Unveiling Spatial Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Spatial Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Heat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Spatial Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Spatial Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Heat Maps

In the realm of data visualization, geographic heat maps stand out as a powerful tool for revealing spatial patterns and trends. They transform complex datasets into visually compelling representations, making it easier to identify hot spots, areas of concentration, and geographical disparities. This guide delves into the intricacies of geographic heat maps, exploring their construction, applications, and benefits across diverse fields.
Understanding the Essence of Geographic Heat Maps
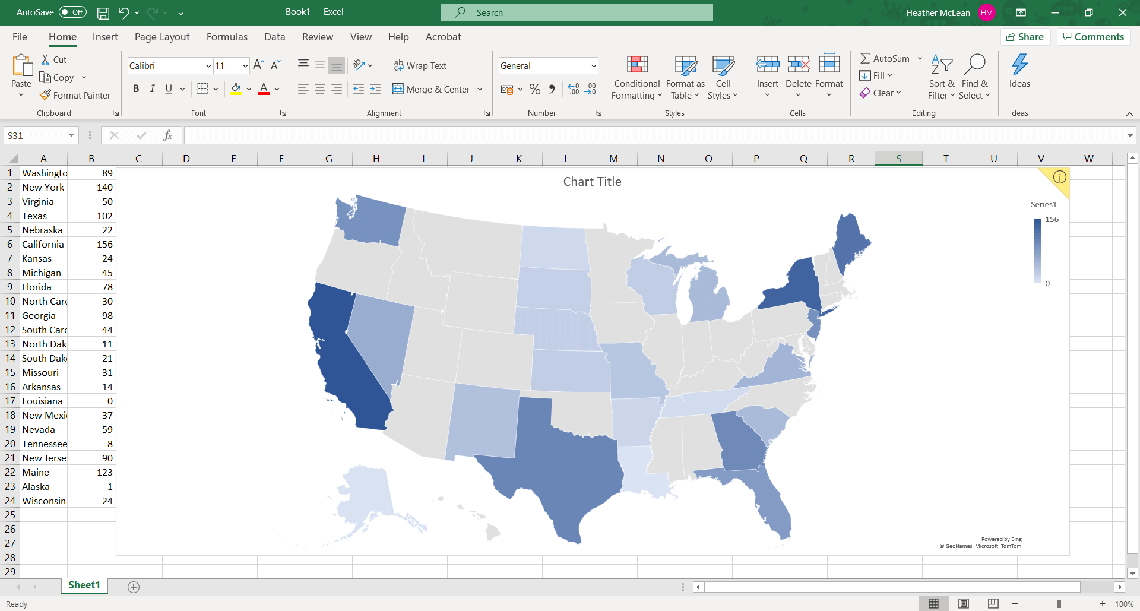
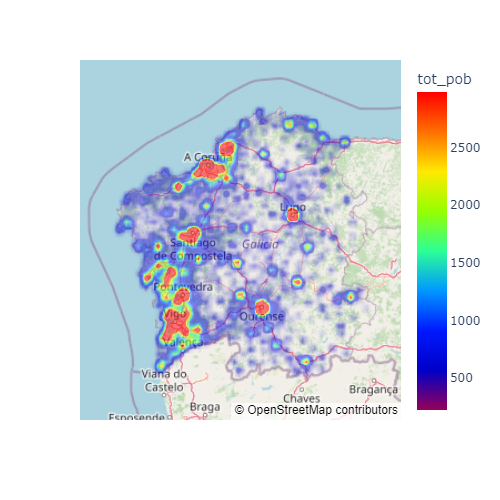
At its core, a geographic heat map is a visual representation of data that is geographically referenced. It utilizes color gradients or intensity levels to depict the density or concentration of a particular variable across a map. Areas with higher values are typically rendered in warmer colors (e.g., red, orange), while areas with lower values are depicted in cooler colors (e.g., blue, green). This color scheme facilitates the identification of regions with high and low values, instantly revealing spatial patterns and trends.
The Construction of a Geographic Heat Map
Creating a geographic heat map involves several key steps:
-
Data Collection and Preparation: The process begins with gathering relevant data, ensuring its accuracy and completeness. This data might include location coordinates, population density, crime rates, sales figures, or any other variable that exhibits geographic variation.
-
Spatial Reference System: The data is then linked to a specific geographical reference system, such as latitude and longitude, allowing it to be accurately positioned on a map.
-
Data Aggregation: Depending on the desired level of detail, data points might be aggregated into specific geographic units, such as counties, zip codes, or census tracts. This aggregation step helps to create a smooth visual representation of the data.
-
Color Scheme and Legend: A color scheme is selected to represent the data values, with warmer colors indicating higher values and cooler colors indicating lower values. A legend is included to clearly indicate the correspondence between color and data range.
-
Visualization Platform: The heat map is then generated using a suitable visualization platform, such as GIS software, online mapping tools, or data visualization libraries. These platforms allow for customization of the map’s appearance, including the addition of base maps, labels, and other relevant information.
