Unpacking the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Wisconsin’s Population Density Map
Related Articles: Unpacking the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Wisconsin’s Population Density Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Wisconsin’s Population Density Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Wisconsin’s Population Density Map

Wisconsin, the "Badger State," boasts a unique blend of urban centers, rural landscapes, and sprawling natural beauty. Understanding the distribution of its population across this diverse terrain is crucial for a range of purposes, from urban planning and infrastructure development to resource allocation and environmental management. This exploration delves into the intricate patterns revealed by Wisconsin’s population density map, providing insights into the state’s demographic makeup and its implications.
Defining Population Density: A Fundamental Concept
Population density, a key demographic indicator, measures the number of people residing within a specific geographic area. It is calculated by dividing the total population of a region by its land area. The result, typically expressed as people per square mile or kilometer, offers a snapshot of how densely populated an area is.
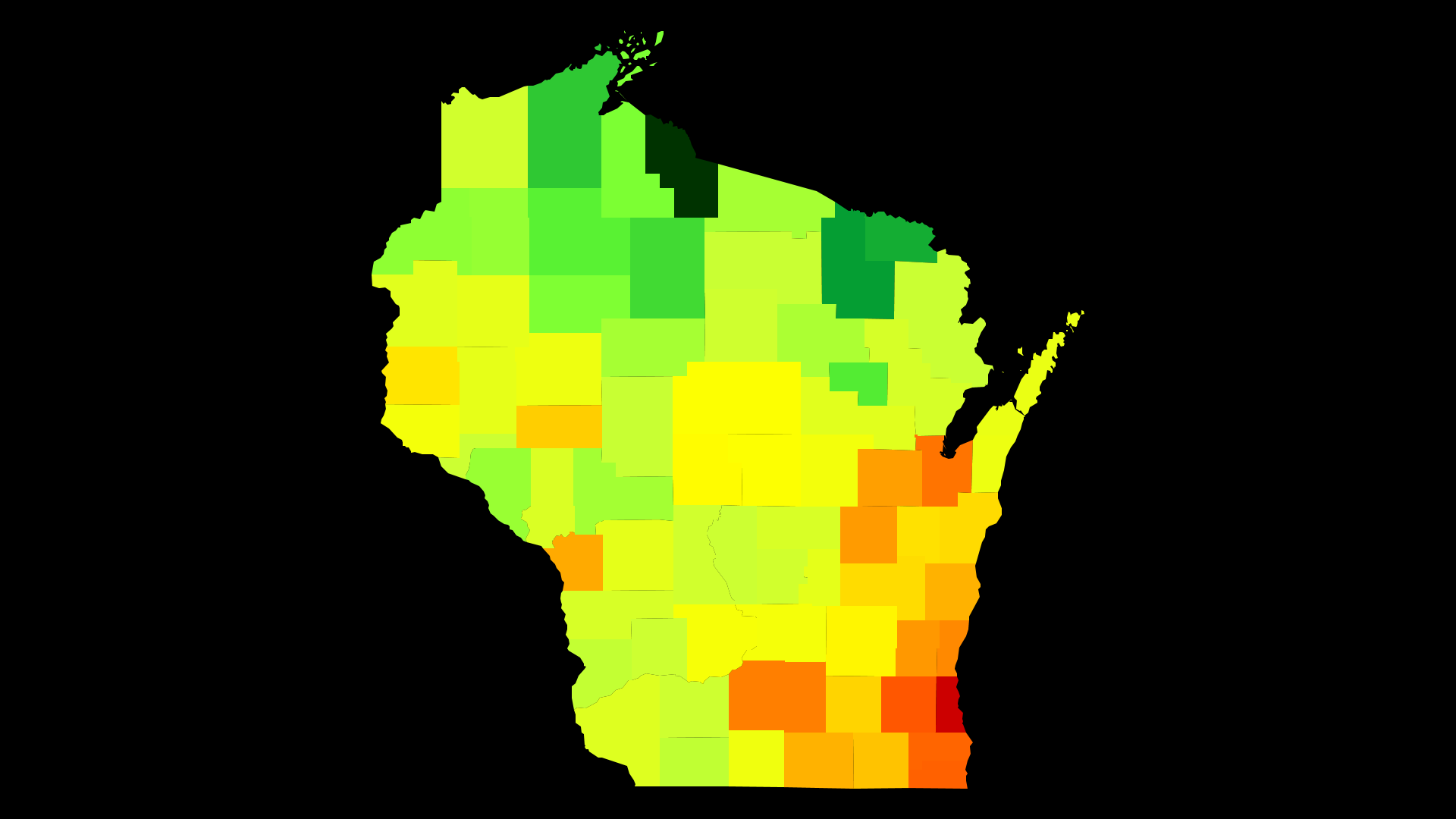
Decoding the Wisconsin Map: Unveiling Spatial Patterns
The population density map of Wisconsin reveals a distinct spatial distribution of its inhabitants. The southeastern region, encompassing Milwaukee and its surrounding counties, stands out as the most densely populated area. This region, home to major urban centers and industrial hubs, attracts a significant concentration of residents.
