The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels
Related Articles: The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels

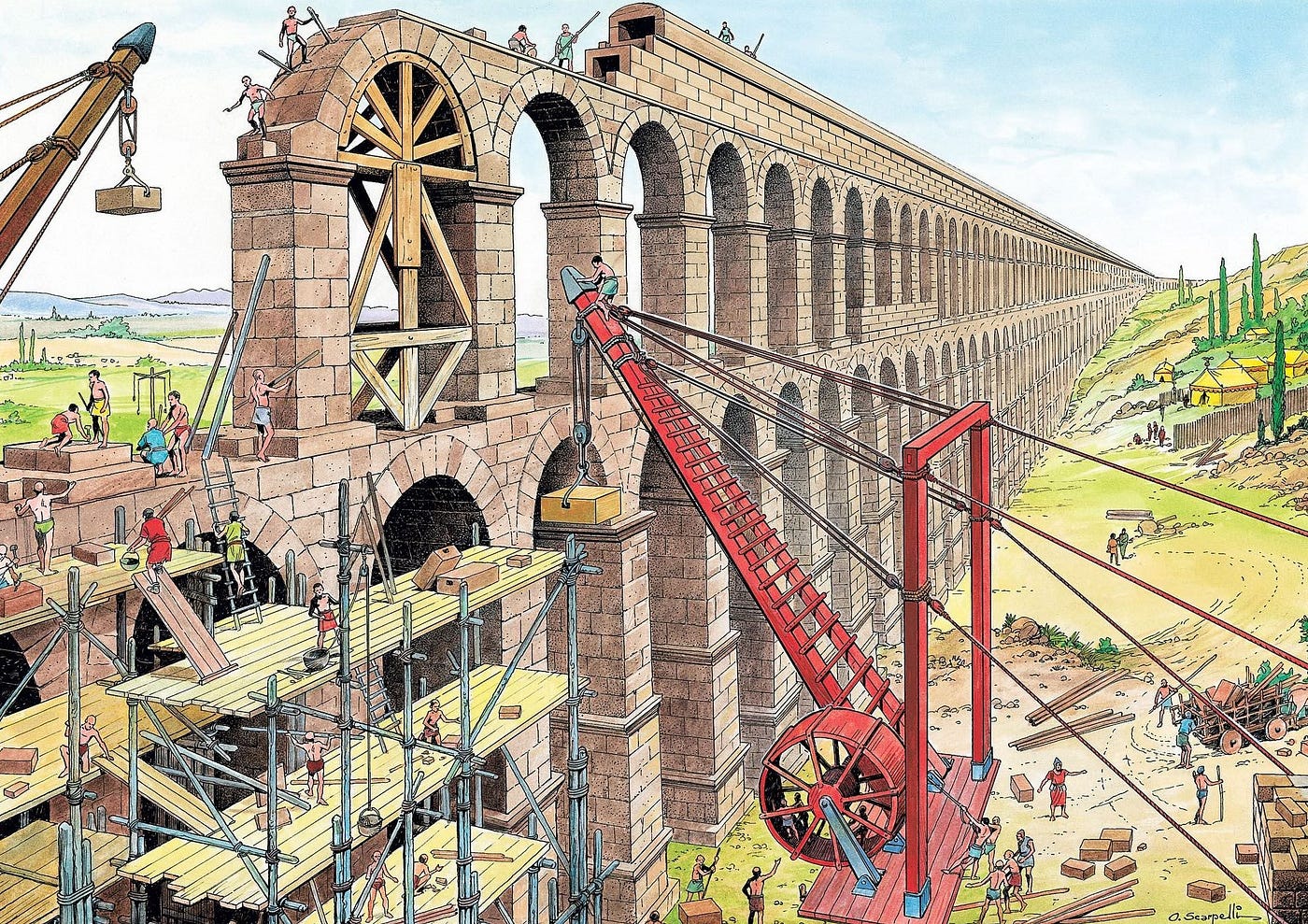
The aqueducts of Rome stand as a testament to the ingenuity and organizational prowess of the ancient Romans. These monumental structures, stretching for miles across the Roman countryside, were a marvel of engineering that supplied the city with a constant flow of fresh water, contributing significantly to its growth and prosperity.
A Network of Life: Understanding the Aqueduct System
The aqueduct system of Rome was a complex and well-organized network that brought water from distant springs and rivers to the city. This intricate system consisted of:
- Sources: The aqueducts drew water from various sources, including springs, rivers, and even lakes. These sources were carefully selected for their purity and abundance.
- Channels: The water was transported through channels, often built underground, to minimize evaporation and contamination. These channels were meticulously engineered with gradients to ensure a steady flow of water.
- Arches: The most iconic feature of the aqueducts, the arches, were used to carry the channels over valleys, roads, and other obstacles. These arches were constructed with remarkable precision and durability.
- Reservoirs: Upon reaching the city, the water was stored in reservoirs, which regulated the flow and ensured a constant supply. These reservoirs also served as settling tanks, allowing sediment to settle before the water was distributed.
- Distribution: From the reservoirs, the water was distributed to public fountains, baths, private homes, and even to the city’s gardens and agricultural fields.
A Map of Roman Ingenuity: Exploring the Aqueducts of Rome
The map of Rome’s aqueducts reveals the extent and sophistication of this ancient engineering feat. Some of the most notable aqueducts include:
- Aqua Appia (312 BCE): The oldest aqueduct in Rome, Aqua Appia was built by Appius Claudius Caecus and brought water from the Colline Hills to the city.
