Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being
Related Articles: Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being
- 3.1 Deciphering Canine Communication: The Language of the Body
- 3.2 Recognizing Potential Health Issues: The Body Speaks Volumes
- 3.3 Optimizing Canine Care: Building a Strong Human-Animal Bond
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions About the Canine Body Map
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing the Canine Body Map
- 3.6 Conclusion: Enhancing the Human-Canine Bond
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being

The canine body map is a visual representation of the various areas on a dog’s body that communicate specific emotions and intentions. It serves as a vital tool for understanding canine behavior, fostering a deeper bond between humans and their furry companions, and ultimately enhancing the well-being of both. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the canine body map, exploring its significance in recognizing canine communication, identifying potential health issues, and optimizing canine care.
Deciphering Canine Communication: The Language of the Body
Dogs, much like humans, rely on a complex interplay of verbal and nonverbal cues to convey their feelings and intentions. While vocalizations like barking, howling, and whimpering play a role, it is the subtle nuances of body language that offer the most profound insights into a dog’s emotional state. The canine body map acts as a guide to these nonverbal signals, allowing humans to interpret the silent messages dogs are constantly sending.
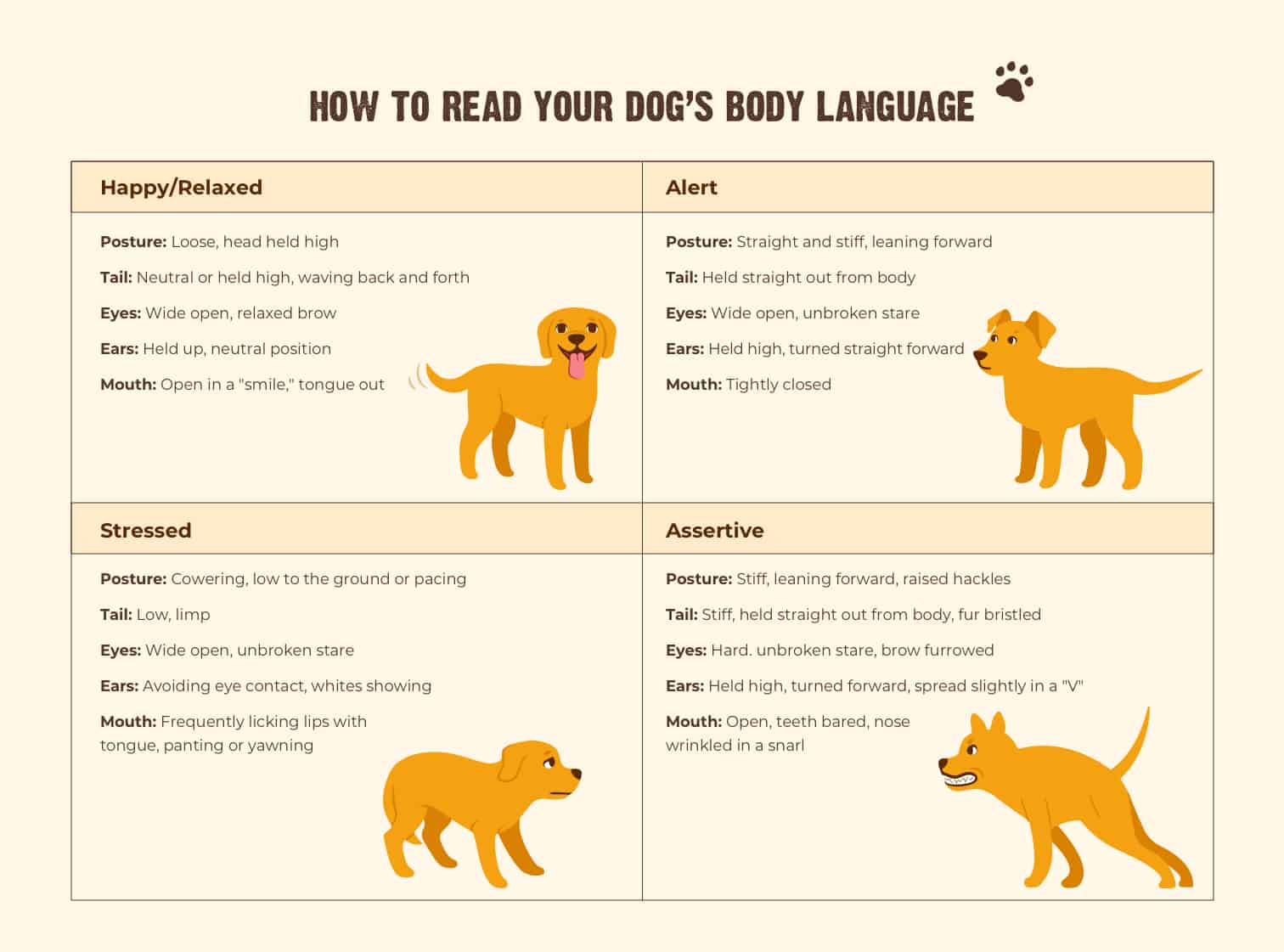
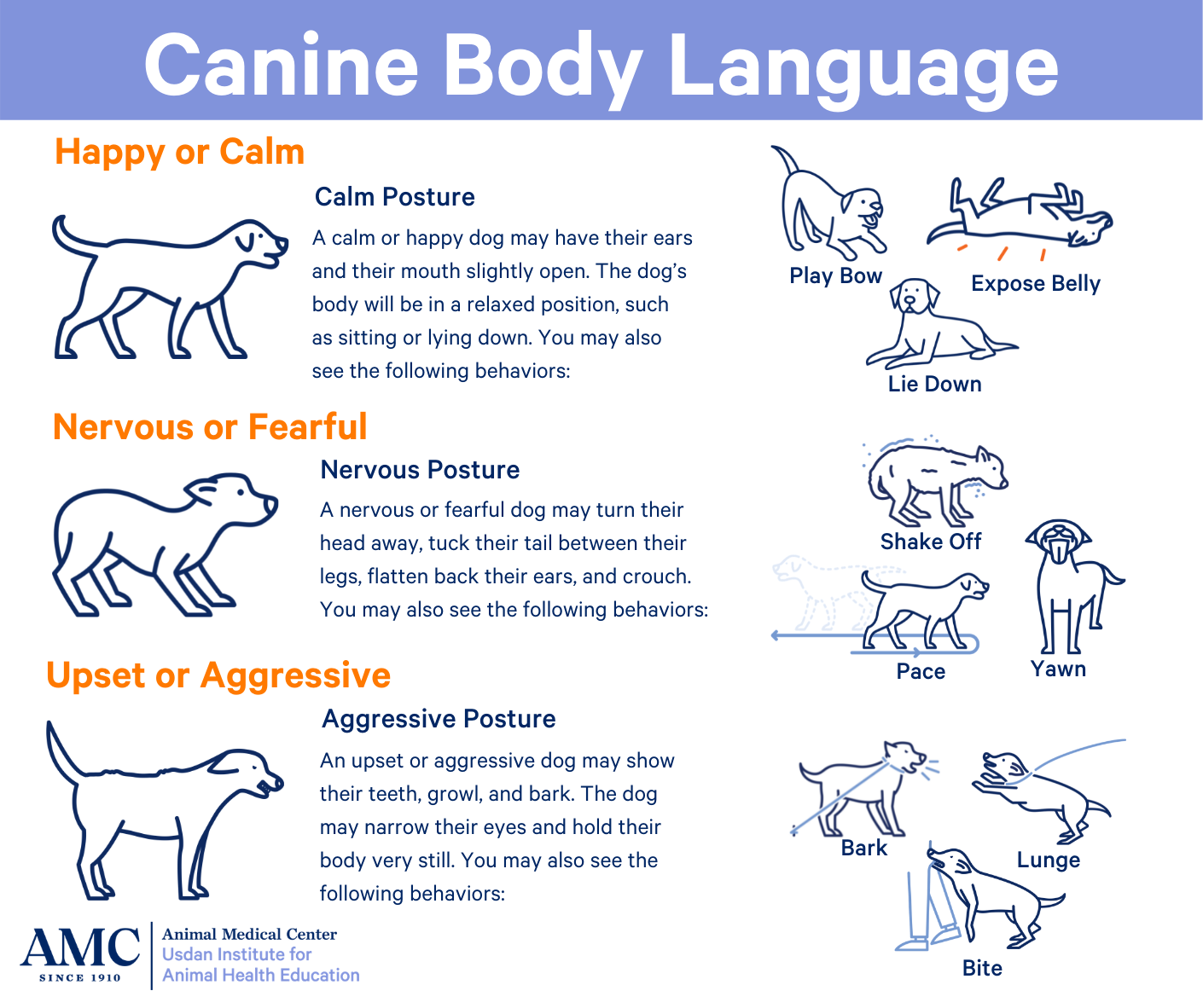
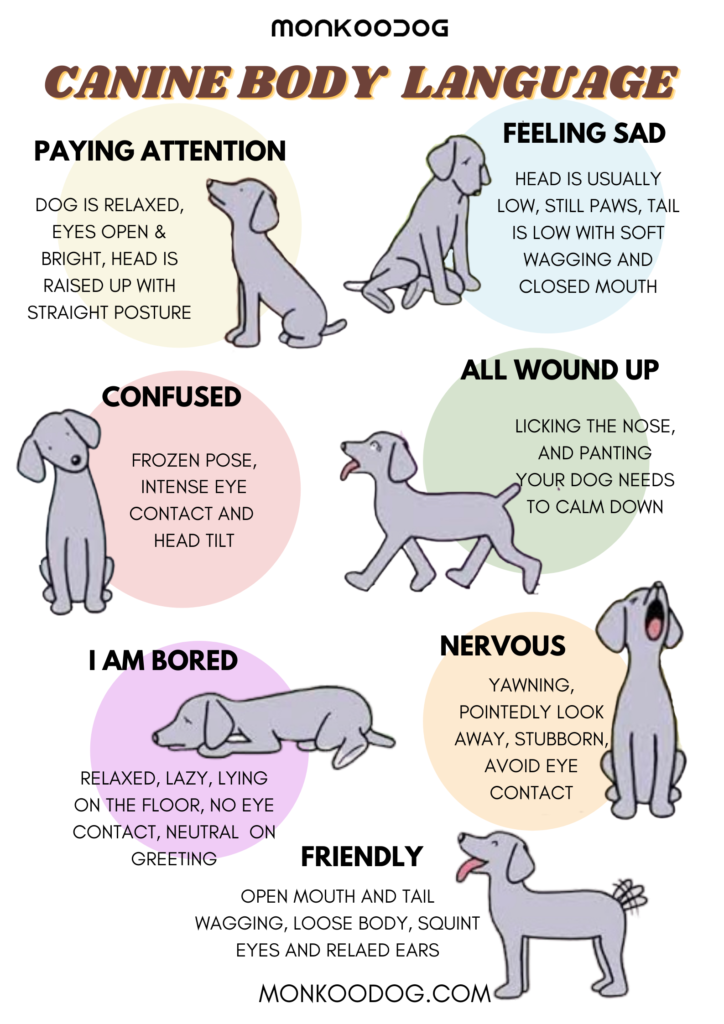
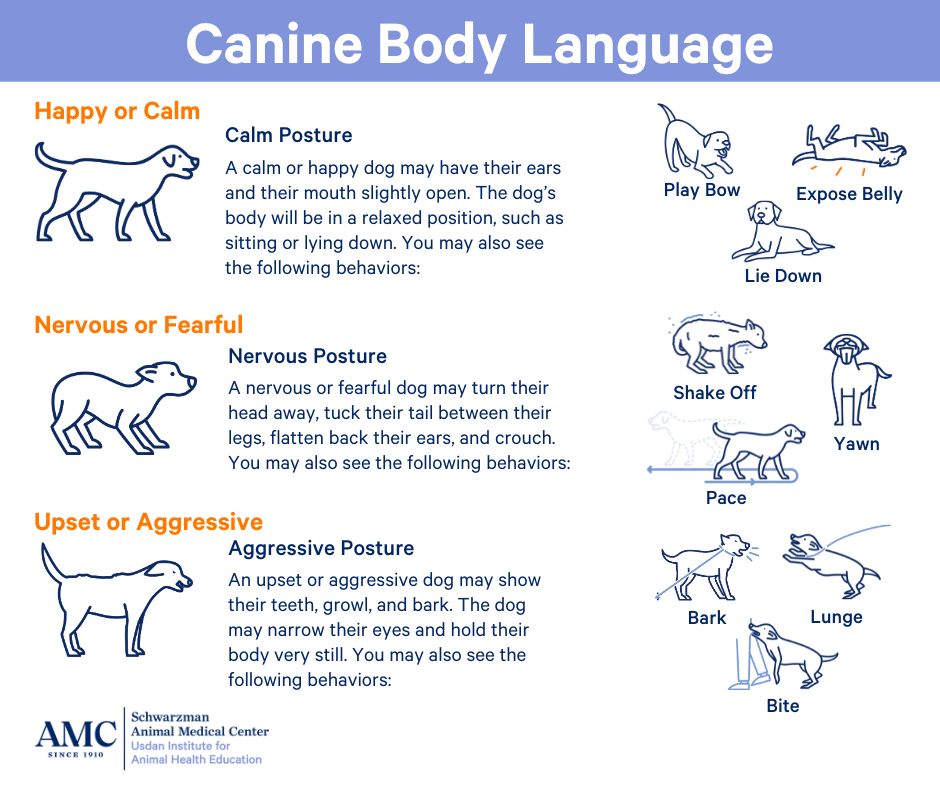
Key Areas of the Canine Body Map and Their Meanings:
- Ears: Erect ears often signify alertness, excitement, or playfulness. Drooped or flattened ears can indicate fear, anxiety, or submission.
- Eyes: Dilated pupils suggest fear, excitement, or arousal. Constricted pupils might indicate aggression or focus. A direct gaze can be a sign of dominance or challenge, while avoiding eye contact often signals submission or fear.
