Unveiling the Weather Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Kansas Radar Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Weather Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Kansas Radar Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Weather Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Kansas Radar Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Weather Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Kansas Radar Maps
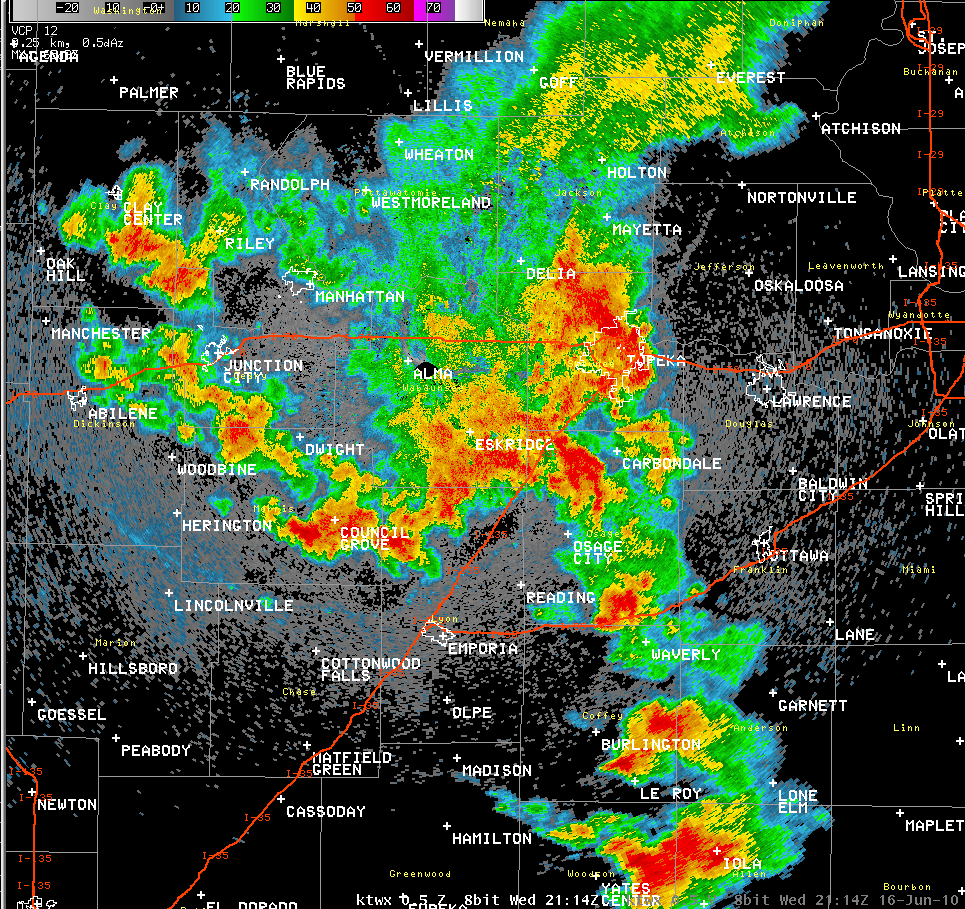
Kansas, known for its vast plains and unpredictable weather, relies heavily on accurate weather forecasting. The state’s radar network, a vital component of the National Weather Service (NWS), provides real-time insights into weather conditions across the state, empowering residents, businesses, and emergency responders to make informed decisions. This guide delves into the intricacies of Kansas radar maps, exploring their functionalities, interpreting their data, and understanding their significance in navigating the state’s diverse weather patterns.
Understanding the Foundation: How Radar Works
Radar, short for Radio Detection and Ranging, utilizes electromagnetic waves to detect objects and measure their distance, speed, and direction. In the context of weather, radar emits pulses of radio waves that bounce off precipitation particles, such as rain, snow, hail, and even dust. The reflected signal, analyzed by a computer, provides valuable information about the type, intensity, and movement of the precipitation.
Navigating the Kansas Radar Map: A Visual Guide
Kansas radar maps are interactive displays that present real-time weather data, offering a comprehensive view of precipitation across the state. These maps are typically displayed on weather websites and mobile applications, providing users with a visual representation of weather conditions.
Key Elements of a Kansas Radar Map:
- Base Map: The underlying map showcasing geographical features like roads, cities, and rivers, providing context to the weather data.
- Color Palette: A range of colors representing different levels of precipitation intensity. Typically, green indicates light rain, yellow represents moderate rain, orange signifies heavy rain, and red denotes intense rain or thunderstorms.
