Unlocking the Secrets of Africa: A Journey Through Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Africa: A Journey Through Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Africa: A Journey Through Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Africa: A Journey Through Longitude and Latitude
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich cultures, and a history spanning millennia. Understanding its geographical layout, particularly through the lens of longitude and latitude, unlocks a deeper appreciation for its complexities and unveils the interconnectedness of its various regions.
The Grid of Geography: Longitude and Latitude
Longitude and latitude form a fundamental grid system used to pinpoint locations on Earth. Imagine a globe sliced into sections like an orange. The lines running vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole represent lines of longitude, also known as meridians. These lines converge at the poles and are measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England.
Lines of latitude, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the globe, parallel to the equator. The equator, situated at 0 degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude is measured in degrees north or south of the equator.
Africa’s Geographic Embrace: A Look at Longitude and Latitude
Africa’s geographical position, stretching across both hemispheres, is defined by its unique relationship with longitude and latitude.
- Prime Meridian and Africa: The Prime Meridian passes through Western Africa, specifically through Ghana, Togo, and Benin. This line marks the starting point for measuring longitude.
- Equator’s Embrace: The equator cuts through the continent, dividing it into two distinct halves. This line marks the point of zero degrees latitude, with areas north of the equator experiencing the Northern Hemisphere’s seasons and areas south experiencing the Southern Hemisphere’s.
- Extremes of Latitude: Africa extends from approximately 37 degrees North latitude at its northernmost point in Tunisia to 35 degrees South latitude at its southernmost point in South Africa. This vast latitudinal range contributes to the continent’s diverse climate zones, from the scorching Sahara Desert in the north to the temperate climates of the southern tip.
- Longitude’s Influence: Africa’s longitudinal span, from 18 degrees West to 51 degrees East, reveals its vastness. This range encompasses a multitude of time zones, with each 15-degree longitude representing a one-hour difference.
Navigating Africa: The Importance of Longitude and Latitude
Understanding the role of longitude and latitude in defining Africa’s geography is crucial for various reasons:
- Accurate Location: Longitude and latitude provide the precise coordinates for any point on the continent, enabling navigation, mapping, and location-based services.
- Climate Understanding: Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate patterns. Areas closer to the equator experience more consistent temperatures and higher humidity, while areas further north or south experience greater seasonal variations.
- Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of resources like water, minerals, and fertile land is essential for sustainable development. Longitude and latitude help map these resources and inform strategies for their effective management.
- Environmental Conservation: Mapping biodiversity hotspots, identifying areas prone to climate change impacts, and monitoring wildlife movements are crucial for conservation efforts. Longitude and latitude are essential tools for these endeavors.
- Cultural Connections: Understanding the geographic distribution of diverse cultures and languages within Africa is crucial for fostering intercultural dialogue and promoting understanding.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of Africa’s Geography
1. What is the significance of the Prime Meridian passing through Africa?
The Prime Meridian’s passage through Africa highlights its central position in the global grid system. This line serves as the reference point for measuring longitude, influencing time zones and geographical calculations across the continent.
2. How does latitude affect Africa’s climate?
Latitude significantly influences Africa’s climate zones. Regions closer to the equator experience more consistent temperatures and higher humidity due to the direct sunlight they receive. As one moves further north or south, the sun’s angle becomes more oblique, resulting in greater temperature variations and distinct seasons.
3. Why is understanding Africa’s longitude and latitude essential for resource management?
Accurate mapping of Africa’s resources, such as water bodies, mineral deposits, and fertile land, is crucial for their sustainable management. Longitude and latitude provide precise coordinates for these resources, enabling their effective allocation and utilization.
4. How does latitude influence biodiversity in Africa?
Latitude plays a significant role in shaping Africa’s diverse ecosystems. The equator’s proximity fosters high biodiversity, with a wide array of plant and animal species thriving in its warm and humid environment. As one moves away from the equator, the diversity of species tends to decrease, influenced by factors like temperature and rainfall.
