Unraveling the Complex Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Israel and Middle East Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Complex Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Israel and Middle East Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Complex Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Israel and Middle East Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Complex Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Israel and Middle East Map

The Israel and Middle East map is a microcosm of a region steeped in history, conflict, and cultural diversity. Its intricate tapestry of borders, nations, and contested territories reflects a complex geopolitical landscape that has captivated the world for centuries. This article delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its historical context, current realities, and the significance it holds for the region and beyond.
A Historical Perspective: Tracing the Evolution of the Map
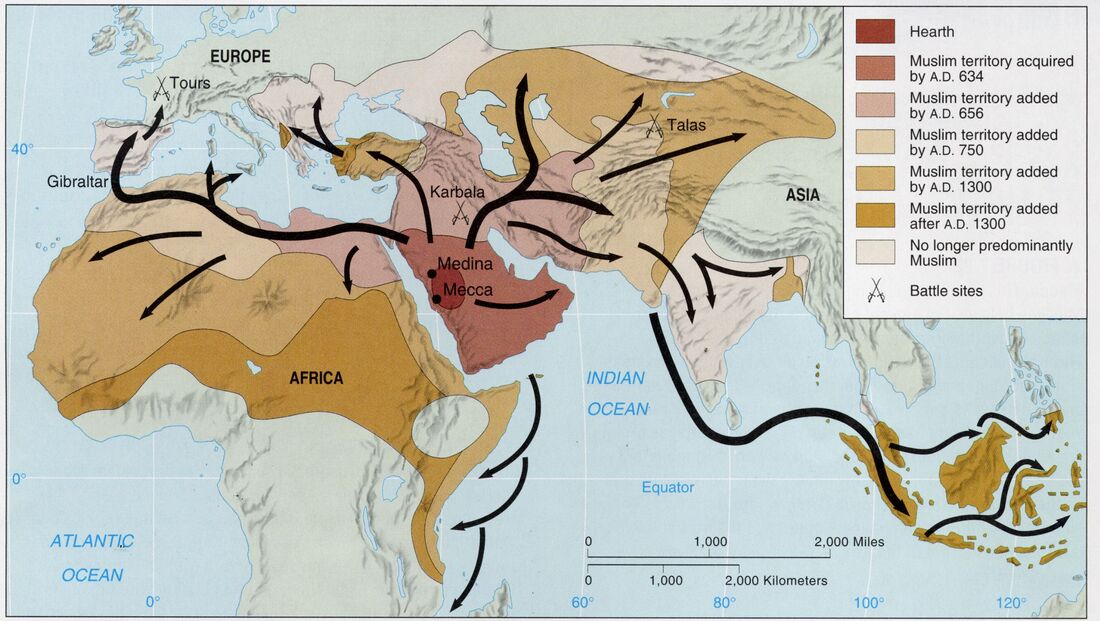
The Middle East, a region geographically defined by the confluence of Asia, Africa, and Europe, has witnessed a dramatic transformation in its political landscape over the centuries. The map we see today is the product of numerous historical events, including:
- The Rise and Fall of Empires: From the ancient empires of Mesopotamia and Egypt to the Ottoman Empire, various powers have shaped the region’s borders and influenced its cultural and political development.
- The Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916): This secret agreement between Britain and France carved up the Ottoman Empire after World War I, creating the modern-day states of Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine. This agreement, however, ignored the complex ethnic and religious realities of the region, laying the foundation for future conflicts.
- The Creation of Israel (1948): The establishment of Israel in 1948, following the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, triggered the first Arab-Israeli War and set in motion a series of conflicts that continue to shape the region today.
