Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction
- 3.1 Deciphering the Symbols: A Visual Guide to Rainfall
- 3.2 Beyond the Map: Factors Influencing Rainfall
- 3.3 Understanding the Benefits of Weather Maps
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Maps and Rainfall
- 3.5 Tips for Interpreting Weather Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Importance of Weather Maps in a Changing World
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction

The sky, a vast canvas of ever-changing hues, holds within it the secrets of our planet’s weather. For centuries, humans have sought to decipher these secrets, striving to understand and predict the capricious dance of rain, sun, and wind. Today, we have powerful tools at our disposal, one of the most significant being the weather map.
This intricate web of lines, symbols, and colors, seemingly a jumble to the untrained eye, holds the key to understanding the movement of weather systems and, crucially, the likelihood of precipitation. Understanding weather maps allows us to prepare for the vagaries of nature, from planning outdoor activities to ensuring the safety of our communities.
Deciphering the Symbols: A Visual Guide to Rainfall
Weather maps, often referred to as synoptic charts, utilize a standardized set of symbols to represent various weather phenomena. Among these symbols, those related to rainfall are particularly important for understanding the potential for precipitation.
1. Rain Symbols:
- Solid Blue Circles: These represent rain, with the size of the circle indicating the intensity of the rainfall. Larger circles signify heavier rainfall.
- Solid Blue Triangles: These represent showers, characterized by intermittent periods of rain. The size of the triangle reflects the intensity of the showers.
- Solid Blue Squares: These denote thunderstorms, characterized by heavy rainfall, lightning, and strong winds. The size of the square indicates the severity of the thunderstorm.
2. Isobars:
Perhaps the most prominent feature on a weather map are the isobars, lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines provide crucial information about the movement of air masses, which directly influences rainfall patterns.
- Closely Spaced Isobars: Closely spaced isobars indicate a steep pressure gradient, signifying strong winds and potentially heavy rainfall.
- Widely Spaced Isobars: Widely spaced isobars suggest a gentle pressure gradient, indicating calmer winds and potentially lighter rainfall.
3. Fronts:
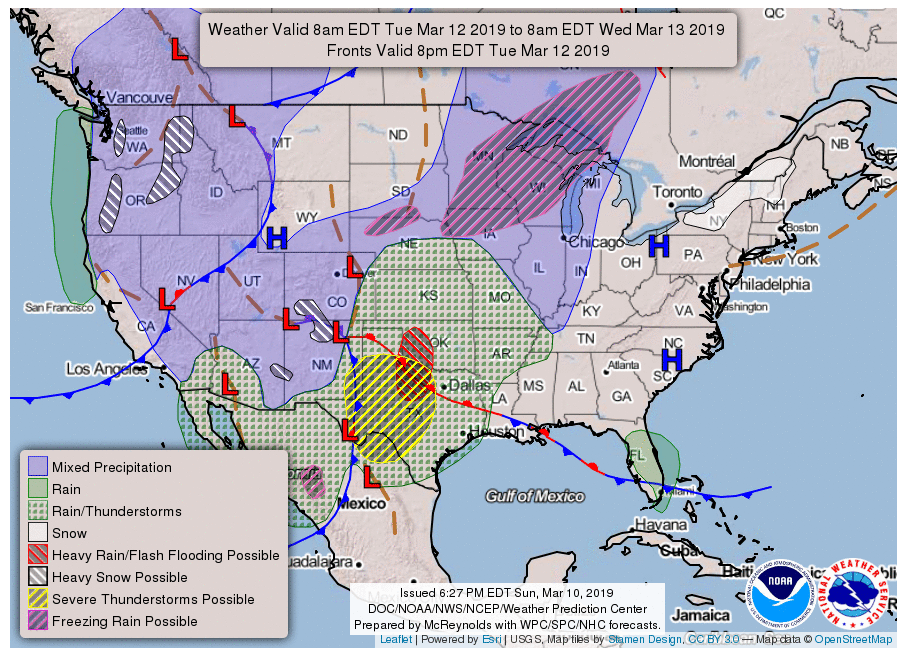
Fronts are boundaries between different air masses, often playing a pivotal role in precipitation events. Weather maps depict fronts using specific symbols:
- Cold Front: Represented by a line with blue triangles pointing in the direction of the front’s movement, a cold front brings a rapid change in temperature, often accompanied by heavy rain or thunderstorms.
