The Bering Sea: A Vital Link Between Continents
Related Articles: The Bering Sea: A Vital Link Between Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Bering Sea: A Vital Link Between Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Bering Sea: A Vital Link Between Continents

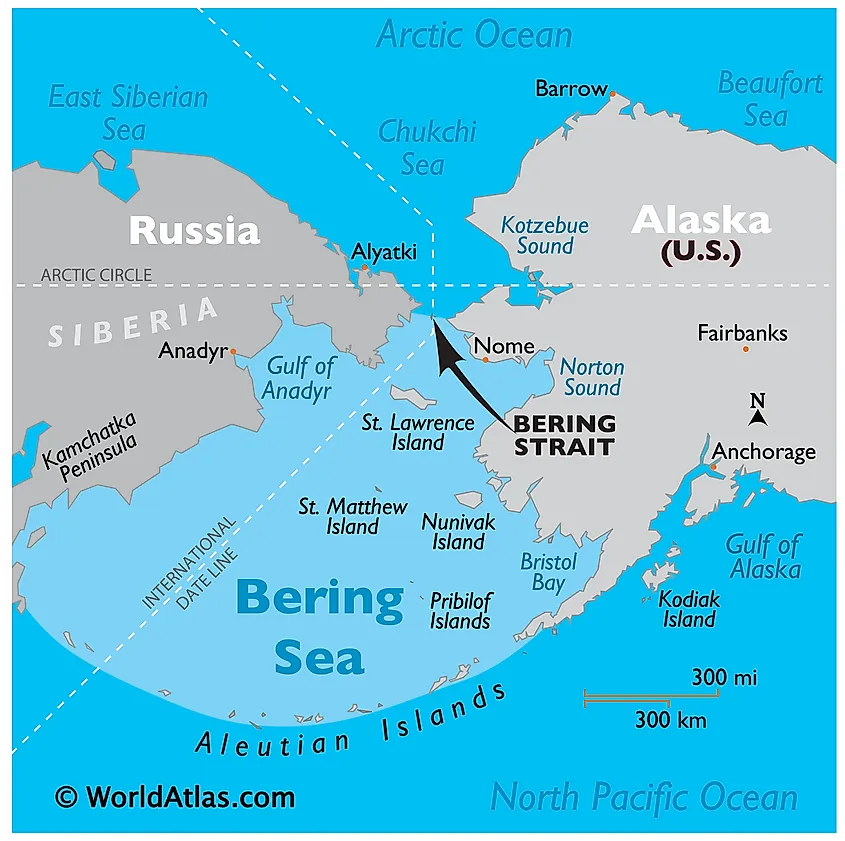
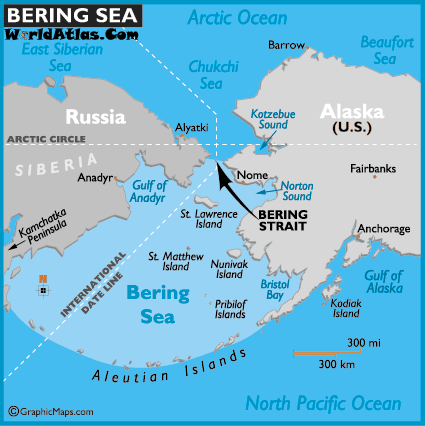
The Bering Sea, a marginal sea of the North Pacific Ocean, occupies a pivotal position on the world map, serving as a crucial link between North America and Asia. Its vast expanse, encompassing over 2.3 million square kilometers, is characterized by its unique ecosystem, rich biodiversity, and significant economic and geopolitical importance.
Geography and Formation:
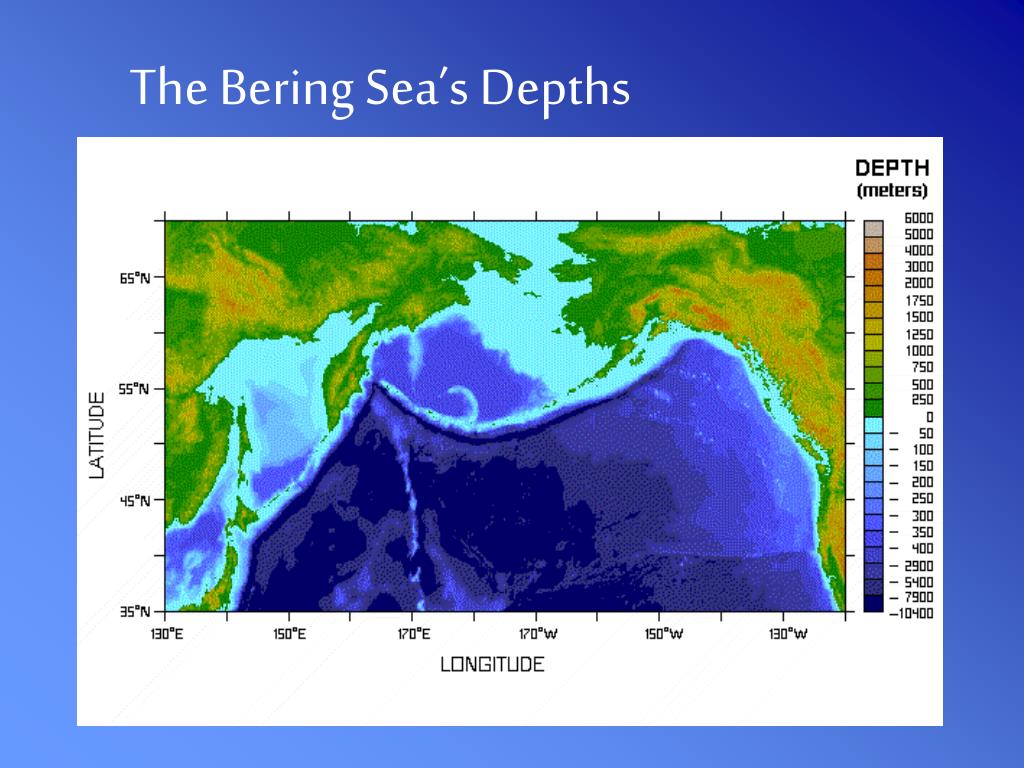
Located north of the Aleutian Islands and east of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the Bering Sea is bordered by Alaska to the east and Russia to the west. Its relatively shallow depth, averaging 1,600 meters, is a consequence of its formation during the Pleistocene epoch. The Bering Land Bridge, an exposed landmass connecting Siberia and Alaska, existed during the last glacial period, allowing for the migration of humans and animals between continents.
