Future in the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Palestine: A Complex History and Uncertain Future in the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Palestine: A Complex History and Uncertain Future in the Middle East
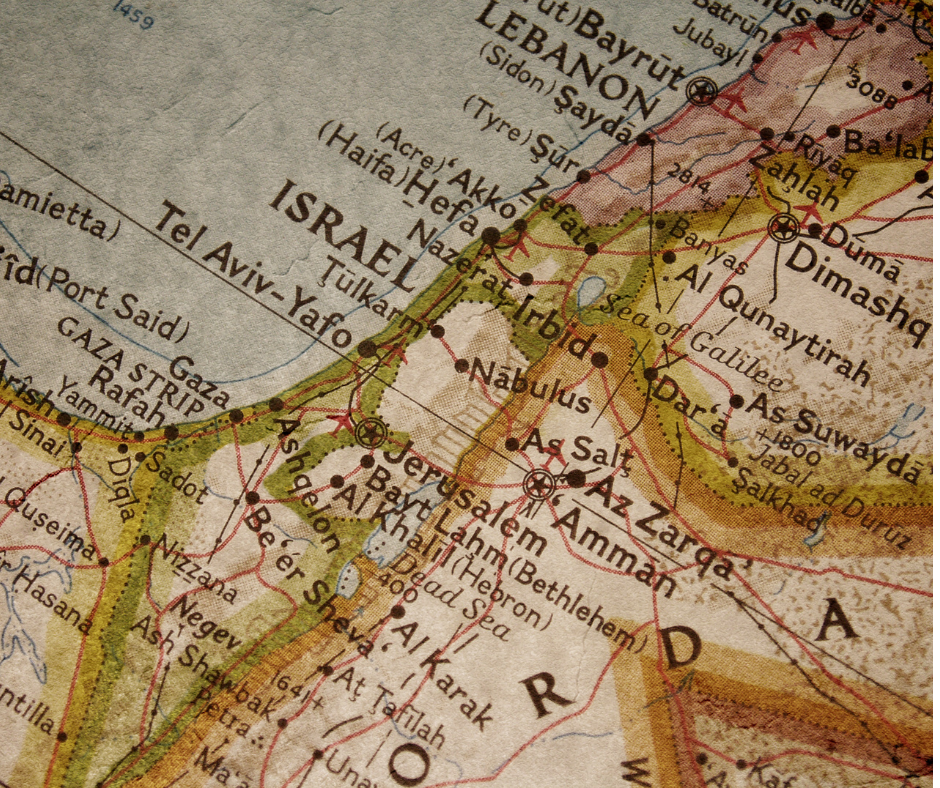
Palestine, a land steeped in history and contested by multiple narratives, occupies a pivotal position within the complex geopolitical landscape of the Middle East. Understanding its geographic location, historical significance, and contemporary challenges is crucial for comprehending the region’s ongoing conflicts and potential pathways to peace.
Palestine’s Geographical Context:
Palestine, as defined by the Palestinian people, encompasses the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem. These territories are located on the eastern Mediterranean coast, bordered by Jordan to the east, Israel to the west and south, and Lebanon to the north. The region’s strategic importance is evident in its proximity to major waterways, including the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and its location at the crossroads of trade routes connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Historical Significance and the Palestinian Narrative:
Palestine’s history is interwoven with the rise and fall of empires, from the ancient Canaanites and Israelites to the Roman, Byzantine, Ottoman, and British periods. The region has been a focal point of religious and cultural significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, with sacred sites like Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Hebron holding deep religious meaning for each faith.
The Palestinian narrative emphasizes a continuous presence in the land dating back millennia. They see themselves as indigenous to the region, their history intertwined with its landscape and culture. The Palestinian struggle for self-determination and statehood is rooted in this historical connection and the desire for recognition and sovereignty.
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict and its Impact on Palestine:
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a complex and protracted struggle for land and resources, has profoundly impacted Palestine’s political, social, and economic landscape. The conflict’s roots lie in competing claims to the same territory, driven by historical narratives, religious beliefs, and political aspirations.
Since the establishment of Israel in 1948, the conflict has resulted in multiple wars, displacement of Palestinian populations, and ongoing tensions. The 1967 Six-Day War led to Israel’s occupation of the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip, creating a new set of challenges for Palestinians living under Israeli control.