- Warm Front: Depicted by a line with red semicircles pointing in the direction of the front’s movement, a warm front brings a gradual rise in temperature, typically accompanied by light to moderate rain.
- Stationary Front: Marked by alternating red semicircles and blue triangles, a stationary front brings prolonged periods of rain or drizzle as the air masses remain relatively stable.
- Occluded Front: Represented by a line with alternating purple triangles and semicircles, an occluded front is a complex system where a cold front overtakes a warm front, often leading to heavy rain and thunderstorms.
4. Other Rainfall Indicators:
- Precipitation Amount: Weather maps may include numbers representing the amount of rainfall expected over a specific period, often measured in millimeters or inches.
- Precipitation Probability: Some weather maps may also display a percentage indicating the likelihood of precipitation occurring in a particular location.
Beyond the Map: Factors Influencing Rainfall
While weather maps offer invaluable insight into the potential for rain, it’s crucial to remember that they are a snapshot in time. Rainfall patterns are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Altitude: Higher elevations typically experience more rainfall due to the cooling effect of rising air and the increased potential for orographic lift, where air is forced upwards by mountains.
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Areas near large bodies of water, such as oceans or lakes, tend to receive more rainfall due to increased moisture in the air.
- Wind Patterns: Prevailing wind patterns can transport moisture-laden air masses, influencing the distribution of rainfall.
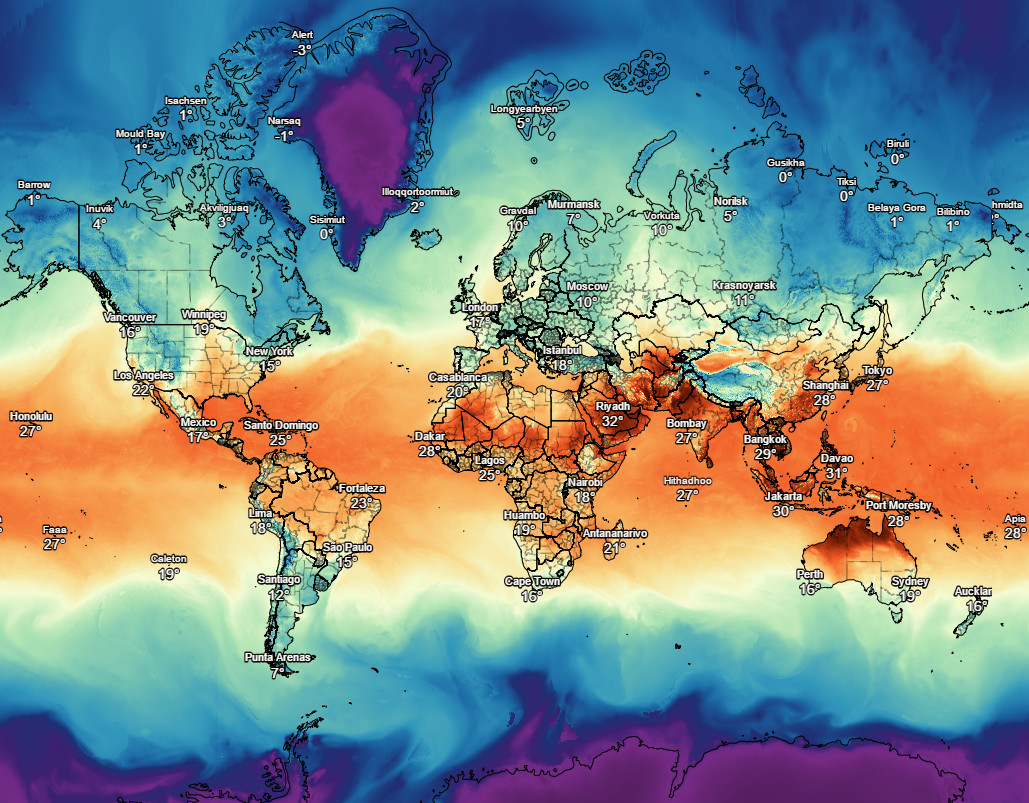
- Temperature: Warmer air can hold more moisture, increasing the potential for heavy rainfall.