- Radar Echoes: Areas on the map where radar signals are detected, representing precipitation.
- Movement Arrows: Arrows superimposed on the map, indicating the direction and speed of precipitation movement.
- Time Stamps: Indicating the time the radar data was collected, ensuring users are viewing the most recent information.
- Legend: A key explaining the color palette and other symbols used on the map.
Decoding the Data: Interpreting Kansas Radar Maps
Understanding the nuances of radar maps is crucial for making informed decisions about safety and planning. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects:
- Precipitation Intensity: The intensity of precipitation is represented by the color of the radar echoes. Darker shades indicate heavier precipitation, while lighter shades represent lighter rain or drizzle.
- Precipitation Type: While radar cannot directly identify precipitation type, the shape and size of the radar echoes can provide clues. For example, elongated echoes often suggest rain, while rounder echoes might indicate hail or snow.
- Storm Movement: The movement arrows on the map indicate the direction and speed of precipitation movement. This information is crucial for anticipating the arrival of storms and planning accordingly.
- Storm Severity: While radar maps do not directly depict storm severity, the presence of intense radar echoes, particularly those associated with strong winds or hail, can suggest a severe storm.
Beyond Precipitation: Additional Radar Capabilities
Modern radar systems, like the Doppler radar used by the NWS, offer capabilities beyond simply detecting precipitation:
- Wind Detection: Doppler radar can detect wind speeds and direction, providing crucial information about the potential for strong winds and tornadoes.
- Hail Detection: Radar can identify areas where hail is likely forming, allowing for timely warnings and safety precautions.
- Tornado Detection: While radar cannot directly detect tornadoes, it can identify the presence of strong rotation in the atmosphere, which is a key indicator of tornado formation.
The Importance of Kansas Radar Maps:
Kansas radar maps play a vital role in:
- Public Safety: Providing timely warnings about severe weather events like tornadoes, hailstorms, and flash floods, allowing residents to take shelter and minimize risks.
- Transportation Safety: Enabling motorists to adjust their travel plans based on real-time weather conditions, reducing the risk of accidents caused by heavy rain, snow, or fog.
- Agriculture: Helping farmers monitor precipitation patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions about irrigation and crop management.
- Emergency Response: Providing crucial information to first responders, guiding their efforts during weather-related emergencies.
- Weather Forecasting: Serving as a valuable tool for meteorologists, helping them to refine their forecasts and provide more accurate predictions.
FAQs about Kansas Radar Maps:
- How often is the radar data updated? Radar data is typically updated every 5-10 minutes, providing near real-time information about weather conditions.
- What is the range of a radar system? The range of a radar system varies depending on the type of radar and its location. However, most radar systems can cover a radius of approximately 100 miles.
- Can radar maps detect all types of precipitation? Radar is most effective at detecting liquid precipitation like rain and snow. However, it can also detect hail, dust, and other particles.
- How accurate are radar maps? Radar maps provide a valuable snapshot of weather conditions, but they are not perfect. Factors like terrain and atmospheric conditions can affect radar accuracy.
- Where can I find a Kansas radar map? Kansas radar maps are readily available on various weather websites and mobile applications, including the National Weather Service website, AccuWeather, and The Weather Channel.
Tips for Using Kansas Radar Maps Effectively:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Map: Take some time to understand the color palette, symbols, and other features of the map.
- Check the Time Stamp: Ensure you are viewing the most recent radar data by checking the time stamp.
- Pay Attention to the Movement Arrows: Use the movement arrows to anticipate the arrival of storms and plan accordingly.
- Look for Areas of Intense Precipitation: Pay close attention to areas of intense radar echoes, as these could indicate severe weather.
- Combine Radar Data with Other Weather Information: Use radar maps in conjunction with other weather sources, such as weather forecasts and warnings, for a more complete picture of the weather situation.
Conclusion:
Kansas radar maps are an invaluable resource for understanding and navigating the state’s diverse weather patterns. By providing real-time insights into precipitation, wind, and other weather phenomena, these maps empower residents, businesses, and emergency responders to make informed decisions and mitigate risks associated with severe weather. As technology continues to advance, radar systems are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering even more accurate and detailed information about weather conditions across the state. By utilizing these maps effectively, Kansas residents can stay informed, prepared, and safe in the face of unpredictable weather.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Weather Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Kansas Radar Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!