- Aqua Anio Vetus (272 BCE): This aqueduct sourced water from the Anio River, significantly increasing the water supply to Rome.
- Aqua Marcia (144 BCE): Known for its high quality and abundant flow, Aqua Marcia sourced water from the Sabine Mountains, providing water to both the city and the surrounding areas.
- Aqua Tepula (125 BCE): Built alongside Aqua Marcia, Aqua Tepula sourced water from the same region, supplying the city with a blend of cool and warm water.
- Aqua Julia (33 BCE): This aqueduct, also built alongside Aqua Marcia and Aqua Tepula, sourced water from the same region, further expanding the water supply to Rome.
- Aqua Virgo (19 BCE): This aqueduct, famously named after a young girl who led the Romans to its source, sourced water from the springs near the present-day city of Tivoli.
- Aqua Alsietina (2 BCE): This aqueduct, built during the reign of Augustus, sourced water from Lake Bracciano, primarily serving the city’s agricultural needs.
- Aqua Claudia (52 CE): Constructed during the reign of Claudius, Aqua Claudia sourced water from the Sabine Mountains, significantly expanding the water supply to Rome.
- Anio Novus (52 CE): Built alongside Aqua Claudia, Anio Novus sourced water from the Anio River, further increasing the water supply to the city.
Beyond Engineering: The Importance of the Aqueducts
The aqueducts of Rome were not just feats of engineering; they were crucial to the city’s development and success. Their impact extended beyond the provision of clean water, influencing various aspects of Roman life:
- Public Health: The aqueducts ensured a consistent supply of clean water, significantly improving public health by reducing the incidence of waterborne diseases.
- Urban Growth: The reliable water supply facilitated the growth of Rome, enabling the construction of extensive public baths, fountains, and gardens, enhancing the quality of life for its citizens.
- Economic Prosperity: The aqueducts supported the city’s economic prosperity by providing water for agricultural purposes, facilitating trade, and enhancing the quality of life, attracting people and businesses to Rome.
- Social Stability: The aqueducts contributed to social stability by ensuring a reliable water supply, reducing tensions and potential unrest that could arise from water scarcity.
- Cultural Significance: The aqueducts became a symbol of Roman ingenuity and organizational prowess, contributing to the city’s reputation as a powerful and sophisticated empire.
FAQs on the Aqueducts of Rome
Q: How long were the aqueducts of Rome?
A: The lengths of the aqueducts varied significantly. For example, Aqua Marcia stretched for approximately 60 miles, while Aqua Claudia was over 45 miles long.
Q: How much water did the aqueducts deliver to Rome?
A: The aqueducts delivered a staggering amount of water to Rome. Estimates suggest that the total daily flow of water through the aqueducts could reach over 300 million gallons.
Q: How were the aqueducts built?
A: The aqueducts were built using a variety of techniques, including:
- Terracing: The channels were often built on terraced slopes, allowing for a gradual descent of water.
- Arching: Arches were used to carry the channels over valleys and other obstacles, minimizing the need for extensive excavation.
- Masonry: The aqueducts were primarily constructed from stone, ensuring their durability and longevity.
Q: How were the aqueducts maintained?
A: The aqueducts required constant maintenance to ensure a smooth flow of water. This included:
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning was essential to remove sediment and debris that could obstruct the flow of water.
- Repairs: Repairs were necessary to address any damage caused by weather, erosion, or other factors.
- Inspections: Regular inspections were conducted to identify potential problems and ensure the aqueducts were functioning properly.
Q: What happened to the aqueducts after the fall of the Roman Empire?
A: After the fall of the Roman Empire, the aqueducts fell into disrepair, with some being destroyed or abandoned. However, some aqueducts continued to be used, albeit on a smaller scale, throughout the Middle Ages and beyond.
Q: How can I visit the aqueducts of Rome today?
A: Many of the aqueducts of Rome are still visible today, offering a glimpse into the ingenuity of the ancient Romans. You can visit the aqueducts by:
- Walking or cycling: Some aqueducts are accessible by walking or cycling paths, allowing you to explore them at your own pace.
- Guided tours: Guided tours are available that provide historical insights and expert explanations about the aqueducts.
- Historical sites: Some aqueducts are incorporated into historical sites, such as the Parco degli Acquedotti, which offers a scenic view of the aqueducts and their surroundings.
Tips for Visiting the Aqueducts of Rome
- Plan your visit: The aqueducts are spread across a wide area, so plan your visit in advance and allocate sufficient time for exploration.
- Wear comfortable shoes: Walking or cycling along the aqueducts can be a long journey, so wear comfortable shoes.
- Bring water and snacks: It’s advisable to bring water and snacks, especially if you’re exploring the aqueducts on your own.
- Take photos: Capture the beauty and grandeur of these ancient engineering marvels with your camera.
- Learn about the history: Before your visit, research the history of the aqueducts to gain a deeper understanding of their significance.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation
The aqueducts of Rome stand as a testament to the ingenuity, organizational prowess, and dedication of the ancient Romans. These monumental structures, spanning miles across the Roman countryside, not only provided a vital water supply but also played a crucial role in the city’s growth, prosperity, and cultural development. Today, the aqueducts continue to inspire awe and admiration, serving as a reminder of the remarkable achievements of ancient civilization. As we explore these ancient marvels, we gain a deeper appreciation for the past and the enduring legacy of human innovation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!