Applications of Geographic Heat Maps: A Diverse Landscape
Geographic heat maps find widespread application across numerous fields, proving invaluable in understanding spatial patterns and trends:
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market Research: Identify areas with high customer concentration, target specific demographics, and optimize marketing campaigns based on location-specific insights.
- Sales Analysis: Track sales performance across different regions, identify high-performing areas, and allocate resources effectively.
- Location Optimization: Determine optimal locations for new stores, restaurants, or other businesses based on customer density and competition.
2. Public Health and Epidemiology:
- Disease Surveillance: Monitor the spread of infectious diseases, identify areas with high incidence, and track the effectiveness of public health interventions.
- Environmental Health: Analyze air and water quality data, pinpoint areas with high pollution levels, and identify potential health risks.
- Emergency Response: Visualize the impact of natural disasters, allocate resources efficiently, and guide emergency response efforts.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use Planning: Identify areas suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial development based on factors such as population density, transportation infrastructure, and environmental constraints.
- Traffic Management: Analyze traffic flow patterns, identify congestion hotspots, and implement measures to improve traffic efficiency.
- Urban Renewal: Visualize areas in need of revitalization, identify potential development opportunities, and guide urban renewal projects.
4. Environmental Science and Climate Change:
- Climate Modeling: Visualize climate change impacts, such as temperature changes, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events, across different geographic regions.
- Species Distribution: Map the distribution of endangered species, identify areas with high biodiversity, and guide conservation efforts.
- Resource Management: Analyze resource availability, identify areas with high resource potential, and manage resource utilization sustainably.
5. Social Science and Demographics:
- Population Distribution: Visualize population density, identify areas with high or low population growth, and understand demographic trends.
- Crime Analysis: Map crime incidents, identify high-crime areas, and guide police resource allocation.
- Social Inequality: Analyze socioeconomic disparities, identify areas with high poverty rates, and guide social welfare programs.
Benefits of Geographic Heat Maps: Illuminating Insights
The adoption of geographic heat maps offers numerous benefits, making them a valuable tool for data analysis and decision-making:
- Visual Clarity: Geographic heat maps transform complex data into easily understandable visual representations, making it easier to identify spatial patterns and trends.
- Spatial Awareness: They provide a strong sense of place, allowing users to understand the geographic context of the data and its implications.
- Data Exploration: They facilitate the exploration of data in a spatial context, allowing users to identify relationships and insights that might not be apparent from tabular data alone.
- Decision Support: They provide valuable insights for informed decision-making, guiding resource allocation, strategic planning, and policy development.
- Communication Tool: They serve as effective communication tools, enabling the sharing of complex spatial data with diverse audiences.
FAQs About Geographic Heat Maps
1. What are the common types of geographic heat maps?
Geographic heat maps can be categorized based on their representation of data:
- Discrete Heat Maps: These maps use distinct colors or symbols to represent data values that fall within specific ranges.
- Continuous Heat Maps: These maps utilize color gradients to smoothly represent data values, with warmer colors indicating higher values and cooler colors indicating lower values.
2. How are geographic heat maps used in real-world scenarios?
Geographic heat maps are widely used in various fields, including:
- Public health: Tracking the spread of infectious diseases, identifying high-risk areas, and allocating resources for disease prevention.
- Marketing: Identifying customer demographics, targeting specific market segments, and optimizing advertising campaigns.
- Urban planning: Analyzing traffic patterns, identifying areas with high congestion, and designing efficient transportation networks.
- Environmental science: Mapping pollution levels, identifying areas with high environmental risks, and guiding conservation efforts.
3. What are the limitations of geographic heat maps?
While geographic heat maps are powerful visualization tools, they have some limitations:
- Data Aggregation: The aggregation of data can mask local variations and lead to oversimplification of the data.
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of the heat map can affect the accuracy of the representation, with coarser resolutions potentially obscuring important details.
- Data Bias: The data used to generate the heat map may be biased, leading to inaccurate or misleading representations.
Tips for Effective Use of Geographic Heat Maps
To maximize the effectiveness of geographic heat maps, consider the following tips:
- Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data used to generate the heat map.
- Spatial Resolution: Choose a spatial resolution that is appropriate for the scale of the data and the desired level of detail.
- Color Scheme: Select a color scheme that is visually appealing, conveys the data effectively, and avoids colorblindness issues.
- Legend: Provide a clear and concise legend that explains the relationship between color and data values.
- Contextual Information: Include relevant contextual information, such as base maps, labels, and other relevant data layers, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the data.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Geographic Heat Maps
Geographic heat maps offer a powerful and versatile approach to data visualization, enabling the identification of spatial patterns, trends, and insights that might otherwise be hidden. By transforming complex data into visually compelling representations, they empower decision-makers across diverse fields to gain a deeper understanding of spatial phenomena, make informed decisions, and drive positive change. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the importance of geographic heat maps as a tool for unlocking spatial insights will only continue to rise.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Spatial Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!