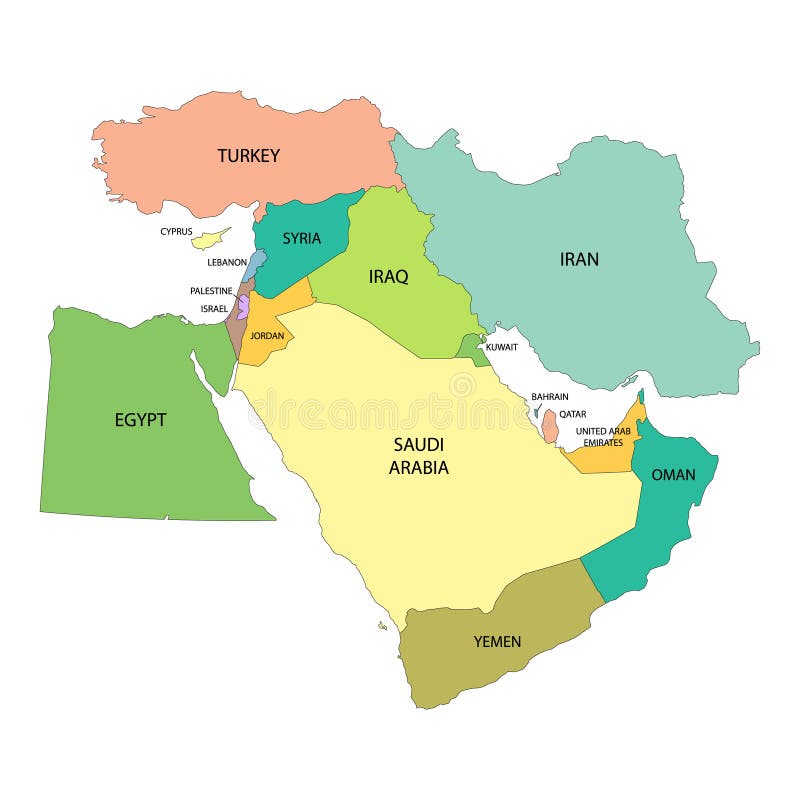
Understanding the Current Landscape: A Complex Mosaic of Nations
The modern Middle East map is a mosaic of diverse nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system. Key countries in the region include:
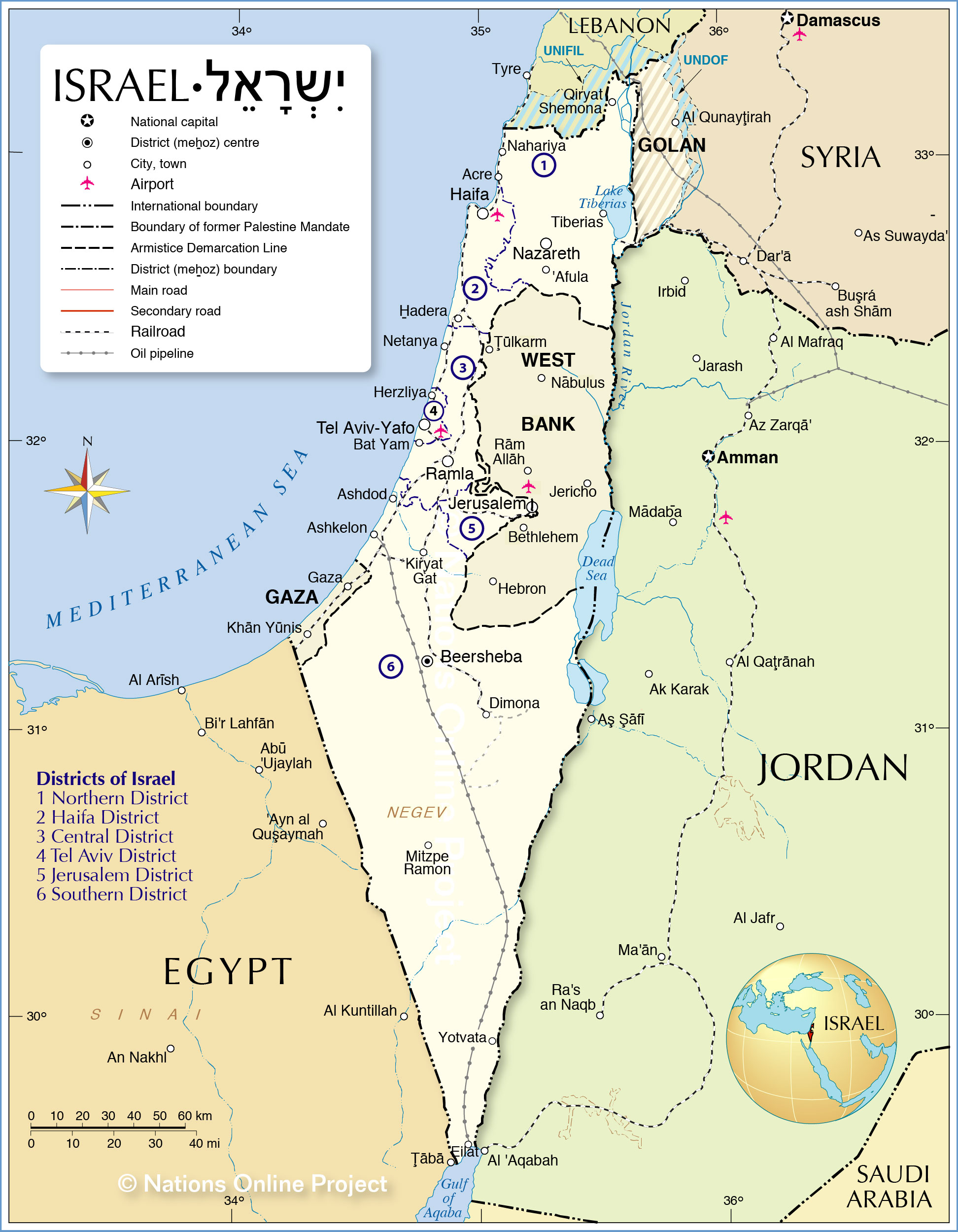
- Israel: Located on the eastern Mediterranean coast, Israel is a modern, technologically advanced nation with a complex relationship with its neighbors. Its territorial boundaries are a source of ongoing dispute, particularly with Palestine.
- Palestine: The Palestinian territories, comprising the West Bank and Gaza Strip, are home to a Palestinian population seeking self-determination and an independent state. The ongoing conflict with Israel has resulted in a humanitarian crisis and international scrutiny.
