The Arizona Redistricting Map: A Tale of Democracy, Representation, and Power
Related Articles: The Arizona Redistricting Map: A Tale of Democracy, Representation, and Power
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Arizona Redistricting Map: A Tale of Democracy, Representation, and Power. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arizona Redistricting Map: A Tale of Democracy, Representation, and Power
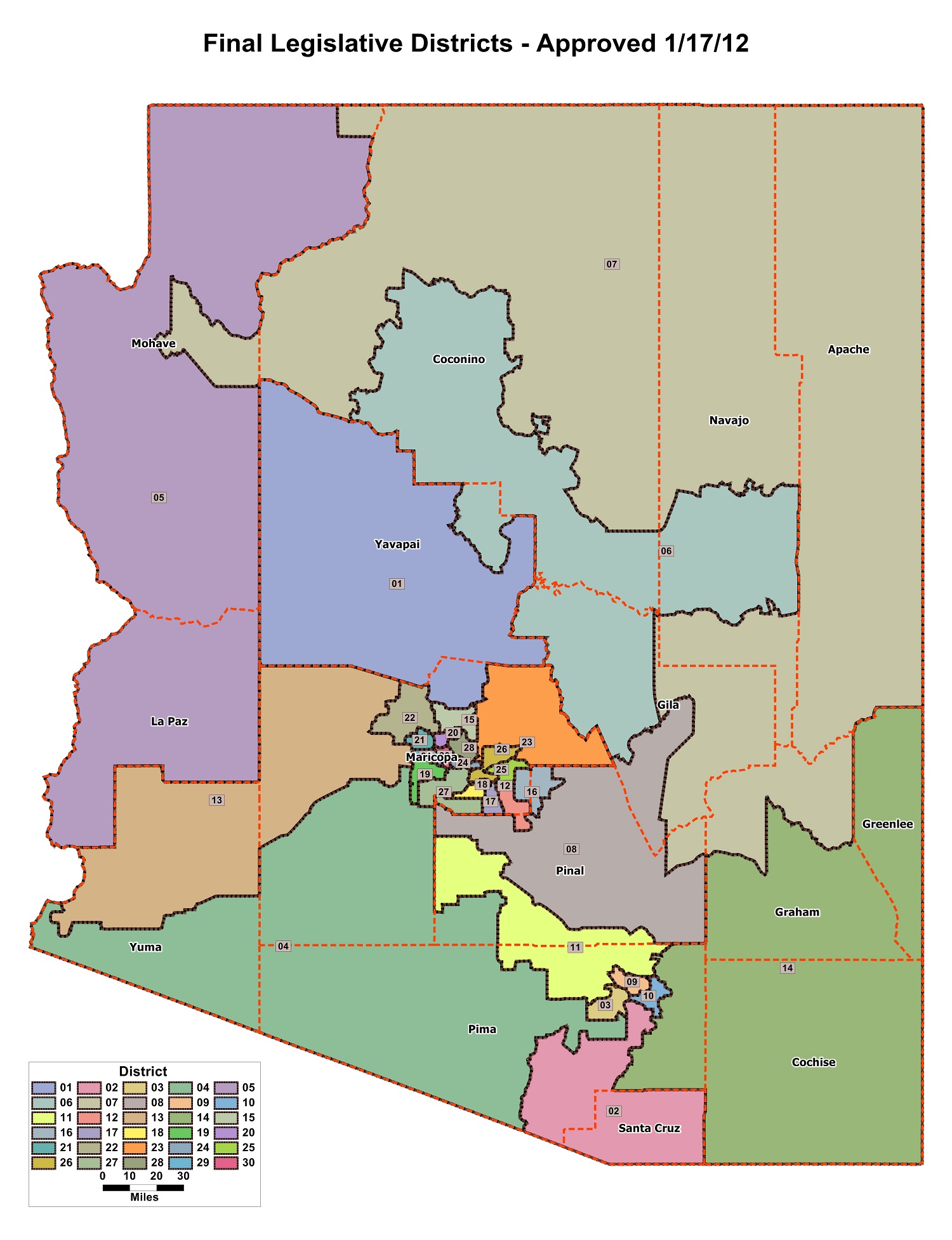
The Arizona redistricting map, a seemingly complex patchwork of lines on a map, holds immense significance. It determines the boundaries of legislative districts, shaping the political landscape and influencing the voices heard in government. Understanding the process of redistricting and its implications is crucial for informed participation in the democratic process.
The Foundation of Redistricting:
Every ten years, following the decennial census, the United States undergoes a process called redistricting. This involves redrawing the boundaries of congressional and state legislative districts to reflect population changes and ensure equal representation. The goal is to create districts with roughly equal populations, adhering to the principle of "one person, one vote."