- Topography: Mountain ranges can act as barriers to air flow, creating rain shadows on their leeward sides where rainfall is significantly reduced.
Understanding the Benefits of Weather Maps
The ability to predict rainfall through weather maps offers numerous benefits:
- Safety and Preparedness: Weather maps provide essential information for preparing for potential storms, flooding, and other weather-related hazards, allowing individuals and communities to take necessary precautions.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers rely heavily on weather maps to plan planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules, maximizing crop yields and mitigating potential losses due to adverse weather conditions.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: Weather maps help transportation authorities plan routes and manage traffic flow, minimizing delays and disruptions caused by heavy rain or snow.
- Outdoor Activities: Weather maps empower individuals to plan outdoor activities, from hiking and camping to sporting events, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Disaster Response: Weather maps play a critical role in disaster response efforts, enabling authorities to anticipate and prepare for potential weather-related emergencies, minimizing damage and loss of life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Weather Maps and Rainfall
1. What is the difference between a weather map and a radar image?
A weather map provides a synoptic overview of weather conditions across a larger area, using symbols and lines to represent various weather phenomena. Radar images, on the other hand, provide a more detailed view of precipitation in real-time, showing the location, intensity, and movement of rain, snow, or hail.
2. How accurate are weather maps in predicting rainfall?
Weather maps, while incredibly powerful tools, are not perfect predictors of rainfall. The accuracy of rainfall predictions depends on factors such as the complexity of the weather system, the quality of data used in the model, and the limitations of forecasting technology. However, advancements in weather modeling have significantly improved the accuracy of rainfall predictions in recent years.
3. Can weather maps predict the exact amount of rainfall?
Weather maps can provide estimates of rainfall amounts, often represented by numbers on the map. However, these estimates are based on models and may not always be completely accurate. The actual amount of rainfall experienced in a specific location can vary due to local factors such as topography and wind patterns.
4. How often are weather maps updated?
Weather maps are typically updated several times a day, with the frequency varying depending on the source and the level of detail provided. Some maps may be updated hourly, while others may be updated every few hours.
5. Where can I find reliable weather maps?
Reliable weather maps are readily available from a variety of sources, including national weather services, meteorological agencies, and online weather websites. It’s essential to choose reputable sources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.
Tips for Interpreting Weather Maps
- Study the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the standard symbols used on weather maps to understand the meaning of different weather phenomena.
- Focus on the Isobars: Pay attention to the spacing of isobars, as they indicate the strength of winds and the potential for heavy rainfall.
- Identify Fronts: Understand the different types of fronts and their associated weather patterns, including the potential for rain, snow, or thunderstorms.
- Consider the Timeframe: Remember that weather maps provide a snapshot in time, and conditions can change rapidly. Check for updated maps regularly to stay informed about the latest forecasts.
- Combine with Other Data: Use weather maps in conjunction with other sources of weather information, such as radar images, satellite imagery, and weather reports, for a more comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
Conclusion: The Importance of Weather Maps in a Changing World
Weather maps are essential tools for understanding and predicting rainfall, providing invaluable information for a wide range of applications. From ensuring personal safety to supporting agricultural planning, transportation, and disaster response, weather maps play a crucial role in our modern world. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the ability to accurately predict rainfall becomes even more critical, enabling us to adapt to the challenges of a changing environment and build a more resilient future. Understanding weather maps is not just about deciphering symbols and lines; it’s about unlocking the secrets of the sky and harnessing the power of knowledge to navigate the unpredictable world of weather.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Rain Prediction. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!