The West Bank:
The West Bank, a mountainous and fertile region, is divided into Area A, under full Palestinian control, Area B, under joint Israeli-Palestinian control, and Area C, under full Israeli control. The majority of the West Bank’s population is Palestinian, facing restrictions on movement, land ownership, and access to resources. The ongoing construction of Israeli settlements within the West Bank further complicates the situation, raising concerns about land annexation and the viability of a two-state solution.
The Gaza Strip:
The Gaza Strip, a densely populated coastal enclave, has been under Israeli blockade since 2007, leading to severe humanitarian challenges. The blockade restricts the movement of goods and people, impacting access to essential supplies, healthcare, and economic opportunities. The ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas, the ruling political party in Gaza, has resulted in recurrent military operations and a humanitarian crisis.
East Jerusalem:
East Jerusalem, home to significant religious sites like the Temple Mount/Haram al-Sharif, holds immense cultural and religious significance for both Israelis and Palestinians. Israel’s annexation of East Jerusalem in 1967 remains disputed by the international community, with Palestinians claiming East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state.
The Palestinian Authority and the Pursuit of Statehood:
The Palestinian Authority (PA), established in 1994, governs the Palestinian territories under Israeli control. The PA’s primary objective is to achieve Palestinian statehood, with East Jerusalem as its capital, through negotiations with Israel. However, the peace process has stalled, leaving the future of Palestine uncertain.
International Perspectives and the Quest for Peace:
The international community acknowledges the Palestinian right to self-determination and a sovereign state. The United Nations has passed numerous resolutions calling for a two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine existing side-by-side in peace and security. However, achieving a lasting peace remains elusive, hampered by ongoing violence, political deadlock, and mistrust between the two sides.
Challenges Facing Palestine:
Palestine faces a multitude of challenges, including:
- Political Division: The ongoing rift between Fatah, the ruling party in the West Bank, and Hamas, the ruling party in Gaza, has hindered Palestinian unity and weakened their negotiating position.
- Economic Constraints: The Israeli occupation, coupled with the blockade of Gaza, has severely impacted the Palestinian economy, leading to high unemployment, poverty, and limited economic opportunities.
- Human Rights Violations: Palestinians living under Israeli control face restrictions on movement, access to resources, and freedom of expression. The ongoing construction of Israeli settlements in the West Bank raises concerns about land annexation and human rights violations.
- Limited International Support: Despite international recognition of the Palestinian right to self-determination, the international community has struggled to effectively pressure Israel to end the occupation and negotiate a lasting peace.
FAQs about Palestine in the Middle East:
Q: What is the current political status of Palestine?
A: Palestine is currently divided between the West Bank, under Israeli control, and the Gaza Strip, under the control of Hamas. There is no independent Palestinian state, and the status of East Jerusalem remains contested.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Palestine?
A: Palestine faces significant challenges, including the ongoing Israeli occupation, political division, economic constraints, human rights violations, and limited international support.
Q: What are the potential solutions to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
A: The most widely supported solution is a two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine existing side-by-side in peace and security. However, achieving this solution remains challenging due to ongoing violence, political deadlock, and mistrust between the two sides.
Q: What role does the international community play in the Palestinian issue?
A: The international community acknowledges the Palestinian right to self-determination and a sovereign state. The United Nations has passed numerous resolutions calling for a two-state solution, and many countries support a peaceful resolution to the conflict. However, the international community has struggled to effectively pressure Israel to end the occupation and negotiate a lasting peace.
Tips for Understanding Palestine in the Middle East:
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from various sources, including Palestinian, Israeli, and international perspectives, to gain a balanced understanding of the complex issues at play.
- Focus on human stories: Explore the experiences of individuals living under Israeli control and the impact of the conflict on their lives.
- Understand the historical context: Learn about the historical narratives of both Israelis and Palestinians to gain a deeper understanding of their claims and aspirations.
- Support organizations working for peace: Engage with organizations advocating for human rights, peace, and a just resolution to the conflict.
