Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map
Related Articles: Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map
- 3.1 The Importance of the Pennsylvania Radon Map
- 3.2 Understanding Radon Levels and Risk
- 3.3 The Health Risks of Radon Exposure
- 3.4 Radon Testing: The First Step to Mitigation
- 3.5 Radon Mitigation: Reducing Radon Levels in Your Home
- 3.6 FAQs About Radon in Pennsylvania
- 3.7 Tips for Reducing Radon Levels in Your Home
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map
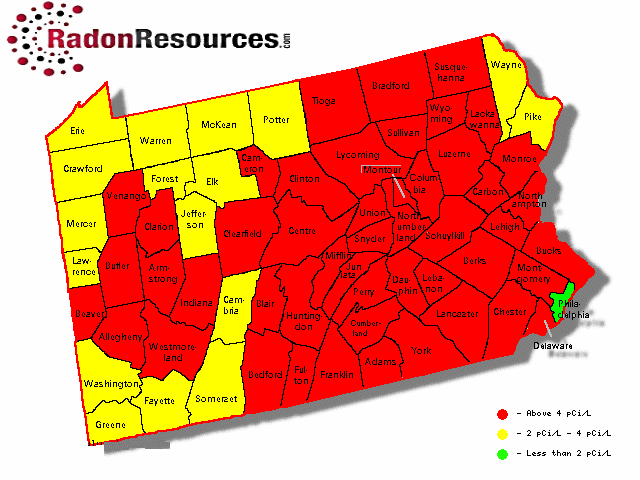
Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, is a significant public health concern. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, making it undetectable without specialized testing. Pennsylvania, due to its geological makeup, experiences varying levels of radon, making it crucial for residents to understand the risks and take necessary precautions.
The Importance of the Pennsylvania Radon Map
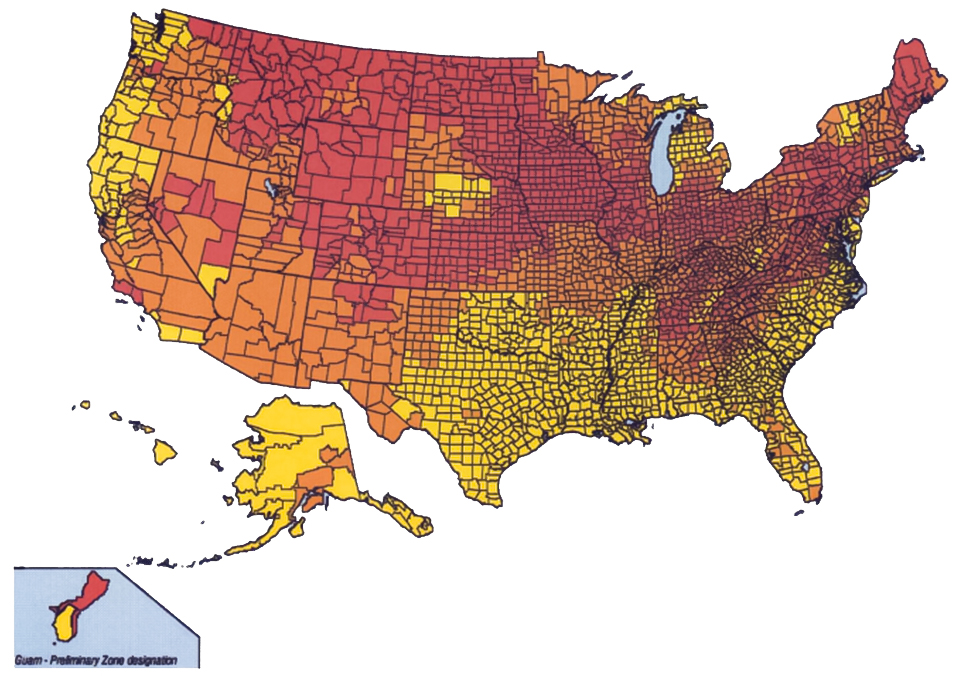
The Pennsylvania Radon Map is a valuable tool for understanding the potential for radon exposure in different areas of the state. This map, developed by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP), displays estimated radon levels based on geological data and historical testing results. It serves as a critical resource for:
- Homebuyers: Identifying areas with higher radon potential can help buyers make informed decisions and prioritize radon testing before purchasing a property.
- Real Estate Professionals: Understanding radon risks allows agents to advise clients on potential hazards and encourage testing, promoting informed property transactions.
- Public Health Officials: The map provides a valuable tool for targeting radon mitigation efforts and educating communities about the importance of testing and mitigation.
