The Bering Strait: A Bridge Between Continents and a Window to the Past
Related Articles: The Bering Strait: A Bridge Between Continents and a Window to the Past
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Bering Strait: A Bridge Between Continents and a Window to the Past. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Bering Strait: A Bridge Between Continents and a Window to the Past
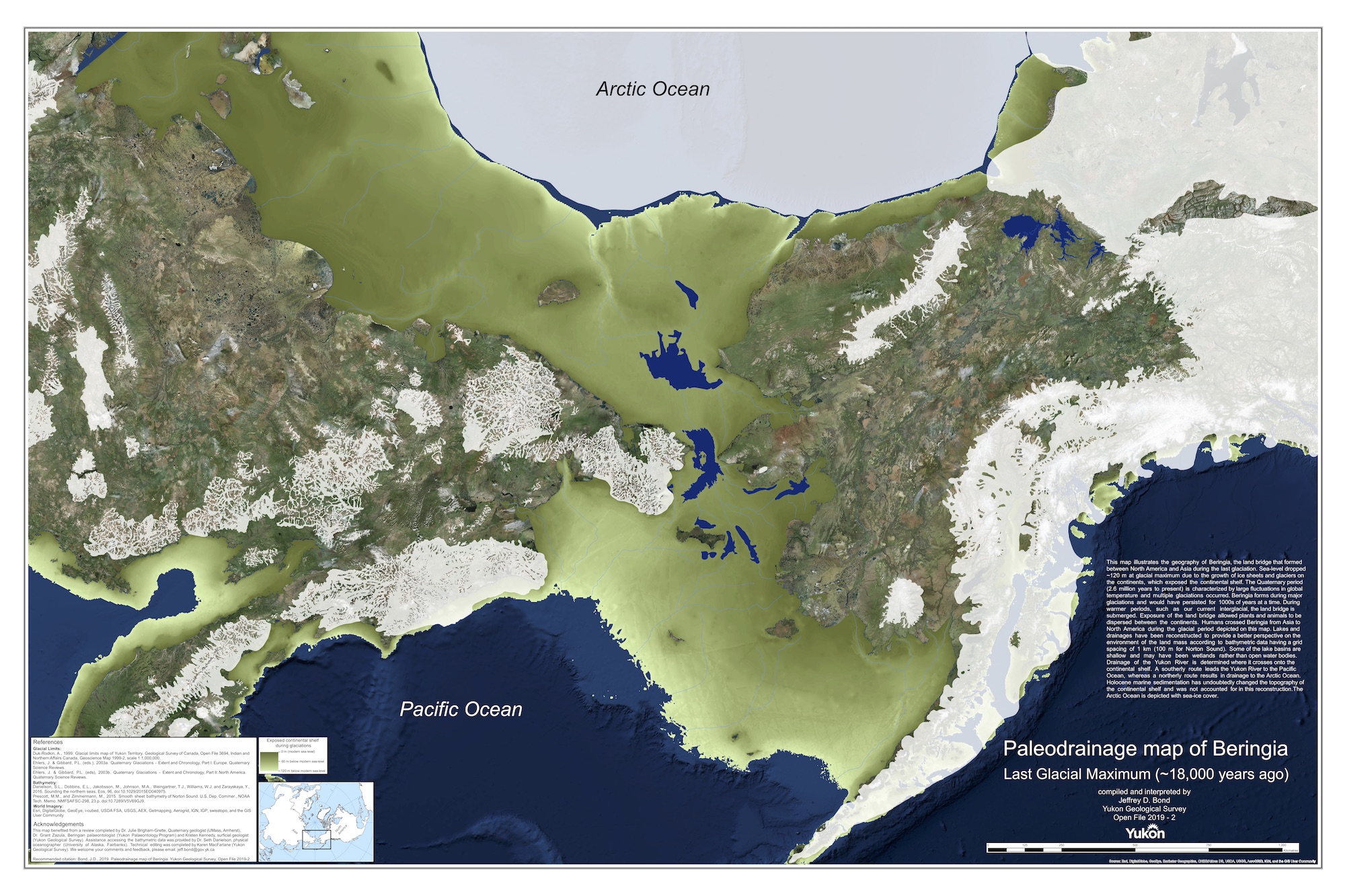
The Bering Strait, a narrow body of water separating the continents of Asia and North America, holds a significance that extends far beyond its geographical location. This frigid passage, a mere 53 miles wide at its narrowest point, serves as a historical gateway for migration, a crucial link in global ocean currents, and a vital ecosystem for a diverse range of marine life.
