The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart
Related Articles: The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart
- 3.1 A Journey Through the Deccan Plateau
- 3.2 A River of Ancient Significance
- 3.3 A Lifeline for Modern India
- 3.4 Challenges and Concerns
- 3.5 The Narmada River: A Vital Resource for the Future
- 3.6 FAQs about the Narmada River:
- 3.7 Tips for Exploring the Narmada River:
- 3.8 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart

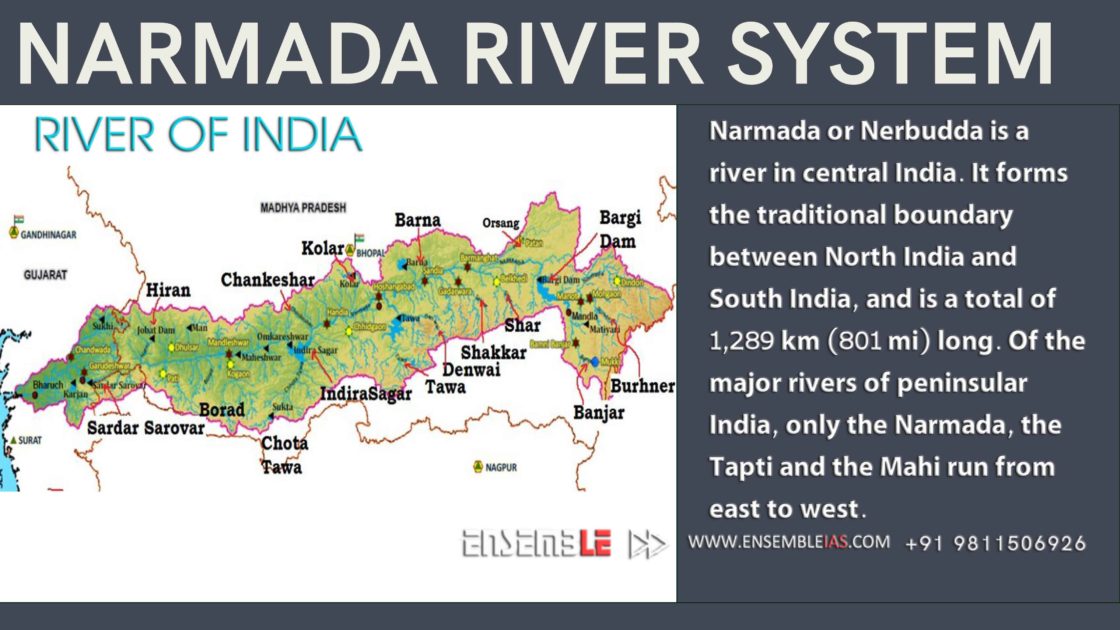
The Narmada River, a significant waterway in India, holds immense cultural, economic, and ecological importance. Its journey, spanning over 1,300 kilometers, traverses through the heart of the country, shaping the landscape and the lives of millions. Understanding the Narmada River’s path and its impact requires a comprehensive examination of its geographical context, historical significance, and multifaceted role in modern India.
A Journey Through the Deccan Plateau
The Narmada River originates in the Maikal Range of the Satpura Mountains in central India. It flows westward, carving a deep valley through the Deccan Plateau, before emptying into the Gulf of Cambay, a branch of the Arabian Sea. This westward flow makes it unique among Indian rivers, most of which flow eastward towards the Bay of Bengal.
The Narmada River’s course can be divided into three distinct sections:
- The Upper Narmada: This section, originating at Amarkantak, is characterized by its swift current and steep gradients. It flows through a narrow valley, creating numerous rapids and waterfalls.
- The Middle Narmada: As the river progresses, the valley widens, and the current slows down. This section is characterized by fertile plains, providing land for agriculture.
- The Lower Narmada: The final section of the river flows through a broad, alluvial plain, gradually widening into a vast estuary before reaching the Arabian Sea.
A River of Ancient Significance
The Narmada River has been a vital part of Indian civilization for millennia. Its banks have witnessed the rise and fall of empires, and its waters have sustained countless generations. Archaeological evidence suggests that human settlements existed along the river as early as the Paleolithic period.