- Mouth: A relaxed, open mouth with a slightly panting tongue indicates contentment. Lip licking can be a sign of anxiety or anticipation. A closed mouth with tightly pressed lips often signals aggression or fear.
- Tail: A wagging tail is generally associated with happiness, but the speed and height of the wag can provide further clues. A low, slow wag might indicate uncertainty or nervousness, while a high, fast wag often signifies excitement or playfulness. A tucked tail indicates fear or submission.
- Body Posture: A relaxed, upright posture with a loose, wagging tail suggests confidence and well-being. A hunched posture with a tucked tail indicates fear or anxiety. A stiff, rigid stance often signifies aggression or territoriality.
- Fur: Raised hackles (the hair along the back) can indicate arousal, excitement, or fear. Shaking or trembling can be a sign of anxiety, fear, or pain.
Beyond the Basics:
Understanding the nuances within each area of the canine body map allows for a more comprehensive interpretation of a dog’s emotional state. For instance, a dog that is panting heavily with a relaxed, open mouth might be experiencing stress or anxiety, while a dog that is panting slightly with a wagging tail is likely just enjoying a game of fetch.
Recognizing Potential Health Issues: The Body Speaks Volumes
Beyond emotional communication, the canine body map also serves as a valuable tool for identifying potential health issues. Subtle changes in a dog’s posture, gait, or facial expressions can signal underlying medical conditions. For example, a dog that is limping or favoring one leg might be experiencing pain or injury. A dog that is constantly licking its paws or scratching its ears could be suffering from allergies or skin infections.
The Importance of Observation:
Regularly observing a dog’s body language and noting any changes can help owners identify potential health problems early on. Early detection of health issues allows for prompt veterinary intervention, leading to better outcomes for the dog.
Optimizing Canine Care: Building a Strong Human-Animal Bond
By understanding the canine body map, humans can foster a deeper connection with their dogs, leading to improved communication, trust, and overall well-being.
Building Trust and Understanding:
When humans can accurately interpret their dog’s body language, they can respond appropriately, building trust and reducing anxiety in the dog. This can manifest in various ways, such as offering comfort during stressful situations, providing reassurance during vet visits, or simply understanding when a dog needs space.
Positive Reinforcement and Training:
The canine body map can also be used to enhance training. By recognizing a dog’s subtle cues, trainers can implement positive reinforcement techniques at the right moment, maximizing learning and reducing stress.
Creating a Safe and Comfortable Environment:
Understanding a dog’s body language can help owners create a more comfortable and safe environment for their pets. By recognizing signs of fear or anxiety, owners can take steps to mitigate those triggers and reduce stress levels.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Canine Body Map
Q: Can I teach my dog to understand human body language?
A: While dogs are adept at interpreting human facial expressions and tone of voice, they do not have the same level of understanding as humans when it comes to complex body language. However, through consistent positive reinforcement and training, dogs can learn to associate specific human gestures with certain actions or commands.
Q: How can I learn more about the canine body map?
A: There are numerous resources available to help you learn more about the canine body map, including books, online articles, and training courses. Consulting a certified dog trainer or behaviorist can provide personalized guidance and support.
Q: Is the canine body map applicable to all breeds?
A: Yes, the canine body map is applicable to all breeds, as it reflects the fundamental communication signals shared by all dogs. However, individual breeds might exhibit subtle variations in their body language due to their unique physical characteristics or temperament.
Q: What are some common misconceptions about the canine body map?
A: A common misconception is that a wagging tail always indicates happiness. While a wagging tail is often a sign of positive emotions, the speed, height, and other accompanying body language signals provide a more accurate interpretation. Another misconception is that a dog that is growling is about to attack. Growling can be a warning signal, but it can also be a sign of fear or anxiety.
Tips for Utilizing the Canine Body Map
- Observe Regularly: Pay close attention to your dog’s body language during everyday interactions, noting any subtle changes or patterns.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult a certified dog trainer or behaviorist to gain a deeper understanding of canine communication and learn to interpret specific body language cues.
- Be Patient and Consistent: Learning to interpret the canine body map takes time and practice. Be patient with yourself and your dog, and focus on consistent positive reinforcement.
- Create a Safe and Comfortable Environment: Identify and address any triggers that might cause your dog anxiety or fear, creating a safe and stress-free environment.
Conclusion: Enhancing the Human-Canine Bond
The canine body map is a powerful tool for fostering a deeper understanding of canine communication, recognizing potential health issues, and optimizing canine care. By recognizing the subtle signals dogs send through their body language, humans can build stronger bonds with their furry companions, creating a more harmonious and fulfilling relationship. The canine body map is not just a guide to understanding canine behavior; it is a bridge that connects humans and dogs, allowing for a more empathetic and enriching partnership.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Canine Body Map: A Guide to Canine Communication and Well-being. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!