- Egypt: A large and influential nation bordering Israel, Egypt played a pivotal role in the Arab-Israeli conflicts. It signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1979, marking a significant development in regional relations.
- Jordan: Located east of Israel, Jordan shares a long border with the Palestinian territories. It has played a crucial role in mediating peace efforts and providing humanitarian assistance to Palestinians.
- Syria: A country ravaged by civil war, Syria shares a border with Israel and Lebanon. Its political instability and ongoing conflict have had a profound impact on the region.
- Lebanon: A small, mountainous country, Lebanon is known for its diverse religious and ethnic communities. It has faced political instability and conflict, particularly with Israel, over the years.
- Saudi Arabia: A dominant power in the region, Saudi Arabia is a major oil producer and a key player in international politics. It has a complex relationship with Israel, with both countries engaging in behind-the-scenes diplomacy.
- Iraq: A country plagued by instability and conflict, Iraq shares a border with Kuwait and Iran. Its political and economic situation has been impacted by the 2003 US-led invasion and subsequent sectarian violence.
- Iran: A powerful regional player, Iran has a long history of conflict with the United States and Israel. Its nuclear program and support for militant groups have been sources of international concern.
The Importance of the Map: A Geopolitical Hub of Global Significance
The Israel and Middle East map holds immense geopolitical significance due to its:
- Strategic Location: The region is located at the crossroads of three continents, making it a vital hub for trade, energy resources, and global power dynamics.
- Natural Resources: The region is rich in oil and gas reserves, making it a crucial player in the global energy market.
- Religious Significance: The Middle East is the birthplace of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, making it a sacred land for millions of people worldwide.
- Cultural Diversity: The region is home to a diverse array of cultures, languages, and traditions, representing a unique tapestry of human experience.
The Challenges of the Map: Conflict, Instability, and the Quest for Peace
The Israel and Middle East map is also a testament to the challenges facing the region, including:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The conflict between Israel and Palestine remains a major source of tension and instability, with ongoing violence and humanitarian crises.
- Regional Conflicts: The region has witnessed numerous conflicts, including wars in Iraq, Syria, and Yemen, further destabilizing the region and causing widespread suffering.
- Political Instability: Many countries in the region face political instability, including coups, authoritarian regimes, and sectarian violence.
- Economic Challenges: The region faces economic challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and a lack of infrastructure development.
The Quest for Peace: Diplomacy, Dialogue, and the Future of the Map
Despite the numerous challenges, there are ongoing efforts to achieve peace and stability in the region. These efforts include:
- Diplomacy and Negotiations: International organizations and individual countries are actively involved in diplomatic efforts to resolve conflicts and promote dialogue between opposing parties.
- Peace Agreements: The Israel-Egypt peace treaty of 1979 and the Oslo Accords of the 1990s represent significant steps towards peace, although their implementation has been challenging.
- Humanitarian Aid: International organizations and governments are providing humanitarian aid to alleviate the suffering caused by conflicts and disasters in the region.
Understanding the Israel and Middle East Map: A Key to Navigating the Future
The Israel and Middle East map is a dynamic and complex entity, reflecting the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing challenges. Understanding its intricate details is crucial for navigating the future of the region and for fostering peace, stability, and prosperity for all its inhabitants.
FAQs about the Israel and Middle East Map:
Q: What are the main historical events that shaped the current map of the Middle East?
A: The map of the Middle East has been shaped by numerous historical events, including the rise and fall of empires, the Sykes-Picot Agreement, and the creation of Israel in 1948. These events have led to the current configuration of borders, nations, and contested territories.
Q: What are the major conflicts in the Middle East?
A: The region has witnessed numerous conflicts, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the wars in Iraq and Syria, and the ongoing conflict in Yemen. These conflicts have caused immense suffering, displacement, and political instability.
Q: What are the key challenges facing the Middle East?
A: The region faces numerous challenges, including political instability, economic hardship, sectarian violence, and the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. These challenges require a multifaceted approach to address their root causes and foster lasting peace and stability.
Q: What are the prospects for peace in the Middle East?
A: The prospects for peace in the Middle East are uncertain, but there are ongoing diplomatic efforts to resolve conflicts and promote dialogue. The success of these efforts will depend on the willingness of all parties to compromise and engage in good faith negotiations.
Tips for Understanding the Israel and Middle East Map:
- Study the history of the region: Understanding the historical events that shaped the current map is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the region.
- Explore the cultural diversity: The Middle East is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and religions. Learn about the different communities and their perspectives.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region, including political negotiations, humanitarian crises, and conflict situations.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Be respectful of different perspectives and engage in constructive conversations about the challenges facing the region.
Conclusion:
The Israel and Middle East map is a testament to the region’s intricate history, diverse cultures, and ongoing challenges. While the map represents a complex geopolitical landscape, it also offers hope for a brighter future. By understanding the region’s complexities, engaging in constructive dialogue, and promoting peaceful solutions, we can contribute to a more stable and prosperous Middle East.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Complex Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Israel and Middle East Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!