The Narmada River holds immense religious significance in Hinduism, revered as a sacred river. It is believed to be the daughter of the God Shiva and is associated with purity and spiritual cleansing. Many pilgrimage sites, such as Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, and Narmada Kund, are located on its banks, attracting pilgrims from across the country.
A Lifeline for Modern India
The Narmada River remains a crucial resource for modern India, supporting various sectors:
- Agriculture: The fertile plains along the Narmada River are ideal for agriculture, producing a variety of crops like wheat, rice, cotton, and pulses. The river’s water is also used for irrigation, ensuring food security for a large population.
- Hydropower: The Narmada River’s swift currents have been harnessed to generate hydroelectric power. Several dams, including the Sardar Sarovar Dam, have been constructed along its course, providing electricity to surrounding areas.
- Transportation: The Narmada River has historically served as a vital transportation route. While its navigability has been limited due to the construction of dams, it still plays a role in transporting goods and people in certain regions.
- Tourism: The Narmada River’s scenic beauty and religious significance attract tourists from around the world. The river is a popular destination for boating, fishing, and exploring ancient temples and pilgrimage sites.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its benefits, the Narmada River also faces numerous challenges:
- Environmental Concerns: The construction of dams, particularly the Sardar Sarovar Dam, has raised environmental concerns, including displacement of communities, habitat destruction, and disruption of the river’s natural flow.
- Water Scarcity: The Narmada River basin is experiencing increasing water scarcity due to rising demand and unpredictable rainfall patterns. This poses a threat to agriculture and other water-dependent sectors.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities along the river’s banks have led to pollution, impacting water quality and harming aquatic life.
The Narmada River: A Vital Resource for the Future
The Narmada River is a vital resource for India, offering a range of benefits. However, its sustainability and the well-being of the communities dependent on it require careful planning and management. Addressing environmental concerns, promoting sustainable practices, and ensuring equitable access to water are crucial for preserving the Narmada River’s ecological and economic value for generations to come.
FAQs about the Narmada River:
1. What is the length of the Narmada River?
The Narmada River is approximately 1,300 kilometers long.
2. Where does the Narmada River originate?
The Narmada River originates at Amarkantak in the Maikal Range of the Satpura Mountains in central India.
3. Where does the Narmada River flow into?
The Narmada River flows into the Gulf of Cambay, a branch of the Arabian Sea.
4. What is the religious significance of the Narmada River?
The Narmada River is considered sacred in Hinduism, revered as the daughter of the God Shiva. It is associated with purity and spiritual cleansing.
5. What are the major dams on the Narmada River?
The major dams on the Narmada River include the Sardar Sarovar Dam, the Narmada Sagar Dam, and the Indira Sagar Dam.
6. What are the environmental concerns associated with the Narmada River?
Environmental concerns associated with the Narmada River include displacement of communities, habitat destruction, disruption of the river’s natural flow, and water pollution.
7. What are the major cities located along the Narmada River?
Major cities located along the Narmada River include Jabalpur, Hoshangabad, and Bharuch.
8. What are some of the popular tourist destinations along the Narmada River?
Popular tourist destinations along the Narmada River include Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, and Narmada Kund.
Tips for Exploring the Narmada River:
- Plan your trip in advance: The Narmada River basin is vast, and planning your itinerary in advance will ensure you see the most important sites.
- Consider the best time to visit: The best time to visit the Narmada River is during the winter months (October to March) when the weather is pleasant and the water levels are low.
- Respect the local culture and traditions: The Narmada River is a sacred river for many Hindus. Respect their beliefs and traditions when visiting temples and pilgrimage sites.
- Be mindful of the environment: Avoid littering and dispose of waste responsibly. Respect the natural beauty of the river and its surrounding ecosystem.
- Learn about the history and culture of the region: Take time to learn about the rich history and culture of the Narmada River basin. Visit museums, historical sites, and interact with local communities.
Conclusion:
The Narmada River is a testament to the intricate relationship between nature and human civilization. It has sustained communities for millennia, offering essential resources and serving as a vital lifeline. As India navigates the challenges of development and environmental sustainability, understanding and managing the Narmada River’s role becomes increasingly crucial. By embracing responsible practices and prioritizing conservation, we can ensure that this vital waterway continues to nourish and enrich lives for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Narmada River: A Lifeline Flowing Through India’s Heart. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!