The Arizona Redistricting Process:
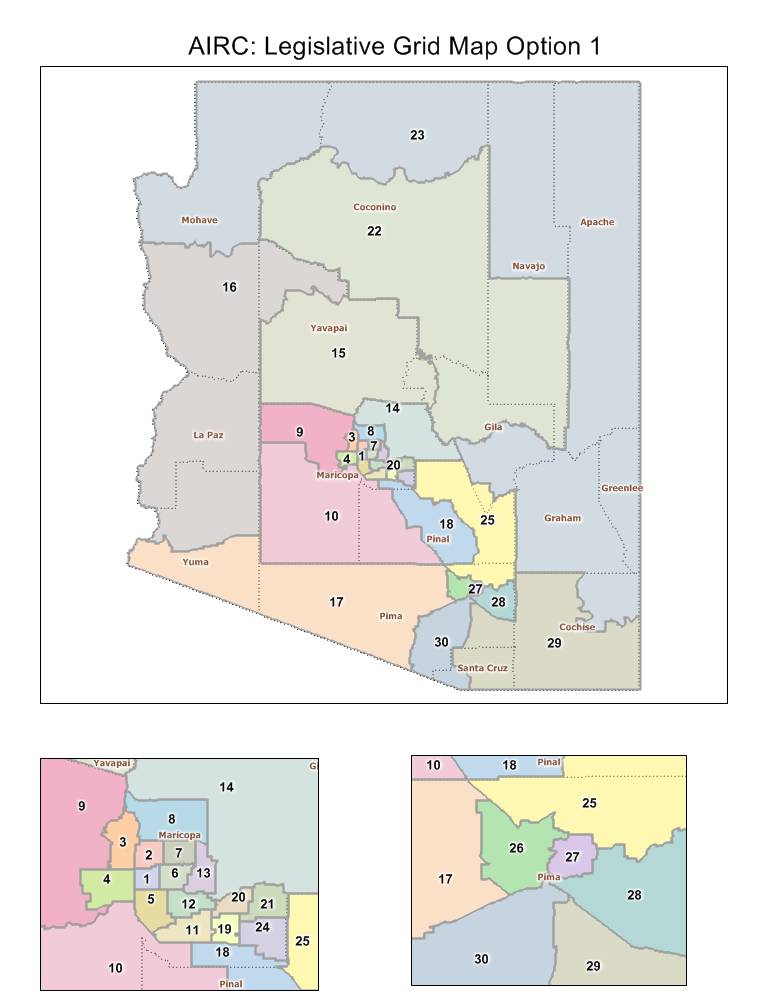
Arizona’s redistricting process is unique, characterized by a blend of political and independent oversight. Unlike many states where legislatures hold sole control over redistricting, Arizona has an independent commission, the Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC), tasked with drawing the state’s congressional and legislative district maps.
The IRC is composed of five members: two Democrats, two Republicans, and one independent. This structure aims to ensure that no single party holds a majority, promoting a balanced and fair process. The commission’s decisions are subject to judicial review, providing an additional layer of oversight.
The 2020 Redistricting Cycle:
The 2020 redistricting cycle in Arizona was marked by intense scrutiny and debate. The IRC faced the challenge of balancing the competing interests of political parties, communities of interest, and the need for fair representation. The commission held numerous public hearings, soliciting input from citizens, community organizations, and political stakeholders.
Key Considerations in Redistricting:
The IRC’s deliberations were guided by specific criteria, including:
- Population Equality: Districts must have roughly equal populations to ensure that each voter’s voice carries equal weight.
- Compactness: Districts should be geographically cohesive, minimizing sprawling and fragmented boundaries.
- Contiguity: Districts must be contiguous, meaning all parts of a district must be connected.
- Communities of Interest: The commission considered the needs and interests of communities, striving to avoid dividing neighborhoods or communities of shared interests.
- Minority Representation: The commission aimed to ensure that minority communities have a fair opportunity for representation.