Conclusion:
Palestine’s position in the Middle East is marked by a complex history, contested narratives, and ongoing challenges. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict continues to cast a long shadow over the region, impacting the lives of millions and hindering the pursuit of peace and stability. While the path to a lasting solution remains uncertain, understanding the complexities of the situation, engaging with diverse perspectives, and supporting efforts towards peace are crucial steps in fostering a future where both Palestinians and Israelis can live in security and dignity.







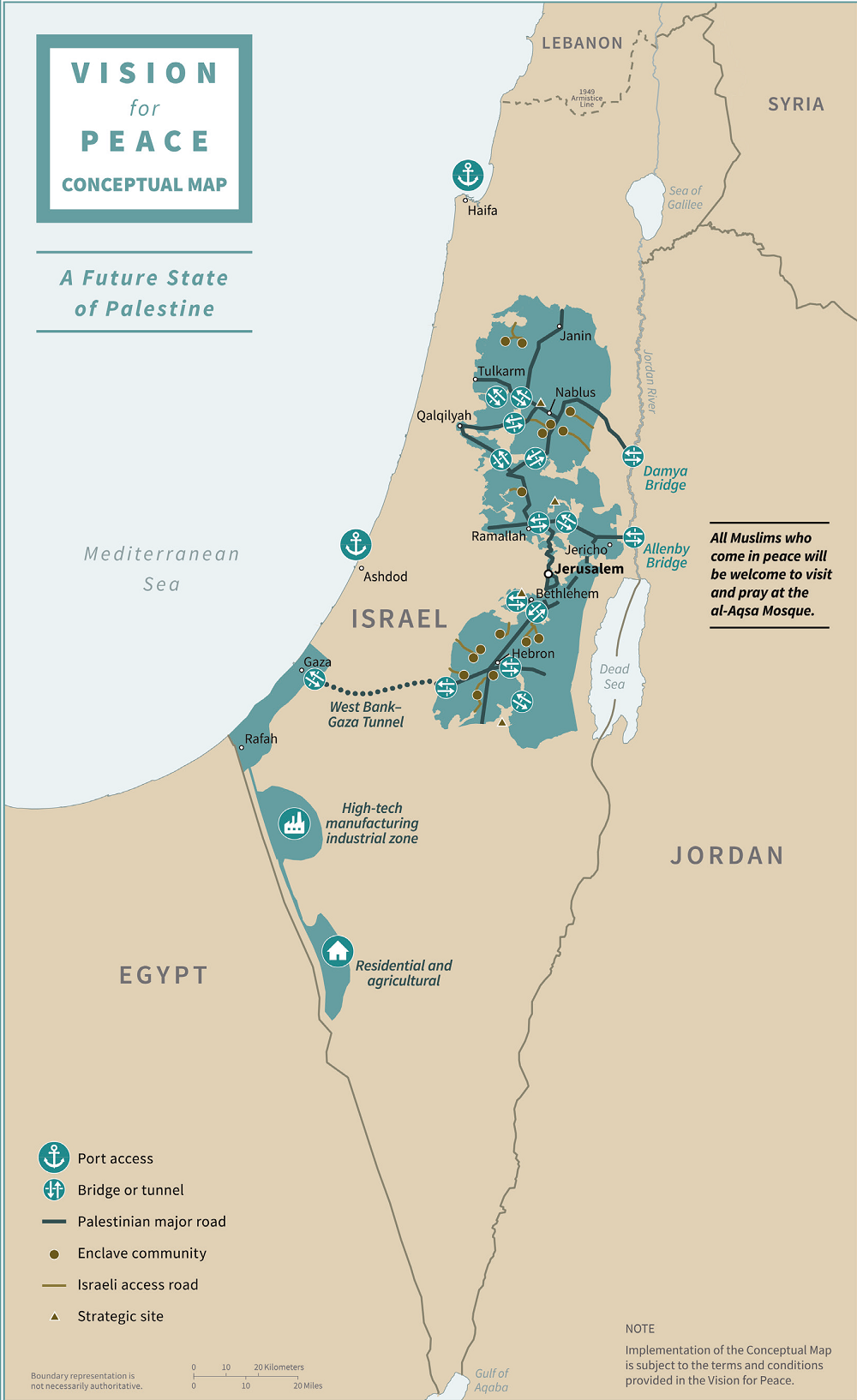
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Palestine: A Complex History and Uncertain Future in the Middle East. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!