In contrast, the northern and western parts of the state, characterized by vast stretches of forests, farmland, and lakes, exhibit significantly lower population densities. This reflects the prevalence of rural communities and agricultural activities in these regions.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding the Factors at Play
The spatial patterns observed on Wisconsin’s population density map are shaped by a complex interplay of factors. These include:
- Economic Opportunities: The presence of major urban centers, industrial complexes, and thriving economies attracts residents seeking employment and higher standards of living.
- Natural Resources: Areas rich in natural resources, such as fertile farmlands, abundant water sources, and scenic landscapes, often attract residents seeking a different lifestyle.
- Historical Development: Wisconsin’s history of settlement patterns, influenced by factors like migration routes, transportation infrastructure, and land availability, has left an indelible mark on its population distribution.
- Accessibility and Infrastructure: Proximity to major transportation hubs, access to healthcare facilities, and availability of essential services influence population density patterns.
- Environmental Factors: Topography, climate, and natural hazards can impact population distribution, leading to higher densities in areas with favorable conditions and lower densities in challenging environments.
The Significance of Understanding Population Density
Understanding the intricacies of population density in Wisconsin is crucial for various stakeholders:
- Government Agencies: Population density data is vital for planning and allocating resources effectively. It informs decisions related to infrastructure development, transportation systems, public services, and emergency response.
- Urban Planners: Understanding population density helps in designing sustainable and livable cities, optimizing land use, and mitigating challenges associated with urbanization.
- Businesses and Industries: Population density data provides valuable insights for market analysis, identifying potential customer bases, and making informed decisions about location and investment.
- Environmental Organizations: Population density data is essential for assessing the environmental impact of human activities, monitoring resource consumption, and developing sustainable land management strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Wisconsin’s Population Density Map
1. What is the average population density of Wisconsin?
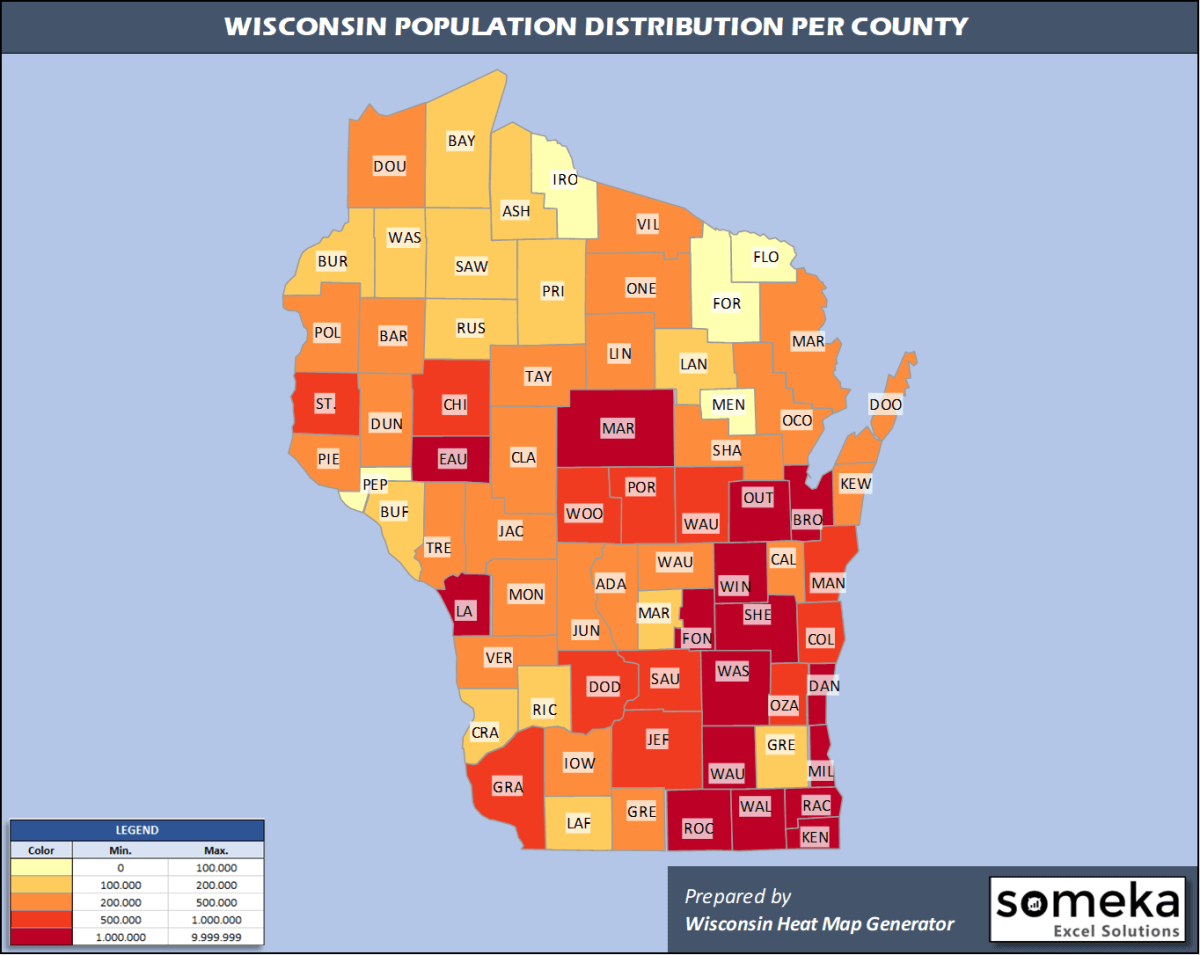
The average population density of Wisconsin is approximately 105 people per square mile. However, this figure is heavily influenced by the wide range of densities observed across different regions.
2. What are the most densely populated counties in Wisconsin?