Understanding Radon Levels and Risk
The Pennsylvania Radon Map utilizes a color-coded system to visually represent estimated radon levels:
- Low Risk: Areas with low radon potential, typically below 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter), are depicted in green.
- Moderate Risk: Areas with moderate radon potential, typically between 4 and 8 pCi/L, are represented in yellow.
- High Risk: Areas with high radon potential, typically exceeding 8 pCi/L, are shown in red.
While the map provides valuable insights, it is crucial to remember that these are estimated levels. Actual radon levels in a specific home can vary significantly due to factors such as soil type, building construction, and ventilation.
The Health Risks of Radon Exposure
Radon is a known carcinogen, and prolonged exposure can significantly increase the risk of developing lung cancer, even for non-smokers. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that radon is responsible for approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths annually in the United States.
Radon exposure is particularly concerning for:
- Children: Children are more susceptible to the effects of radon due to their developing lungs and higher breathing rates.
- Individuals with pre-existing lung conditions: People with conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be more vulnerable to the effects of radon.
- Smokers: The combination of smoking and radon exposure significantly increases the risk of lung cancer.
Radon Testing: The First Step to Mitigation
The only way to determine the actual radon level in a home is through testing. The EPA recommends testing every two years, and it is essential to test any home that is being purchased or rented.
Types of Radon Tests:
- Short-Term Tests: These tests typically run for 2-7 days and are suitable for initial screenings or when quick results are needed.
- Long-Term Tests: These tests run for 90 days or more and provide a more accurate representation of average radon levels.
Where to Obtain Radon Test Kits:
- Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP): The DEP offers a list of certified radon testing laboratories on its website.
- Private Laboratories: Numerous private laboratories offer radon testing kits and services.
- Home Improvement Stores: Many home improvement stores carry radon test kits.
Radon Mitigation: Reducing Radon Levels in Your Home
If radon levels are found to be above the EPA’s recommended action level of 4 pCi/L, it is crucial to take steps to mitigate the risk. Radon mitigation involves reducing radon levels in the home by:
- Installing a Radon Mitigation System: This system typically involves a vent pipe that draws radon from beneath the house and releases it into the outdoor air.
- Sealing Cracks and Openings: This helps prevent radon from entering the home from the ground.
- Improving Ventilation: Opening windows and doors can help reduce radon levels, but this is not a permanent solution.
Cost of Radon Mitigation:
The cost of radon mitigation can vary depending on the size and complexity of the home. However, it is a worthwhile investment in protecting your health and the health of your family.
FAQs About Radon in Pennsylvania
1. Why is radon a concern in Pennsylvania?
Pennsylvania has a significant amount of uranium in its bedrock, which decays into radon gas. This geological makeup contributes to elevated radon levels in many parts of the state.
2. How can I find out if my home has high radon levels?
The only way to determine the actual radon level in your home is through testing. You can purchase test kits online, at home improvement stores, or from certified radon testing laboratories.
3. What should I do if my radon test results are high?
If your radon test results are above the EPA’s recommended action level of 4 pCi/L, you should contact a qualified radon mitigation contractor to install a mitigation system.
4. How much does radon mitigation cost?
The cost of radon mitigation can vary depending on the size and complexity of the home. However, it is a worthwhile investment in protecting your health and the health of your family.
5. Are there any government programs to help with radon mitigation costs?
The Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) does not offer financial assistance for radon mitigation. However, some local governments may have programs available.
6. Is radon testing required in Pennsylvania?
Radon testing is not currently mandated by law in Pennsylvania. However, it is highly recommended for all homes, especially those built before 1980.
7. Can I mitigate radon myself?
While some basic steps like sealing cracks and improving ventilation can help, installing a radon mitigation system is best left to a qualified contractor.
8. What are the signs of radon exposure?
Radon exposure does not have any immediate symptoms. The health effects of radon are long-term and typically manifest as lung cancer.
9. Is radon a problem in all parts of Pennsylvania?
Radon levels can vary significantly across Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Radon Map provides a good indication of areas with higher radon potential.
10. What are the long-term health effects of radon exposure?
Prolonged exposure to radon can significantly increase the risk of developing lung cancer. The risk is even higher for smokers and individuals with pre-existing lung conditions.
Tips for Reducing Radon Levels in Your Home
- Test your home for radon regularly: The EPA recommends testing every two years.
- Seal cracks and openings in your foundation: This can help prevent radon from entering your home.
- Improve ventilation: Open windows and doors to allow fresh air to circulate.
- Install a radon mitigation system: If your radon levels are high, a mitigation system can effectively reduce radon levels.