The Impact of the 2020 Redistricting Map:
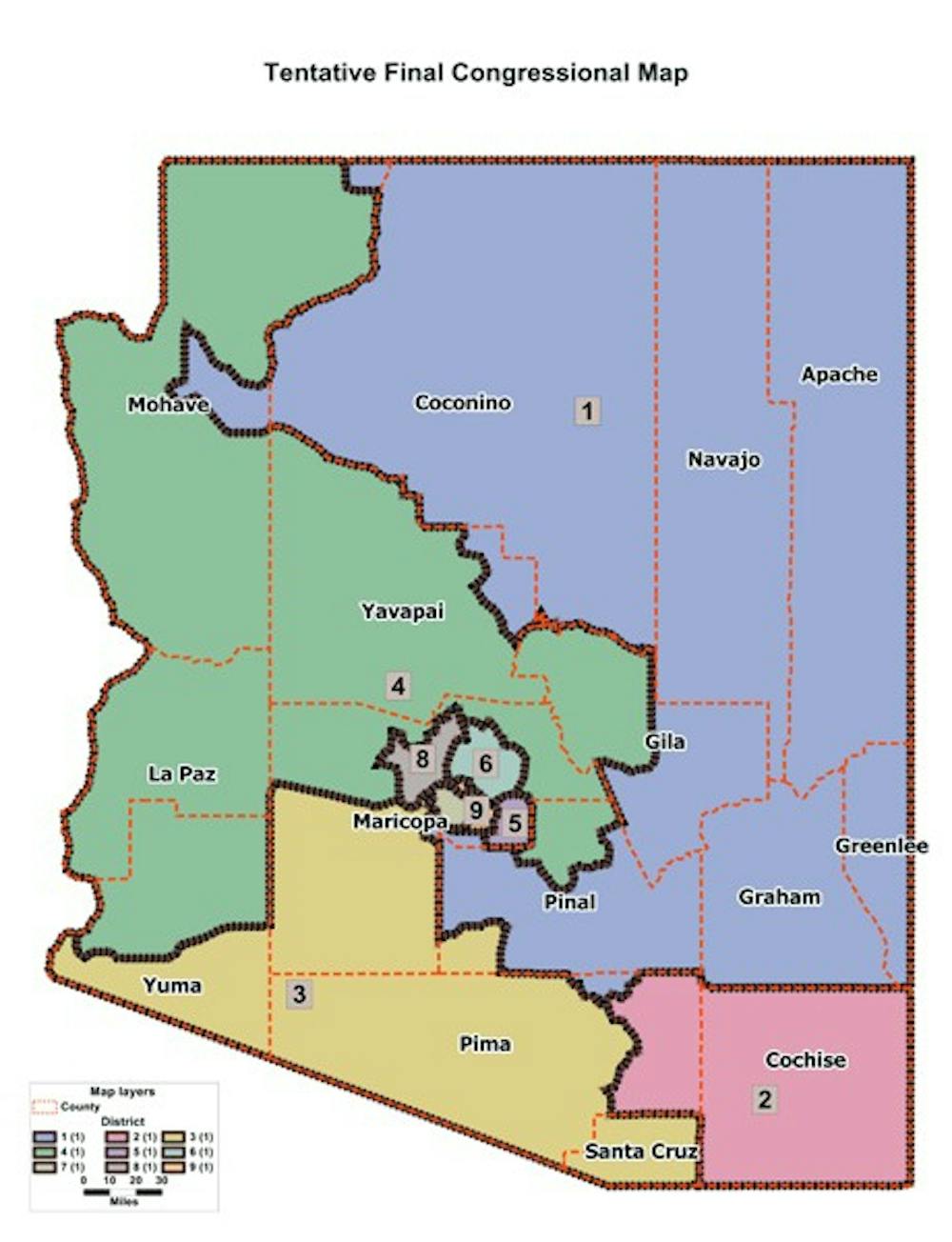
The 2020 redistricting map in Arizona has had a significant impact on the state’s political landscape. It has influenced the competitiveness of congressional and legislative races, impacting the balance of power in the state legislature and the composition of the state’s congressional delegation.
Consequences of Gerrymandering:
Redistricting, when manipulated for partisan advantage, can lead to gerrymandering. This practice involves drawing district lines in a way that favors one party over another, often by concentrating opposing voters in a few districts while spreading out the party’s own supporters across multiple districts. Gerrymandering can undermine fair representation, reduce voter choice, and contribute to political polarization.
Benefits of an Independent Redistricting Commission:
Arizona’s independent redistricting commission is seen as a safeguard against gerrymandering. By removing the process from direct political control, the commission aims to ensure that district lines are drawn based on objective criteria rather than partisan advantage.
The Future of Redistricting in Arizona:
The Arizona redistricting process continues to evolve. The commission’s work is subject to ongoing scrutiny and legal challenges. The debate over redistricting is likely to continue, as stakeholders seek to ensure fair representation and a balanced political landscape.
FAQs on Arizona Redistricting Map:
1. What is the purpose of redistricting?
Redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes and ensure equal representation.
2. Who is responsible for redistricting in Arizona?
The Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC) is responsible for drawing the state’s congressional and legislative district maps.
3. What are the key criteria for redistricting?
The IRC considers factors such as population equality, compactness, contiguity, communities of interest, and minority representation.
4. What is gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering is the manipulation of district boundaries to favor one political party over another.
5. How does the IRC help prevent gerrymandering?
The IRC is an independent body, free from direct political control, aiming to draw district lines based on objective criteria.
6. How often does redistricting occur?
Redistricting occurs every ten years following the decennial census.
7. What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering can undermine fair representation, reduce voter choice, and contribute to political polarization.
8. How can citizens participate in the redistricting process?
Citizens can engage in the process by attending public hearings, providing input to the IRC, and advocating for their interests.
Tips for Engaging in Redistricting:
- Stay informed: Follow news coverage and research the redistricting process and its impact.
- Participate in public hearings: Attend hearings and share your views with the IRC.
- Advocate for fair representation: Contact elected officials and advocate for policies that promote fair redistricting.
- Support organizations working on redistricting reform: Contribute to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to ensuring fair representation.
Conclusion:
The Arizona redistricting map is a vital component of the state’s democratic process. It influences the representation of communities, the balance of power in the legislature, and the composition of the state’s congressional delegation. Understanding the process and its implications is crucial for informed participation in the democratic process. By engaging in the redistricting process, citizens can contribute to shaping a fair and representative political landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arizona Redistricting Map: A Tale of Democracy, Representation, and Power. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!