Milwaukee County, home to the city of Milwaukee, is the most densely populated county in Wisconsin, with a density exceeding 1,300 people per square mile. Other densely populated counties include Dane County (Madison), Waukesha County, and Brown County (Green Bay).
3. How has population density changed in Wisconsin over time?
Wisconsin has witnessed a gradual increase in population density over the past century, driven by urbanization, economic growth, and migration patterns. However, the rate of change has varied across different regions, with some areas experiencing more significant shifts than others.
4. What are the implications of population density for the environment?
Higher population density often translates to increased resource consumption, pollution, and pressure on natural ecosystems. It is essential to consider the environmental impact of population growth and to implement sustainable practices to mitigate these challenges.
5. How can population density data be used to promote economic development?
Population density data can help identify areas with strong economic potential, attracting businesses and investments. It can also inform the development of infrastructure and services that support economic growth and job creation.
Tips for Utilizing Population Density Data
- Visualize the data: Create maps and charts to effectively represent population density patterns and identify trends.
- Analyze the data in context: Consider the factors influencing population density in specific regions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Compare data over time: Track changes in population density to assess growth, decline, and shifts in distribution.
- Integrate data with other sources: Combine population density data with other relevant information, such as economic indicators, environmental data, and infrastructure details, for a comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion
The population density map of Wisconsin offers a valuable window into the state’s demographic landscape, revealing the spatial distribution of its inhabitants and the factors shaping these patterns. Understanding the intricate interplay of economic, historical, environmental, and social forces driving population density is crucial for informed decision-making in a wide range of sectors, from government planning and urban development to business strategy and environmental management. By leveraging the insights gleaned from this map, stakeholders can contribute to the sustainable growth and well-being of Wisconsin’s diverse communities.
![Wisconsin population density map [600 x 600]. : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/K0jBM5NP7WUATUpw7Iqc7VIXQpHVBfKMwOz2PSfpR_o.png?auto=webpu0026s=4d2182e4d3a440c4d1b9255b8e2987259b6d9571)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Wisconsin’s Population Density Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!