5. How can longitude and latitude contribute to peacebuilding in Africa?
Understanding the geographical distribution of ethnic groups, languages, and cultural practices within Africa is crucial for promoting peaceful coexistence. Mapping these elements through longitude and latitude can help build bridges between communities and foster understanding across different regions.
Tips for Exploring Africa’s Geography:
- Interactive Maps: Utilize online interactive maps that allow you to zoom in on specific areas, explore different layers of information, and gain insights into the continent’s geographic features.
- Satellite Imagery: Explore satellite imagery to visualize the vastness of Africa’s landscapes, from its sprawling deserts to its lush forests.
- Geographic Data: Access geographic data sets, such as those provided by organizations like the World Bank or NASA, to analyze specific aspects of Africa’s geography, such as population distribution, resource availability, or environmental conditions.
- Travel and Exploration: Immerse yourself in the beauty of Africa by traveling to different regions and experiencing firsthand the diverse landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems that make this continent so unique.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
Africa’s geography, meticulously defined by longitude and latitude, holds a wealth of information that shapes our understanding of its diverse landscapes, climate patterns, and cultural tapestry. By delving into the intricacies of this grid system, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the continent’s complexities and gain valuable insights into its resources, ecosystems, and cultural heritage. Through continued exploration and understanding, we can contribute to the sustainable development and peaceful coexistence of this remarkable continent.
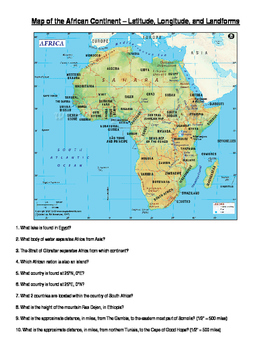
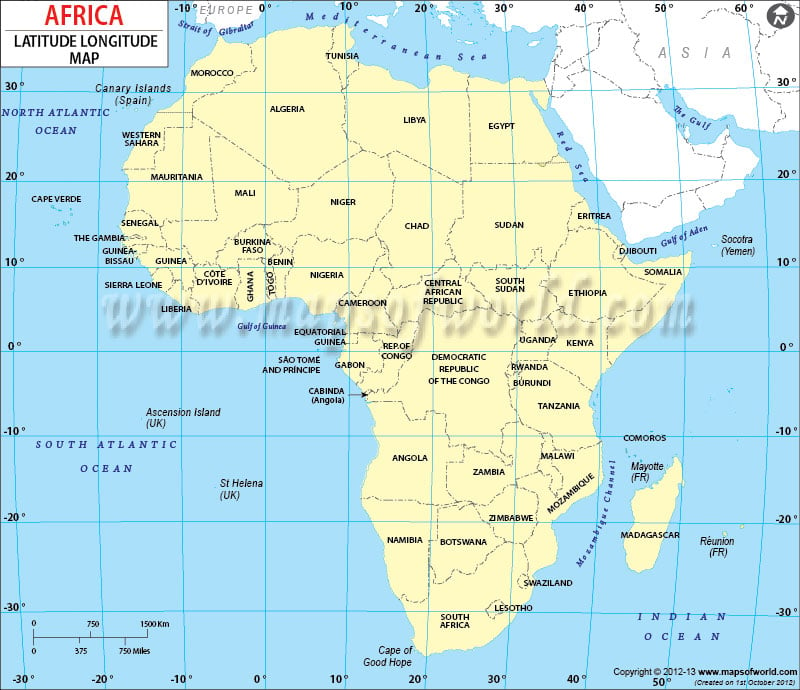



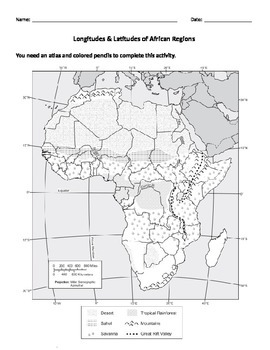
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Africa: A Journey Through Longitude and Latitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!