A Land Bridge and a Corridor of Migration:
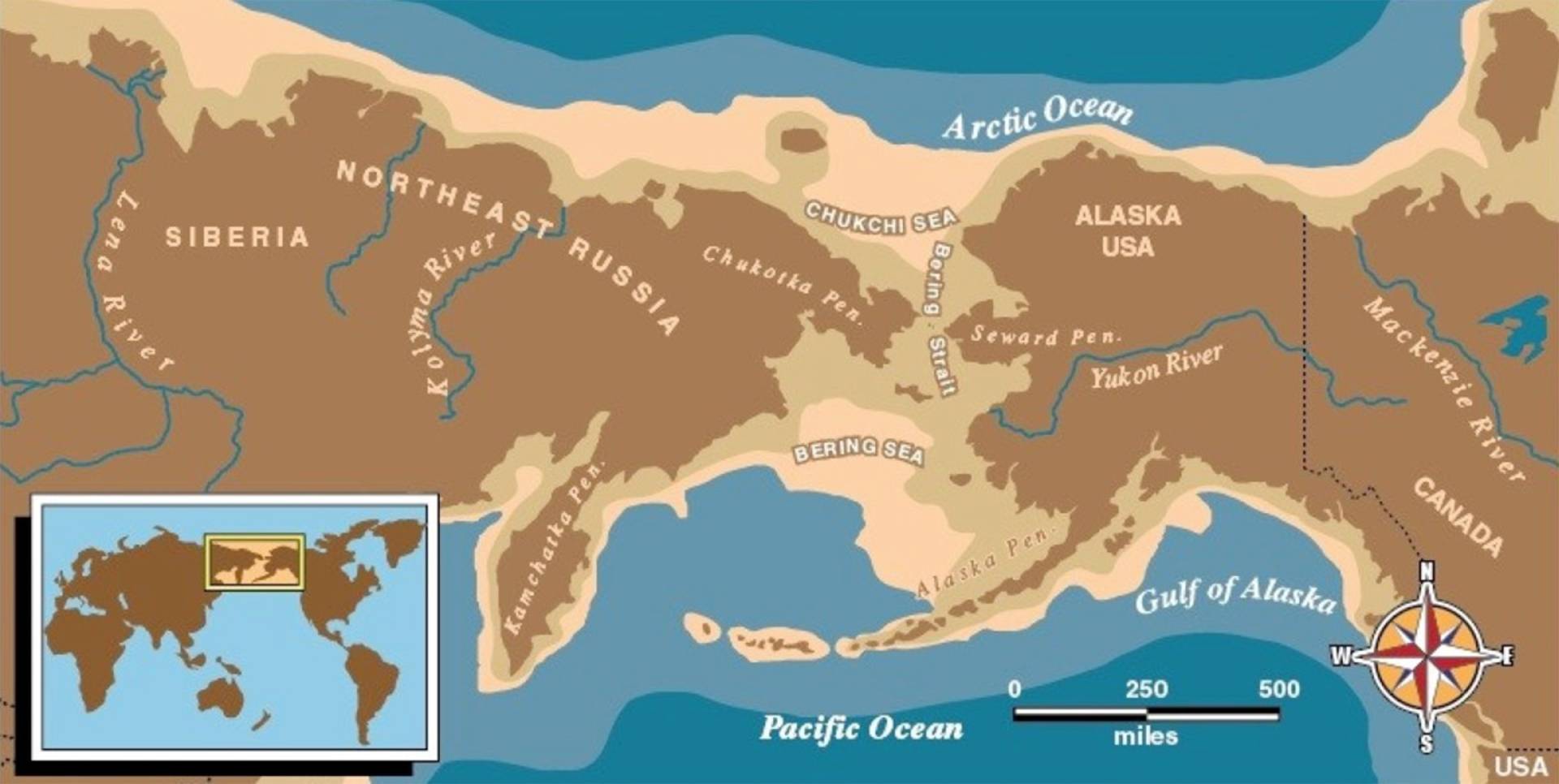
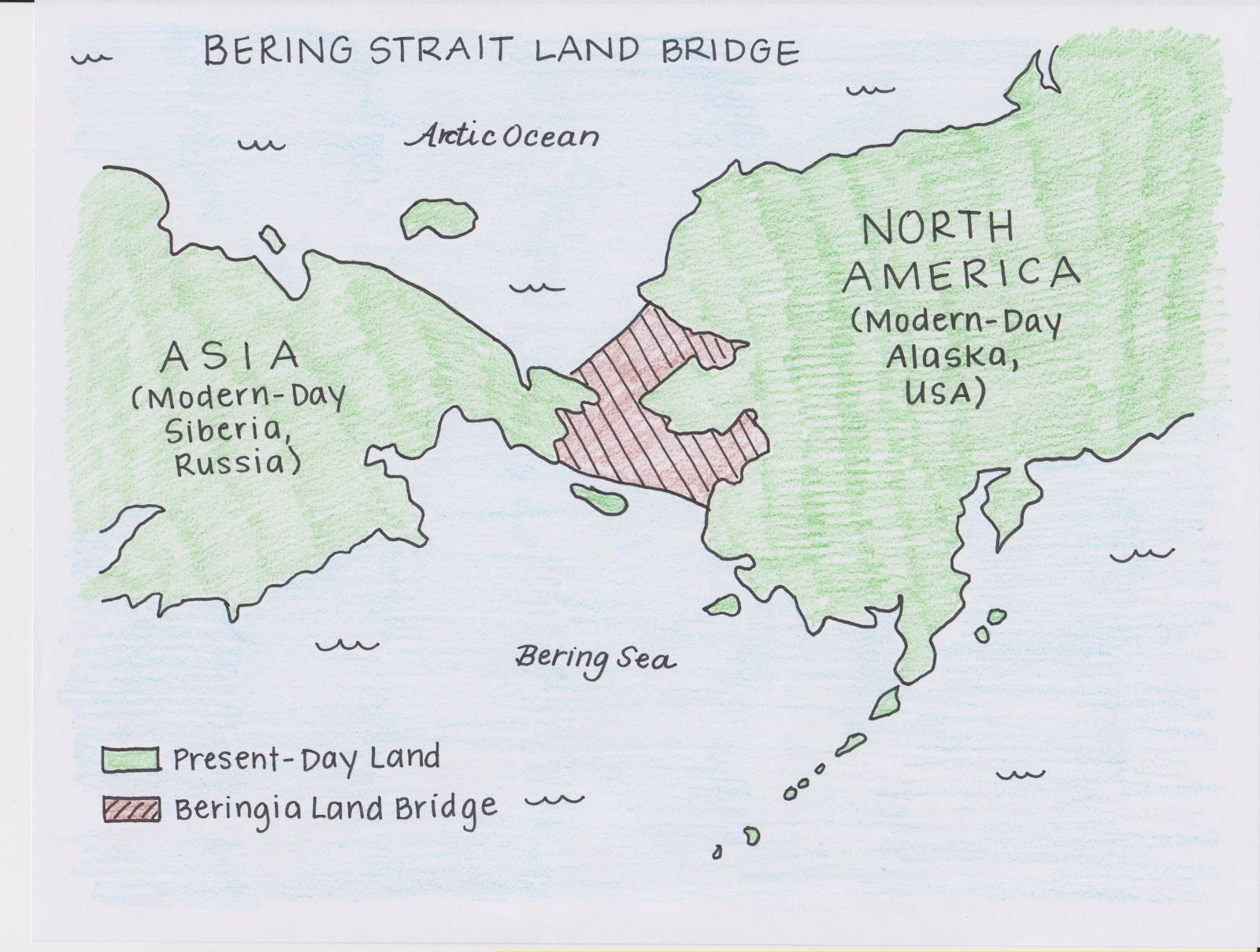
For millennia, the Bering Strait was not a strait at all, but a land bridge, known as Beringia. During the last glacial period, when vast amounts of water were locked up in ice sheets, sea levels dropped significantly, exposing a vast expanse of land connecting Siberia and Alaska. This land bridge, which existed for thousands of years, provided a crucial pathway for the migration of humans, animals, and plants between the continents.