- Educate yourself and your family about radon: Understanding the risks and how to mitigate them is crucial.
Conclusion
Radon exposure is a serious public health concern, and Pennsylvania residents should be aware of the potential risks. The Pennsylvania Radon Map provides a valuable resource for understanding radon levels in different areas of the state. Testing your home for radon and taking steps to mitigate high levels is essential to protect your health and the health of your family. By understanding the risks and taking appropriate action, you can reduce your exposure to this invisible threat.
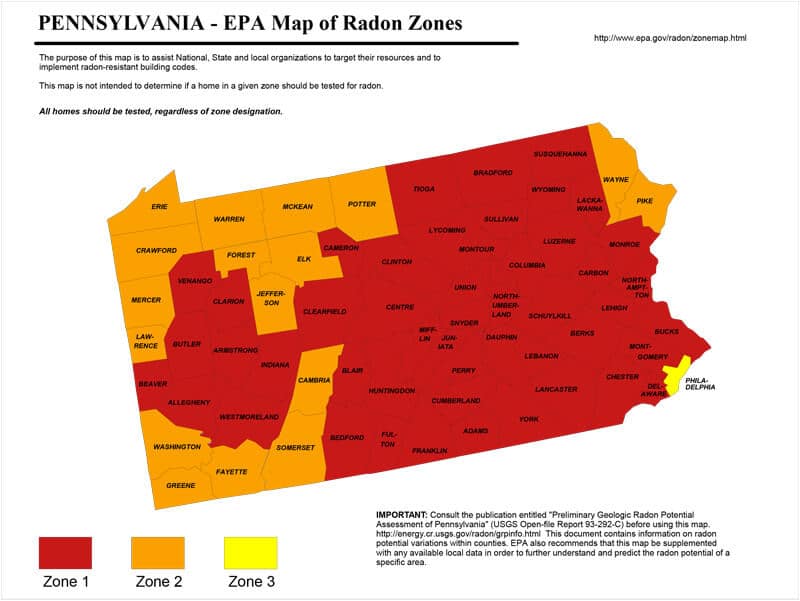

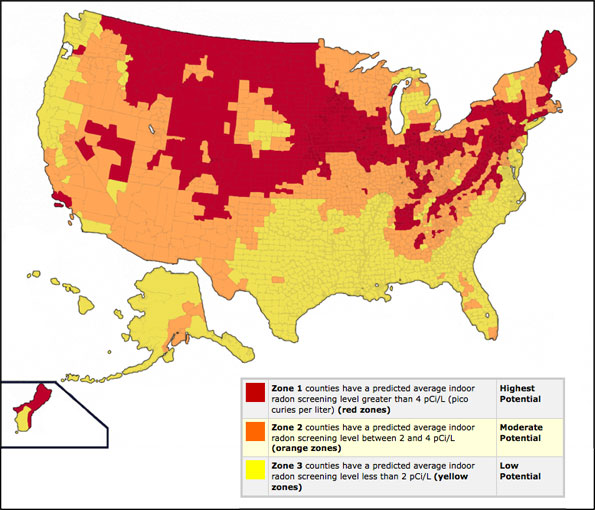
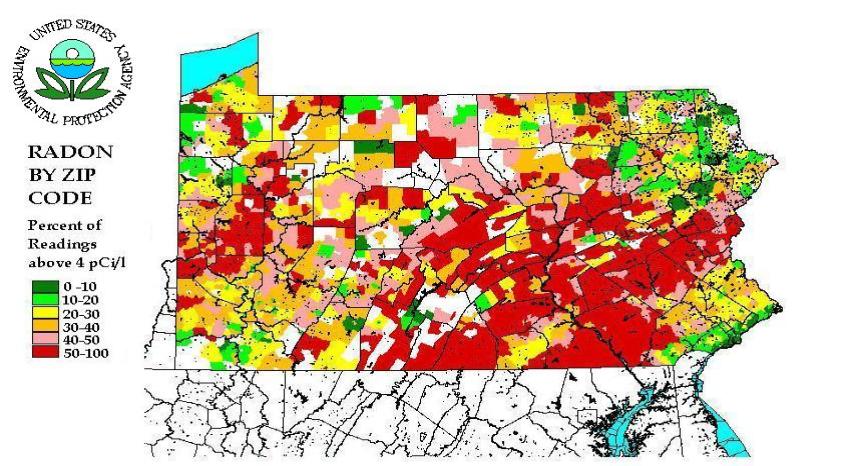


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Radon in Pennsylvania: A Guide to the State’s Radon Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!