Climate and Oceanographic Features:
The Bering Sea is known for its harsh climate, with frigid winters and cool summers. Its unique oceanographic features include:
- The Bering Strait: This narrow strait, connecting the Bering Sea to the Arctic Ocean, plays a crucial role in the exchange of water and nutrients.
- The Anadyr Current: Originating from the Arctic Ocean, this cold current carries nutrient-rich waters into the Bering Sea, supporting its diverse marine life.
- The Alaska Current: This warm current, originating from the Pacific Ocean, flows northward along the Alaskan coast, bringing warmer water and moderating the climate.
- The Bering Sea Gyre: This clockwise circulation pattern, driven by winds and ocean currents, influences the distribution of nutrients and marine organisms.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem:
The Bering Sea is a rich and diverse ecosystem, supporting a wide array of marine life. Its cold, nutrient-rich waters provide a suitable habitat for:
- Marine Mammals: The Bering Sea is home to a significant population of marine mammals, including whales, seals, walruses, and polar bears.
- Fish Species: The sea is a major fishing ground, supporting commercially valuable species like cod, pollock, crab, and salmon.
- Seabirds: Abundant seabird populations, including auks, gulls, and albatrosses, rely on the Bering Sea for food and breeding grounds.
- Invertebrates: The seafloor is teeming with invertebrates, including sea stars, sea urchins, and clams.
Economic Importance:
The Bering Sea plays a vital role in the economies of the United States and Russia. Its rich fisheries contribute significantly to both countries’ seafood industries, providing employment and revenue. Other economic activities include:
- Oil and Gas Exploration: The sea’s potential for oil and gas reserves has attracted interest from energy companies.
- Tourism: The Bering Sea’s stunning landscapes and abundant wildlife draw tourists from around the world.
- Transportation: The Bering Sea serves as a vital transportation route, connecting ports in Alaska and Russia.
Geopolitical Significance:
The Bering Sea’s strategic location has made it a point of geopolitical interest. It is a crucial maritime passage connecting the Arctic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and serves as a potential route for future trade and transportation. The sea also holds significant military importance, as it is home to naval bases and military installations.
Environmental Challenges:
The Bering Sea faces a number of environmental challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changes in ocean circulation are impacting the Bering Sea’s ecosystem, affecting marine life and fisheries.
- Pollution: Industrial activities, shipping, and oil spills pose threats to the sea’s water quality and marine life.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish stocks and disrupt the marine ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts:
Efforts are underway to protect the Bering Sea’s unique ecosystem. These include:
- International Cooperation: The United States and Russia have established joint management agreements for the Bering Sea’s fisheries.
- Marine Protected Areas: Designated areas within the Bering Sea are protected from certain human activities to safeguard marine life.
- Sustainable Fishing Practices: Organizations and governments are promoting sustainable fishing methods to ensure the long-term health of the sea’s fisheries.
FAQs:
What is the largest city on the Bering Sea coast?
The largest city on the Bering Sea coast is Anchorage, Alaska, with a population of over 290,000.
What is the average depth of the Bering Sea?
The average depth of the Bering Sea is 1,600 meters (5,200 feet).
What is the Bering Land Bridge and why is it significant?
The Bering Land Bridge was an exposed landmass connecting Siberia and Alaska during the last glacial period. It played a crucial role in the migration of humans and animals between continents, contributing to the genetic diversity of both regions.
What are some of the major fishing grounds in the Bering Sea?
The Bering Sea is known for its rich fisheries, including the Bering Sea pollock fishery, the Bering Sea crab fishery, and the Bering Sea salmon fishery.
What are some of the environmental threats facing the Bering Sea?
The Bering Sea faces a number of environmental threats, including climate change, pollution, overfishing, and habitat loss.
What are some of the conservation efforts being undertaken to protect the Bering Sea?
Conservation efforts include international cooperation, marine protected areas, sustainable fishing practices, and research programs to monitor and understand the Bering Sea’s ecosystem.
Tips for Visiting the Bering Sea:
- Plan your trip during the summer months: The Bering Sea is best visited during the summer months, when temperatures are milder and wildlife is more active.
- Book a cruise or tour: A cruise or tour is the best way to experience the Bering Sea’s beauty and wildlife.
- Be respectful of the environment: Avoid littering and disturbing wildlife.
- Pack appropriate clothing: The Bering Sea can be cold and windy, so pack layers of warm clothing.
Conclusion:
The Bering Sea, a vital link between North America and Asia, is a unique and valuable ecosystem. Its diverse marine life, rich fisheries, and strategic location make it a critical resource for both the United States and Russia. However, the Bering Sea faces a number of environmental challenges, including climate change and pollution. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this vital ecosystem for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Bering Sea: A Vital Link Between Continents. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!