The Bering Land Bridge played a pivotal role in the peopling of the Americas. It is widely accepted that the first humans to reach the Americas crossed Beringia from Asia, eventually spreading across the continent and giving rise to the diverse indigenous populations that exist today. This migration, which likely began around 15,000 years ago, is a testament to the enduring power of human adaptability and the importance of land bridges in shaping the course of human history.
A Vital Link in the Global Ocean System:
The Bering Strait is not merely a geographical barrier; it is a critical component of the global ocean system. It acts as a conduit for the exchange of water, heat, and nutrients between the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. The cold, dense waters of the Arctic Ocean flow south through the Bering Strait, while warmer, saltier waters from the Pacific flow north, contributing to the global thermohaline circulation, a vast system of ocean currents that plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate.
The Bering Strait also plays a significant role in the exchange of marine life. The cold, nutrient-rich waters flowing from the Arctic support a diverse ecosystem, including species like walruses, seals, whales, and a variety of fish. These species often migrate through the Bering Strait, making it a vital corridor for marine biodiversity.
A Region Under Pressure:
The Bering Strait is a region of immense ecological and cultural significance. However, this region is increasingly under pressure from climate change and human activities. Rising global temperatures are causing sea ice to melt at an alarming rate, leading to a loss of habitat for Arctic marine species and impacting the traditional hunting and fishing practices of indigenous communities.
Furthermore, the Bering Strait is a potential route for shipping and resource extraction, raising concerns about the potential for environmental damage. As the Arctic ice melts, the Bering Strait becomes more accessible to shipping, leading to increased traffic and the risk of oil spills and other environmental hazards. The region also holds significant oil and gas reserves, and the potential for exploitation raises concerns about the impact on the delicate Arctic ecosystem.
Understanding the Bering Strait: A Key to the Future:
The Bering Strait serves as a crucial reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet and the delicate balance of its ecosystems. Understanding the history, geography, and ecological significance of this unique region is essential for addressing the challenges of climate change, resource management, and preserving the rich cultural heritage of the Arctic.
FAQs about the Bering Strait:
1. How deep is the Bering Strait?
The Bering Strait has an average depth of about 30-50 meters (100-165 feet).
2. What is the significance of the Bering Land Bridge?
The Bering Land Bridge played a crucial role in the migration of humans, animals, and plants between Asia and North America during the last glacial period. It is believed to be the pathway through which the first humans reached the Americas.
3. What are the major environmental concerns related to the Bering Strait?
The Bering Strait faces significant environmental challenges due to climate change, including sea ice melt, rising sea levels, and the potential for increased shipping and resource extraction activities.
4. What are the cultural and economic importance of the Bering Strait?
The Bering Strait is home to indigenous communities who rely on the region’s resources for their livelihoods and cultural practices. The strait is also a potential route for shipping and resource extraction, which could have significant economic and environmental implications.
5. How is the Bering Strait affected by climate change?
Climate change is causing the Bering Strait to experience significant changes, including sea ice melt, rising sea levels, and changes in marine ecosystems. These changes are impacting the livelihoods of indigenous communities and the overall health of the Arctic environment.
Tips for Further Exploration:
- Visit museums and archives: Many museums and archives have exhibits and collections related to the Bering Strait, including artifacts from indigenous cultures, historical maps, and scientific research data.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and online databases offer information about the Bering Strait, including its history, geography, ecology, and cultural significance.
- Read books and articles: There are many books and articles available that delve deeper into the history, geography, and ecology of the Bering Strait.
- Connect with experts: Reach out to experts in the field, such as anthropologists, archaeologists, oceanographers, and climate scientists, to learn more about the Bering Strait and its significance.
- Support organizations working to protect the Arctic: Many organizations are dedicated to protecting the Arctic environment and supporting indigenous communities. Consider supporting their efforts through donations or volunteering.
Conclusion:
The Bering Strait stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of our planet and the enduring power of nature. Its role in human migration, its significance as a link in the global ocean system, and its importance as an ecosystem for diverse marine life make it a region of profound historical, geographical, and ecological significance. As we face the challenges of climate change and resource management, understanding the Bering Strait and its unique role in the world is essential for ensuring the future of this fragile and vital region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Bering Strait: A Bridge Between Continents and a Window to the Past. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!